- Zoom
- Type
Table of Contents
Where to buy Ethereum?
| # | Source | Pair | Volume | Price | Change | Updated |
|---|
Historical Ethereum price
* Currency in USD
| Date | Open | Close | High | Low | Volume |
|---|
Ethereum Calculator
- BTC
- ETH
- USDT
- XRP
- BNB
- SOL
- USDC
- ADA
- DOGE
- TRX
- STETH
- LBTC
- PI
- WBTC
- LEO
- LINK
- HBAR
- USDS
- XLM
- AVAX
- WSTETH
- SHIB
- SUI
- LTC
- BCH
- TON
- OM
- DOT
- USDE
- WETH
- BSC-USD
- BGB
- HYPE
- WBT
- XMR
- WEETH
- UNI
- SUSDS
- DAI
- APT
- NEAR
- PEPE
- ONDO
- ETC
- ICP
- AAVE
- CBBTC
- MNT
- GT
- OKB
- CRO
- TAO
- TKX
- TRUMP
- VET
- FDUSD
- ENA
- TIA
- KAS
- POL
- FIL
- FTN
- ATOM
- ALGO
- IP
- RENDER
- ARB
- S
- USDT
- OP
- JUP
- KCS
- SOLVBTC
- FET
- MOVE
- WETH
- RSETH
- NEXO
- XDC
- DEXE
- USD0
- STX
- IMX
- MKR
- RETH
- INJ
- WLD
- FLR
- THETA
- GRT
- SEI
- USDT
- BNSOL
- SOLVBTC.BB
- BONK
- LDO
- EOS
- METH
- XAUT
- GALA
- PYUSD
- XTZ
- USDC.E
- USDC
- WBNB
- BTT
- WBTC
- SAND
- BERA
- IOTA
- BSV
- MONKEYS
- JTO
- JASMY
- KAIA
- USDX
- BUIDL
- FLOW
- PAXG
- MSOL
- EZETH
- FLOKI
- NEO
- ENS
- TEL
- USR
- HONEY
- CRV
- PYTH
- BDX
- HNT
- JUPSOL
- EGLD
- AXS
- RON
- MANA
- TUSD
- WIF
- ZEC
- PUMPBTC
- RAY
- DYDX
- STRK
- KAVA
- USDC.E
- CAKE
- WETH
- XCN
- CMETH
- DOGE
- STBTC
- NFT
- BTC.B
- WETH
- AERO
- CLBTC
- XEC
- CHZ
- RUNE
- APE
- OUSG
- USYC
- USDB
- CORE
- CFX
- AR
- VIRTUAL
- FRAX
- MATIC
- USDY
- IBERA
- KAITO
- EETH
- COMP
- PENGU
- TWT
- OHM
- TBTC
- CGETH.HASH
- AMP
- PENDLE
- AXL
- AKT
- LUNC
- OSETH
- USDT
- BUSD
- GRASS
- VRSC
- GNO
- SPX
- BEAM
- BRETT
- MINA
- GLM
- RSR
- MORPHO
- AIOZ
- BERASTONE
- JST
- FARTCOIN
- CTC
- CBETH
- PLUME
- EIGEN
- SNX
- WETH
- SFP
- 1INCH
- DEUSD
- WBTC
- ETHX
- DASH
- MX
- SNEK
- KSM
- SATS
- TFUEL
- W
- CWBTC
- ZK
- ATH
- EBTC
- SUPEROETHB
- SWETH
- QGOLD
- FRXETH
- LAYER
- ZIL
- ASTR
- BLUR
- SAFE
- CKB
- QTUM
- NOT
- USDD
- ETHDYDX
- BAT
- MASK
- AIC
- USDC.E
- ROSE
- VTHO
- DEEP
- ABTC
- LPT
- ZRX
- CHEX
- GHO
- ZRO
- LSETH
- MEOW
- TOSHI
- SUPER
- PRIME
- USDA
- BABYDOGE
- HOT
- WEMIX
- TRAC
- FLUID
- STG
- AI16Z
- BORG
- CHEEMS
- ARKM
- OSMO
- DCR
- CELO
- GAS
- KET
- WSTUSR
- ACT
- AGENTFUN
- ORDI
- XCH
- RVN
- MWC
- DOG
- SFRXETH
- RLB
- APFC
- TRIP
- SAVAX
- MOG
- ELF
- GOMINING
- XEM
- ANKR
- SC
- MOCA
- YFI
- $RCGE
- RED
- ETH
- T
- AUCTION
- ENJ
- BTSE
- MEW
- VANA
- PNUT
- HONEY
- POPCAT
- TRIBE
- TETH
- CET
- DAG
- SDEUSD
- SUN
- IOTX
- ETHFI
- ZETA
- SKL
- WOO
- CVX
- ETHW
- ACT
- TURBO
- KUB
- DRIFT
- DGB
- XNO
- UXLINK
- FAI
- XYO
- POLYX
- VENOM
- WAVES
- LCX
- ZEN
- WETH
- GMX
- WBETH
- HMSTR
- KOGE
- CSPR
- MPLX
- SOL
- EURC
- ONE
- ME
- BIO
- KAU
- EURS
- WAVAX
- RLUSD
- KDA
- BBSOL
- B3
- MYTH
- LUNA
- GMT
- MAG7.SSI
- WMTX
- USDG
- LRC
- USDC
- FXS
- ONT
- AMAPT
- GAL
- KAG
- GIGA
- GPRO
- GCB
- ZKJ
- DAI
- MMX
- SXP
- NXM
- EUTBL
- IO
- ETH+
- COW
- SUSHI
- BAND
- STPT
- ACH
- NKYC
- PTGC
- COTI
- SWFTC
- USUAL
- HIVE
- SYRUP
- USDC.E
- USDZ
- RPL
- ZIG
- FIDA
- QUBIC
- PROM
- XPR
- BICO
- UXP
- AUDIO
- SOLO
- G
- NEIRO
- REG
- MELANIA
- ICX
- STEAKUSDC
- VVV
- ILV
- AEVO
- METIS
- EUL
- USDF
- RLP
- UMA
- MEME
- VVS
- QUSDT
- ID
- FLUX
- IOST
- AVAIL
- VEE
- IGT
- IAG
- ANIME
- ALEO
- ALT
- CETH
- ECOIN
- MANTA
- SUPRA
- LSK
- FRXUSD
- BOME
- ACX
- SNT
- SPELL
- SAROS
- BORA
- DESO
- AIXBT
- DSOL
- AGLD
- PHA
- ZANO
- CPOOL
- TNSR
- VELO
- BAL
- IQ
- XVS
- GAMA
- ZEUS
- ASBNB
- SSOL
- ORBS
- POWR
- USDT
- OKT
- DF
- RLC
- CTF
- ZRC
- POND
- FRXUSD
- TEMPLE
- SBTC
- REQ
- LON
- SONIC
- CHR
- GLMR
- PAAL
- ONG
- DKA
- FBTC
- GEOD
- METFI
- YGG
- BLAST
- USDT0
- BIGTIME
- WAXP
- ELX
- ZENT
- MVL
- ORCA
- USDP
- BDCA
- SYRUPUSDC
- WETH
- XVG
- PEOPLE
- BMX
- AVL
- WATC
- CVC
- CGPT
- COREUM
- ABT
- WBTC
- STRAX
- HT
- AGI
- DYM
- SGB
- PXT
- USDX
- DOLA
- PUNDIX
- OAS
- LVLUSD
- PEAQ
- ELON
- PUFF
- TRB
- HSK
- MLK
- GFI
- 0X0
- XRD
- KEEP
- SLP
- CRVUSD
- ZBCN
- TAIKO
- JOE
- ARC
- SHELL
- WETH
- SFRAX
- RARE
- XAI
- NOS
- DENT
- SLND
- AGIX
- OMI
- LQTY
- USTBL
- DODO
- NMT
- API3
- KMNO
- BWB
- CLANKER
- ISLM
- PIN
- USTC
- DOGS
- AGETH
- PUNDIAI
- SAAS
- NMR
- SCR
- ANON
- MED
- C98
- STEEM
- ERG
- DAKU
- OETH
- CETUS
- PCI
- CFG
- SOLV
- AMPL
- EZSOL
- GPS
- HEART
- USDF
- CTSI
- MTL
- OBT
- WELL
- ARK
- ACS
- NPC
- BUSD
- MPL
- USDL
- OLAS
- B2M
- CARV
- USUALX
- CORGIAI
- GAME
- QUAI
- OMNI
- ARDR
- TST
- GL-BTC
- WSTETH
- WIN
- SCRT
- MWETH
- ANT
- AAI
- BAN
- COOKIE
- WEETH
- USDC.E
- KNC
- PZETH
- AURORA
- TON
- DEGEN
- M87
- AXGT
- GOAT
- CELR
- MIM
- UFD
- VANRY
- $FARTBOY
- H2O
- AIAT
- BONE
- JET
- DEVVE
- MOVR
- ALCH
- USDT
- BITCOIN
- CTK
- GUSD
- BTG
- FMC
- EWT
- VCNT
- FIUSD
- ERN
- TRUAPT
- SSV
- EKUBO
- PONKE
- WILD
- BANANA
- WETH
- SHX
- TARA
- BOBA
- CAT
- UDS
- LUSD
- QANX
- QKC
- JNFTC
- LOOM
- QI
- SHFL
- ALICE
- HUNT
- USD+
- USDM
- BB
- CBK
- USDC
- DIA
- FORT
- REZ
- OI
- APEX
- WETH
- VELO
- BEL
- USDC
- ORAI
- NYM
- DUSK
- GRIFFAIN
- USDC.E
- PRO
- APU
- ACA
- SUSDA
- MERL
- HIFI
- SUNDOG
- SURE
- EURCV
- FUEL
- TRU
- GNS
- BNT
- CYBER
- SQD
- OCEAN
- COQ
- SWARMS
- PURR
- METAL
- VIC
- HPO
- AITECH
- OXT
- ASM
- EGGS
- AVA
- DBR
- ALU
- RAD
- FWOG
- BFC
- EDU
- WBTC
- OGN
- PEPECOIN
- SKI
- STRIKE
- HIPPO
- DEGO
- EDGE
- UQC
- ANDY
- MAGIC
- AVA
- ZUSDC
- NCT
- TAI
- WBTC
- STORJ
- RIF
- CCD
- ZEDXION
- SFUND
- WXRP
- SN
- ALI
- TMG
- SDEX
- CX
- SB
- BERAETH
- PWEASE
- MBL
- XTER
- SAGA
- SYN
- AZERO
- MBX
- FINVESTA
- RUSD
- STMX
- IOT
- SWEAT
- MOODENG
- ANVL
- D
- AVAX
- SD
- LISUSD
- JETT
- HFT
- SILO
- BRBTC
- BAKE
- KUJI
- ROAM
- SYS
- PLT
- CUSDC
- BADGER
- OSAK
- NTRN
- REACT
- ELA
- XT
- HDX
- RACA
- DAI
- TLOS
- THAPT
- MIN
- MBOX
- BROCCOLI
- SOSO
- GODS
- TRUMATIC
- STONKS
- CUSD
- USD3
- MAV
- MCDULL
- INF
- NKN
- XMW
- SOLVBTC.CO
- MNDE
- BINK
- BIM
- ACE
- A1C
- META
- ALPHA
- FLIP
- BC
- GRND
- VR
- ETN
- REUSDC
- LUMIA
- DEP
- WNXM
- ALPH
- RAIL
- SOC
- CXT
- NFP
- F
- HMT
- PEPU
- HBD
- XION
- PEAS
- PYR
- SLVLUSD
- DAO
- XTUSD
- LOOMOLD
- PNG
- TKP
- CATI
- NEIRO
- WPOL
- GPU
- TT
- MIM
- DEFI
- CRE
- CXO
- HOOK
- HEI
- CLV
- RSC
- USN
- AERGO
- LEVER
- ZEREBRO
- ORDER
- CTXC
- VINE
- WOLF
- PRQ
- SRX
- TJRM
- ATA
- DXI
- CULT
- BTU
- DG
- TLM
- SAUCE
- MARSO
- BNKR
- LISTA
- UNIETH
- LCAT
- UFO
- CUDOS
- USDT.E
- KEYCAT
- RBNT
- FTW
- MFT
- VSC
- MRB
- PIXEL
- SPA
- MOR
- BURN
- KYSOL
- FORTH
- NEON
- NAVX
- XPLA
- GFAL
- PHB
- META
- SLERF
- MIGGLES
- MAPO
- ASUSDF
- MOC
- J
- BOLD
- RDNT
- AQT
- OMIKAMI
- WHITE
- ZCX
- HASHAI
- OMG
- CHILLGUY
- VITA
- VRO
- LAT
- TOKEN
- FCT
- SERAPH
- PSP
- CAM
- GEAR
- BRISE
- BMEX
- LBT
- L3
- MIMATIC
- T99
- WFRAGSOL
- RSS3
- EURT
- MATICX
- LYX
- DOGINME
- NEURAL
- PRCL
- MLN
- GRS
- LMWR
- AQUA
- IXS
- IDEX
- LTO
- WHY
- DRV
- SAI
- ARPA
- SVM
- SUSD
- VON
- FIS
- GGP
- OS
- POKT
- USDC
- POLY
- ANYONE
- EUSD
- MATH
- MYRIA
- LADYS
- ICE
- EL
- TORN
- ALEX
- SFM
- QUIL
- X33
- PERP
- WZRD
- SPEC
- CAW
- A8
- ARRR
- CDAI
- SDL
- GME
- RARI
- A47
- PLXY
- TPT
- PROS
- CROWN
- SIREN
- DAI
- REI
- QRL
- ALCX
- SUSD
- GYD
- HOPR
- ANKRETH
- NPXS
- BOUNTY
- COL
- XSGD
- SHDW
- PALM
- ATLAS
- STEP
- $DOGEAI
- NAKA
- AI
- HEGIC
- STRD
- DADDY
- NNN
- VRTX
- HFUN
- OGY
- UM
- BLUE
- MCADE
- AHT
- STTON
- PIKA
- MLC
- XAI
- ELON4AFD
- LIT
- POLS
- PINKSALE
- KMD
- SX
- SEND
- WGBERA
- OHO
- SNAI
- TREE
- PUFFER
- DORA
- APX
- WAN
- OSOL
- SLF
- SHADOW
- SETH
- SBETH
- CKBTC
- NATI
- ULT
- FT
- DMTR
- HTM
- WAGMI
- VARA
- KOMA
- ELG
- ANON
- FUN
- QUICK
- NS
- DEXT
- XUSD
- MNGO
- LAINESOL
- XPRT
- FRONT
- $ADS
- ECOX
- AUKI
- BMT
- GTC
- UOS
- ALOT
- SWELL
- CBAT
- FLM
- TRUNEAR
- GHST
- UNX
- CONX
- BTCPX
- BANANAS31
- QUICK
- ADS
- FLIX
- COS
- MMUI
- BTY
- MNEE
- COCA
- KLV
- BLD
- EURA
- STHYPE
- BOOE
- HARD
- GXC
- REEF
- STRIKE
- STRX
- DNT
- LOFI
- INDY
- GLC
- INV
- PURPE
- ZUSD
- MPT
- TDROP
- BLZ
- LMT
- OPUL
- WCFG
- DIMO
- NFTX
- BEAR
- USDC
- MOOX
- ZND
- CWEB
- SSUI
- BASEDAI
- THE
- USDTE
- COLLAT
- OL
- ADCO
- USDC
- FARTCOIN
- EURE
- PIPPIN
- BFG
- DIONE
- CAW
- ASD
- WUF
- KARRAT
- NST
- RETARDIO
- SPECTRE
- PAIN
- IBGT
- MCOIN
- BXN
- YULI
- PEP
- AVT
- FB
- USDC
- ATR
- BETA
- POLIS
- KISHU
- PUPS
- WOJAK
- FARM
- IDRT
- CHESS
- DAI
- ORN
- LAVA
- MGP
- IDIA
- HAI
- FIRO
- NUM
- NRN
- WXM
- IXT
- SERV
- USDC.E
- FIDU
- CSWAP
- DUCK
- BZZ
- CHEQ
- GEL
- METH
- MSM
- FOX
- BSW
- XBG
- ARMY
- DRGN
- IMO
- WOS
- USDC
- NOW
- $MYRO
- OFT
- VRA
- DRB
- TSWAP
- HANU
- MOZ
- COPI
- VOXEL
- OG
- OX
- SDT
- SCRVUSD
- STRDY
- SANTOS
- SKEY
- $NUMBER
- TOKE
- BENJI
- ALPHA
- LIBRA
- USDC
- CEEK
- USDBC
- CUSDO
- FLEX
- HAIR
- WETH
- WOD
- PSG
- STSOL
- GGAVAX
- $GROK
- AURABAL
- GAME
- KIN
- PHB
- ADX
- BAR
- CTX
- TRIAS
- GHX
- RBTC
- CLOUD
- MDT
- PORK
- OORT
- PORTAL
- USX
- USDX
- ROOT
- LOOKS
- PEPE
- RAMP
- BOSON
- STUFF
- ALUSD
- DINERO
- STATOM
- CRT
- B3TR
- BOBO
- RBN
- MERC
- SPC
- USC
- TERA
- QASH
- AKI
- GEMS
- LEASH
- VOLT
- SUKU
- KEKIUS
- UCASH
- XCP
- SEAM
- YNE
- MEMDEX
- TROY
- OXA
- QUACK
- LRDS
- USA
- ENQ
- USDC.E
- NULS
- TKO
- DATA
- JKL
- DEXNET
- SYNT
- AIDOGE
- JOE
- DAI
- BIFI
- BOB
- MOCHI
- PIVX
- PHAR
- XCM
- BTR
- EVER
- TOPIA
- BROCCOLI
- ZKCRO
- GAFI
- WING
- HENLO
- DOGE
- XRETH
- LINA
- FROK
- XEN
- OZO
- SHIRO
- RAI
- MOODENG
- DLC
- CACAO
- AVUSD
- GS
- REKT
- BKN
- CREAM
- FIO
- XDATA
- LYXE
- FXUSD
- OX OLD
- ORA
- ZCHF
- MAX
- ODINDOG
- MONKY
- TRUMP
- $MICHI
- ECET
- OCTA
- VINU
- MASA
- DOG
- USDT
- KRL
- NIM
- JMPT
- ALEPH
- COMBO
- AUSD
- LOCK
- NATIX
- LOKA
- SFLR
- SAMO
- PIRATE
- SWBTC
- ARENA
- DEFI.SSI
- FOXSY
- CLY
- TRYB
- FLAY
- VLX
- KARATE
- PYTHIA
- BTC
- PHNIX
- SVL
- CAST
- 10SET
- RIO
- FARM
- PROPC
- UNION
- EPS
- LOOPIN
- GOLDAO
- WMNT
- HYPERSKIDS
- VERTAI
- FLEXUSD
- ALPACA
- AMO
- MON
- MAG
- FOOM
- WUSD
- PIXL
- IRON
- BGSC
- NTX
- WSTEAMX
- MEOW
- BOTTO
- USSI
- YUSD
- OWN
- WEPE
- AURA
- LCT
- QTCON
- BOMB
- ZEX
- CA
- REE
- STAPT
- BGSOL
- SOV
- BLUB
- FUL
- USDC.E
- EMP
- CLUSTR
- BERT
- USDC.E
- DPI
- UPC
- CLORE
- ODOS
- XPM
- PTU
- ASF
- KASTA
- TRUMP
- MODE
- HTR
- PPC
- ZYPTO
- FPIS
- GUD
- BELLS
- NXRA
- CRTS
- ZKL
- STRONGSOL
- PAID
- SLT
- NOOT
- LAZIO
- PDA
- TREAT
- SETH2
- AGRS
- MOBY
- MERY
- BNBX
- KONET
- INDEX
- XX
- BUTTHOLE
- LWA
- SOVRN
- NVL
- GOG
- SFTMX
- REN
- CGO
- MPC
- OBSR
- STREAM
- GALEON
- FASTUSD
- USDC
- MOBILE
- SEND
- DMAIL
- GST-SOL
- MANEKI
- MONEY
- GAL
- PSTAKE
- LUNA
- GME
- NC
- SPECTRA
- PAI
- TAOBOT
- SIDUS
- VNO
- VCHF
- MIX
- WINK
- THOR
- AVC
- EPENDLE
- SCS
- ARMA
- TIME
- GYEN
- NIBI
- HERO
- KWEEN
- YFII
- CELL
- THL
- ALPINE
- ALB
- BCUT
- JAM
- HIGHKEY
- UFT
- KRD
- PNK
- PIB
- SIGMA
- 42
- EQB
- TET
- VAI
- GRAIL
- JAILSTOOL
- ASTO
- KTA
- SWAP
- RIFT
- LINGO
- FEG
- OPN
- OCT
- WCGUSD
- BUNNI
- MVC
- KAI
- PINTO
- XBT
- PUSS
- EOS
- ZKML
- WETH
- CONAN
- ETHIX
- STTAO
- YNETH
- SSE
- JUV
- DMT
- ZTX
- MEMEFI
- AST
- WINK
- BBB
- PEIPEI
- BROCCOLI
- CERE
- $SIR
- NACHO
- KYVE
- BTCP
- SEDA
- STOS
- PNP
- USDT
- STNK
- WRX
- CAR
- VIDT
- PROPS
- KNDX
- CKP
- CITY
- GOUT
- PKOIN
- BSDETH
- ZUSDT
- EVA
- PLU
- AUTOS
- XAVA
- XSWAP
- FOXY
- ASR
- HAWK
- BTCUSD
- $1
- HGPT
- AE
- OUSDT
- BAD
- STON
- YLAY
- EFI
- PLMC
- WEMIX$
- SQGROW
- UTON
- MFER
- LAI
- EMC
- DEL
- COOK
- $BORGY
- DOGI
- PACK
- USDT
- MIU
- SFRXUSD
- FLX
- $MICRO
- ARCH
- LM
- USDT
- SBD
- PARTY
- AURY
- BBT
- MTLX
- STARDOGE
- PAW
- TONIC
- ATM
- QLC
- TRADE
- BLOK
- PRIMATE
- REI
- STC
- WAGMIGAMES
- KP3R
- VISTA
- REX
- WTN
- VIB
- NPCS
- WALLET
- RYU
- JUNO
- INCO
- EXTRA
- SOUL
- GATSBY
- MEED
- GXA
- $BEAR
- CHAMP
- AXEL
- ZERC
- FNCT
- TXAU
- WBTC
- PKIN
- ROUTE
- TOBY
- COMBO
- MCB
- OUSD
- NEXA
- MUSE
- HOLD
- LAOS
- TORUS
- USDC
- OFN
- DATOM
- LIT
- TALOS
- DEAI
- LNQ
- BDC
- VEIL
- SIPHER
- NAI
- WAMPL
- USDQ
- BEETS
- FACT
- USDT
- NBLU
- GTAI
- XSUSHI
- WFI
- HOPPY
- EEIGEN
- MOXIE
- MOON
- BUZZ
- VALOR
- FPIBANK
- DINGO
- FLOCK
- DBC
- GRIFT
- KENDU
- TGT
- GLQ
- HSUITE
- HBTC
- ORE
- OBT
- SUEDE
- ZYN
- EBET
- ZNN
- LQR
- SHRAP
- CDX
- KIKI
- USDT
- BERRY
- PEPECAT
- HEGE
- KING
- BID
- TMAI
- DVPN
- DOVU
- CLEAR
- KILT
- MYST
- STARS
- CAH
- MAS
- PUNK
- DCK
- FTD
- TYBG
- WEXO
- CEUR
- MEX
- BNC
- MYST
- VADER
- SRM
- AEROBUD
- UFO
- OSMI
- 3ULL
- HERB
- TAROT
- ACM
- BRUSH
- STFLOW
- GGMT
- USDR
- MAX
- ML
- LUCE
- MAVIA
- PAI
- RLY
- EPIC
- METRO
- TIG
- VIVI
- BCD
- MUMU
- SIXP
- DFI
- ACOLYT
- KAI
- AVIA
- EVR
- JEWEL
- THALES
- POZO
- KWENTA
- EAI
- AUDIT
- SMT
- VSTR
- ZAI
- DIVI
- SCA
- DCD
- MBC
- XRT
- PATRIOT
- PIKA
- G7
- WINR
- SAVUSD
- OVR
- ADP
- ARC
- PANDORA
- HPO
- ELYS
- SYMM
- SSLX
- BMX
- GENOME
- SDAO
- PINGO
- EDWIN
- MLG
- DEXTF
- ARTY
- PORT3
- AGRI
- VGX
- BOBAOPPA
- INTER
- MNTA
- KOKO
- LIF3
- LIKE
- WXT
- CANTO
- KATA
- LOCKIN
- VTRADING
- DHT
- PEPE2.0
- ⌘
- PLI
- POLA
- APW
- 1GUY
- ALVA
- KPN
- ARIA20
- FUSE
- HAT
- B4FWX
- XEL
- ASTRA
- SAITO
- MUBI
- XFI
- EXRD
- GSWIFT
- ICETH
- BAC
- TITS
- DNX
- MARS
- YOM
- HUBSOL
- FX
- STOP
- XCAD
- HDRO
- KOIN
- MARS
- SWISE
- LMEOW
- HIGHER
- CAPTAINBNB
- XETA
- MEY
- SWORLD
- WBTC
- CHAIN
- TSOTCHKE
- WRLD
- KAR
- FLOCK
- SLIM
- FRIC
- DMD
- BRAT
- RENBTC
- ZGD
- CROID
- KLIMA
- BAMBOO
- DOLZ
- FLT
- SNSY
- SIX
- XDB
- USDF
- SLOTH
- LZUSDC
- GDP
- CATE
- BIZA
- GENE
- ROA
- USDC
- USDT
- BEAM
- ABSTER
- TRAC
- GBYTE
- RCH
- AKUMA
- WCO
- OXY
- UCJL
- USDH
- TADA
- BST
- CLAY
- OWC
- BNUSD
- VVAIFU
- UNCX
- HNS
- VIRAL
- JESUS
- SCF
- MOTHER
- DCB
- ANT
- ASIA
- INFRA
- STOSMO
- HELLO
- SWELL
- EVERY
- BLOCK
- XZK
- ROCK
- SNK
- JOULE
- STTIA
- BEETS
- WHALE
- MAGA
- USDC.E
- OIIAOIIA
- RVF
- WIFI
- BUBBLES
- STARL
- 00
- MXC
- SFG
- BLUB
- USDC
- LEA
- ASK
- HUSD
- DIGITS
- NECT
- CULT
- METAV
- COT
- LAIKA
- RGOAT
- RE7WETH
- MNW
- XCHNG
- AFR
- $NAP
- STAT
- MOD
- EGP
- WISE
- BBONK
- SDN
- ASM
- XEP
- FORWARD
- SEN
- SWASH
- CUNI
- LOAN
- PDT
- WIKEN
- NAVI
- FP
- TRT
- VAI
- APL
- MINIMA
- BCN
- HANDY
- JELLYJELLY
- SINGULARRY
- SNPAD
- TROLL
- XOT
- MAN
- CREO
- ASTRO
- BOTIFY
- PASG
- 888
- CHAD
- SWPX
- HARAMBEAI
- LL
- USDT
- EMAID
- DKP
- MAD
- CAGA
- DC
- BXX
- SHD
- OPCAT
- GHUB
- WETH
- XAND
- ISLAND
- ETUS
- REP
- PPT
- KIMA
- APP
- CELL
- PAL
- GRAB
- MEMES
- QMV
- MEUSD
- MG8
- ABEL
- MINT
- SCFX
- TEVA
- FARM
- L1
- GOGLZ
- RONKE
- BMC
- SLN
- OXEN
- DNA
- GIKO
- RAIN
- PLAY
- AINTI
- ICHI
- SKEB
- AVINOC
- SOIL
- $KEKEC
- SHIDO
- RADAR
- NEX
- KOLIN
- DIVER
- BOA
- HI
- WELSH
- 7007
- XDAG
- SAN
- $PURGE
- AIUS
- LIMBO
- MOE
- PAI
- CVR
- TRIO
- SHOGGOTH
- CUBE
- $BILLY
- O
- FITFI
- POOLX
- KNCL
- GOAL
- ORBT
- VITA-FAST
- BRETT
- BOB
- POLYDOGE
- NUB
- DJED
- ETH2X-FLI
- WETH
- UW3S
- AMETA
- ATS
- BTCMT
- CSIX
- LORDS
- AVB
- BIG
- PTS
- HDN
- M3M3
- SQT
- ESE
- HMND
- ISK
- HOGE
- WOOF
- CUMMIES
- SEED
- DMC
- AIPAD
- NWC
- DOME
- THRUST
- USDT
- FURM
- SOFI
- JEFF
- CAPS
- ASTRAFER
- TOMI
- WELF
- QBX
- LOGX
- SHI
- LISTEN
- MBS
- SNFTS
- LAUNCH
- VUSD
- AIR
- MNTC
- FLUXB
- KANGO
- VEUR
- TYPUS
- EDGESOL
- TRISIG
- SIS
- MIAO
- NATIVE
- ARCA
- DEGENAI
- BLENDR
- SUAI
- LLD
- DAY
- AGIXT
- HYUSD
- TVK
- ABX
- OMZ
- TRVL
- FRED
- N3
- EBTC
- AIT
- BIDZ
- GPCX
- HYPER
- TOP
- WOW
- THT
- KIP
- WETH
- VC
- LVN
- HARAMBE
- NHT
- PLN
- LTX
- OPUS
- XNA
- $EVA
- AVI
- PRISMA
- CRAI
- HXD
- NAVI
- SPURS
- KAN
- VAL
- MCRT
- PUSH
- ALD
- MOVE
- TRUF
- GPT
- MYSTERY
- SAI
- NAP
- MINI
- PREMIA
- IRIS
- DIP
- MAK
- LEDGER
- BAX
- NSASTR
- USDT
- YEET
- GMEE
- IMGNAI
- BLK
- CEL
- HAROLD
- AURA
- LANA
- CRU
- LYA
- BEER
- NYA
- KOMPETE
- ARG
- " "
- SEKOIA
- USDC
- CFGI
- CHOMP
- WITCH
- AZIT
- USDGLO
- LAND
- NOCHILL
- DERO
- CPH
- EEFI
- FIRE
- XPACK
- ATH
- TRA
- WUSDM
- UBU
- REGEN
- ZKP
- TN100X
- FIVE
- NRS
- GOVAI
- HAPPY
- EUSD
- KIBSHI
- CARROT
- LEOX
- ETF500
- BULL
- KNS
- HENLO
- HOLD
- ASIX
- SCOT
- MOEW
- DUKO
- WHINE
- PNDC
- RJV
- PZM
- PINO
- WINNIE
- AKIDS
- REF
- HERA
- BIGJIM
- BAN
- LQDR
- QORPO
- DUEL
- KLEVA
- ISP
- SNC
- EFL
- WBTC
- USDC.E
- BRYAN
- BCT
- ICBX
- IVT
- 🦝
- NRG
- LUMO
- NETVR
- LUSH
- DKING
- SWITCH
- YAYSTONE
- BTM
- EQUAL
- IBEX
- LCS
- FEI
- TITAN
- BTCB
- RE7WBTC
- STIMA
- BTC2X-FLI
- MINT
- ITHACA
- ANLOG
- DOP
- WOM
- HMX
- SOLNIC
- CAMEL
- ADX
- MAHA
- $SIGMA
- VY
- FUD
- BUT
- KEY
- BAAS
- OMAX
- EVMOS
- MZR
- PPKAS
- TAKI
- YAYAGETH
- RISE
- STFX
- MUSKIT
- USDN
- AGVE
- QUEEN2
- IMG
- DOLAN
- LTAI
- NEURON
- NSTR
- SOCKS
- SBR
- DEMI
- LMCSWAP
- USDC
- DROP
- USDT
- TOKEN
- NLS
- IMPT
- PIKA
- MSTR
- BUY
- AFC
- $CATBAL
- REWARD
- BARSIK
- SOLID
- AZUR
- GLEEC
- $POM
- JUICY
- EZEIGEN
- SPARKLET
- ZEPH
- TREMP
- APRS
- SPS
- REDO
- GUI
- VITARNA
- WEL
- FROG
- GMM
- LMR
- SPE
- SBR
- PUNDU
- SNS
- EMT
- TAOCAT
- PRE
- $SYMP
- YAK
- RWA
- Y2K
- PSPS
- MUSD
- ZARP
- FUTURE
- WANBTC
- BONGO
- RBX
- STRP
- CYG
- SCHIZO
- $CWIF
- W3S
- FARTGIRL
- MV
- NYAN
- VTC
- ELIZA
- GRIN
- 1000X
- OPSEC
- BUDDY
- USDC
- CREDI
- STORM
- RBC
- KCT
- SYLO
- SOON
- EPIK
- ANGLE
- WAFFLES
- BTS
- MASQ
- CGX
- LKY
- DIKO
- POR
- FURI
- NEUR
- ROCO
- WHISP
- PIP
- TSUKA
- QVRS
- OMNOM
- TANK
- $SCRATCH
- AGIXBT
- CNHT
- BEEPER
- MEDIA
- REV
- PERRY
- AIXCB
- NTMPI
- TNQ
- XTN
- AIKEK
- BODEGA
- ADM
- GOD
- UNIBOT
- USDC.E
- POOL
- CAIR
- $SMH
- MDX
- PMT
- SEXY
- RIKO
- BOOP
- BOO
- USDC
- BOZO
- YUSD
- TGC
- MYT
- TLX
- WEFI
- COCO
- MTRG
- FAR
- WARPED
- SWAN
- U
- KIZUNA
- AREA
- BRAINLET
- FREYA
- SOL
- XCB
- ION
- SWCH
- X314
- AIMONICA
- AGENT
- DOBO
- USDC
- DG
- POWER
- MINIDOGE
- FLRETH
- ASCAKE
- IQ
- WAAC
- KPOP
- STARS
- EPIK
- ANDY
- ADO
- X
- FJO
- ALL
- SAFEMARS
- JAM
- AA
- CTN
- USDC
- CONVO
- HAPI
- RAI
- APX
- LIQUIDIUM
- SLC
- TTG
- PIDOG
- Q*
- BABYSHARK
- SG
- ORT
- OXI
- FRIEND
- BROCK
- BALN
- SHRUB
- KASPY
- AUDF
- LAKE
- WOOLLY
- SAN
- UPT
- TXT
- RATS
- WIBE
- THC
- TANGO
- DOMI
- CHAT
- $KIT
- TWIN
- G3
- MAJOR
- DEFX
- TIRED
- BLND
- MAZZE
- CABAL
- DAI
- RAMEN
- PHIL
- HUAHUA
- DREAMS
- DOJO
- GIZMO
- BSX
- BITCI
- BENDOG
- RXD
- MTD
- UNFI
- MIR
- CTRL
- BRO
- COMAI
- CAT
- BYTE
- BOND
- STRIKE
- NEXT
- WIT
- 0XGAS
- GARI
- WACME
- GNON
- NEST
- BFT
- INTX
- EDUM
- WBTC
- WHALE
- CTG
- VOI
- TON
- CAT
- DREAM
- USOL
- KEX
- GET
- MDAO
- SPORE
- PAR
- TAG
- BILLY
- PERC
- RSAVAX
- BXBT
- GRELF
- GTCBBTCC
- PAPPLE
- WUD
- SMURFCAT
- LMY
- EVAN
- MDEX
- DUCX
- RIZ
- TALK
- TUSD
- BRN
- JAV
- CNG
- USDT
- XNET
- MCONTENT
- OOE
- ZJOE
- LI
- SSDX
- AION
- RIZO
- ARCAS
- SATORI
- IBEUR
- DVI
- SERO
- FAN
- RFD
- BTC2
- PEPPER
- ZERO
- ANDY
- TRKX
- FLY
- ECS
- TPRO
- SCP
- TBULL
- VIA
- ROKO
- VPAD
- COR
- M
- SCI
- BABY
- TERMINUS
- HXRO
- BIB
- DOGEGF
- CYB
- PLSR
- GAU
- MAXETH
- NXS
- USDT
- WSDM
- USUI
- HSUSDC
- CLARITY
- PRD
- NINJA
- LUFFY
- LIXX
- NAV
- MKL
- FACTR
- NFD
- KRAV
- RWA
- ARGO
- REALIS
- MINTME
- FP
- BLOCK
- XAR
- HENLO
- NUTS
- TURBOS
- UCO
- LKI
- RKEY
- NX
- SCIHUB
- AIV
- PONGO
- GRPH
- BRAINERS
- $ROAR
- SCPT
- SOLAMA
- DAI
- DAI
- WHISKEY
- LIQD
- SKOP
- BRLN
- AIN
- GNUS
- LYNK
- ((=ↀωↀ=))
- GO
- TOLY
- PEP
- AIAGENT
- NILE
- DTRXBT
- FU
- WART
- SAMA
- SEAMANIA
- SXETH
- METAL
- SILK
- DOGC
- KOTO
- DEPAY
- OGV
- ISC
- JYAI
- FAYA
- GROW
- SCLP
- RDPX
- BEPRO
- FXN
- SDT
- SILLY
- CARR
- MUSD
- VEX
- SUDO
- ZOO
- IBTC
- NYX
- SAGE
- IPOR
- ZBIT
- GRC
- CHATOSHI
- BUTTCOIN
- POGS
- FOMO
- CKETH
- USDT
- $MONKO
- APES
- AXOL
- KEKE
- WQOM
- LOULOU
- GOATSEUS
- HODL
- ONI
- SWTH
- DIO
- TNT
- LUCA
- MVI
- STABLE
- IOUSDT
- LAUGH
- ETH
- RING
- UP
- EXA
- AI23T
- CAT
- MACHI
- HEU
- SLAP
- USDC
- ETHOS
- JOY
- UXRP
- WLTH
- LNDX
- CATBAT
- KNIGHT
- POOH
- GOODBOY
- WOLF
- RNT
- LBR
- COFE
- GEEQ
- HEHE
- $WOLF
- SCUSD
- BMP
- BM
- MARSH
- UNIT0
- ARI
- GAMMA
- USDT
- CAI
- SFI
- PHRZ
- JURIS
- LAVA
- THE DOGEFA
- ITA
- PENG
- RDT
- NOVA
- SIGNA
- RFOX
- SEAL
- USDC
- SKR
- WMC
- SERSH
- VMANTA
- XPX
- XOXO
- LQNA
- TRACY
- CRASHOUT
- SHU
- THUSD
- SDM
- YOSHI
- FLORK
- NUUM
- RWA
- UBT
- OTK
- GYAT
- IVFUN
- WEPC
- AIR
- WARS
- RUSSELL
- DEDI
- TIME
- PBX
- VSP
- DARK
- SHIBDOGE
- MONG
- FAKEAI
- KASPER
- ARTHERA
- GAINS
- KUDAI
- MONOPOLY
- NEOX
- SMOL
- SABAI
- TDE
- LOU
- FOUR
- SKBDI
- MUSIC
- BABYBONK
- INSP
- GZIL
- GCR
- WSM
- PUMPIT
- TSUKI
- ONE
- XTT
- VAPOR
- GALAXIS
- TABOO
- FRA
- PEPO
- QI
- CLXY
- VERSE
- BREW
- BOB
- RTM
- EMC
- CTA
- FER
- CBY
- AIFUN
- ROME
- FILM
- TARDI
- RDD
- CONWAI
- SPACE
- HINT
- GOATS
- YUSD
- UFI
- WBTC
- KBL
- HTS
- SQR
- DEFI
- OOKS
- NAV
- FARTY
- SC
- $RIF
- LPETH
- ORX
- LIKE
- CHKN
- EURR
- PZP
- BRAIN
- HVH
- MBTC
- HELIO
- RAKE
- OPTI
- XPI
- MTO
- MET
- RC
- BZRX
- KOS
- STEAKUSDC
- DOGA
- MUSIC
- DUST
- TOKE
- POX
- TETSUO
- AMORE
- AWR
- $H2
- DOK
- WCHI
- 4EVER
- SLAM
- DOR
- HYDRA
- UMJA
- PACE
- STS
- MPS
- GOOFY
- LYRA
- RMNER
- DYOR
- FXN
- GZONE
- QUNT
- BSCPAD
- DEPIN
- ANC
- SOMM
- FLD
- CATS
- XER
- WIGO
- NBT
- AIINU
- IOUSDC
- AKA
- WATER
- FLX
- STASH
- $NMKR
- MOBI
- SPH
- CONDO
- UX
- KIMBO
- BODEN
- CHAPZ
- TDC
- PEEZY
- DICKBUTT
- MDAI
- LEGIT
- HOA
- CITADAIL
- SP
- ENQAI
- DUSD
- WSI
- KDX
- CHADETTE
- SPHYNX
- WOLF
- XDEFI
- PNIC
- CRYO
- STAVAIL
- XELS
- TROG
- 21BTC
- ENF
- DBR
- TNSR
- WETH
- BREW
- VETH
- XIDO
- SENATE
- DFL
- CHRP
- USDT.E
- PIP
- TAPT
- BVM
- ZF
- LFT
- RWN
- NCR
- XCFX
- SONIC
- $ANTY
- PLEB
- FU
- CAI
- USDC
- MORI
- DDX
- VCX
- AAX
- BOX
- $URO
- SEND
- EYWA
- ABR
- GBEX
- KHAI
- YAPSTER
- ALTT
- RTB
- HST
- BTRFLY
- FAFO
- DCI
- USDT
- BOOMER
- SAY
- SSWP
- PTC
- SIMP
- LBL
- PART
- NCDT
- LSS
- ZAI
- BOOT
- RGT
- NVT
- KOI
- EGO
- ASKJ
- DOGE
- UNO
- KALIS
- EURQ
- OBOT
- BIT
- FULLSEND
- RSVETH
- KM
- IXC
- BLACKDRAGO
- CKUSDC
- STEAM
- BLUSD
- MAIAR
- LOC
- GRG
- FOX
- MTA
- DEFIT
- MANC
- $WELL
- GUSDC
- DEUS
- MLT
- POLC
- BRRR
- NASDAQ420
- GG
- RMV
- ELU
- FLX
- DDBAM
- $OG
- SELFIE
- ICE
- OMNIA
- WPAY
- XR
- AIYP
- $UNFK
- VEXT
- MEME.SSI
- GOTTI
- YUKO
- MORPHAI
- CGV
- SYL
- XNK
- JBX
- DMAGA
- PIKA
- BERRY
- DOP
- GRP
- WING
- SUIP
- USV
- YEL
- XTM
- IST
- HACD
- CLANKFUN
- BIRDDOG
- TOMB
- BULLY
- XFUND
- PUPPIES
- TRONKEY
- DOOM
- TREB
- RWAX
- IDO
- PROJECT89
- BDOGITO
- MNT
- BABYNEIRO
- C3
- HUND
- BUZ
- BCAT
- NGL
- SEIYAN
- NITRO
- SYK
- CHUD
- BTX
- OBI
- PEUSD
- USK
- VIS
- FOLD
- TYPE
- MAMA
- LCC
- KOL
- BOOK
- DOGL
- UPO
- IOL
- TALENT
- LUNAR
- REV
- MEMESAI
- BNX
- EGC
- FDX
- CLUTCH
- FLNCHY
- SUNCAT
- SHA
- CHONKY
- LYNX
- DSRUN
- HELP
- ATETH
- VPT
- INTOS
- STELLA
- CATCH
- BONZO
- SIN
- KARAT
- RPLS
- BPT
- UBC
- GMRT
- HEEHEE
- $BLS
- CNFI
- ID
- MBP
- EMYC
- HART
- RBD
- PIRATE
- ADAPAD
- SAGE
- OKI
- GHOAD
- ZKF
- DYAD
- WHALES
- ANZ
- $FATCAT
- SKYA
- TEMA
- VIDYA
- BUBBLE
- EQUAD
- REVV
- NOTE
- LUX
- RST
- ZULU
- CAG
- TONY
- SUIAI
- PKF
- UMB
- NAMI
- SOBULL
- PROB
- BAG
- VELAR
- MCHC
- LIBRE
- PURSE
- SAL
- QOM
- TUT
- PXC
- ASH
- AI9000
- PER
- COVAL
- ORC
- SKH
- DITH
- FMC
- DETF
- FREN
- BWEN
- FEENIX
- MTV
- PSY
- SATOSHI
- CLOUDY
- WANUSDT
- SHROOMY
- MARS
- VBNC
- USDT
- HOTCROSS
- PRISM
- FLOPPA
- BDP
- KNINE
- MINX
- CAS
- SMT
- CVP
- COSA
- PND
- OSCAR
- USDC
- $JIM
- MNTL
- MNFT
- MELD
- NATO
- KOM
- TAONU
- SUGAR
- MIND
- USTRY
- EDEN
- PEAR
- BRWL
- WETH
- FUZN
- DIME
- BSX
- PIPO
- INDI
- UFC
- CJPY
- BIGSB
- HZN
- BENFICA
- SAVM
- QBIO
- NOTAI
- SKAI
- $KOKU
- USDC[HTS]
- BANANA
- RUGPULL
- CALVIN
- LUM
- CHIRP
- EJS
- AIW
- SPACEM
- FTC
- EDOGE
- CARD
- LEV
- GQ
- RE7USDT
- SNS
- VOYAGE
- IXO
- DTF
- WBTC
- SPLASH
- PLYR
- VSYS
- PIG
- CPT
- ORAIX
- NFTXBT
- TRCL
- SENSI
- VDA
- FSN
- ASX
- VEE
- GMTO
- JEST
- USDT
- DINO
- KRO
- HVLO
- WAR
- GUMMY
- SEILOR
- AMB
- SYNK
- WAVE
- HAMMY
- CRAZE
- IVY
- RITE
- USDS
- DISTRIBUTE
- USDC.E
- GUAC
- SOPH
- STGWETH
- BSKT
- ZARA
- POT
- MIM
- WYAC
- MM
- DORKY
- LVL
- STDYDX
- VTX
- GLUTEU
- NORMIE
- MC
- TIA
- SENTAI
- QST
- STATE
- BONDLY
- RIDE
- OKAYEG
- IBIT
- ASYM
- PKT
- AXV
- RTBL
- DTEC
- PANDA
- RAM
- SOBA
- USDC.ETH
- VMINT
- ART
- YBTC
- XKR
- ACQ
- XI
- CHAMPZ
- XFI
- DESCI
- APY
- KAON
- MZC
- EFC
- DESU
- ELONRWA
- AIX9
- BABYPEPE
- NOTE
- FROGE
- AI
- RING
- BTORO
- ANTIRUG
- STEPSOL
- MP
- TRONPAD
- RAMON
- QAI
- KLAUS
- RICH
- ROCK
- ASM
- LESTER
- SBX
- NIBBLES
- MK
- GST-ETH
- NAV
- HLN
- FUKU
- USDT
- MUNDI
- GURU
- XSP
- APM
- POWSCHE
- BAZED
- OUSDC
- ENG
- NGC
- NOBL
- YAKU
- GRRR
- RETIRE
- XYRO
- T3AI
- INTR
- LOL
- MOOV
- FLUT
- SNIFT
- EXPERT
- TERMINAL
- FA
- WECAN
- PUPS
- NSTK
- XENCAT
- TEN
- WANUSDC
- BLEND
- POLY
- PIRB
- OMIRA
- BRICK
- SHR0
- JUSDT
- XGC
- PPCOIN
- MUMU
- CAU
- TOONA
- GIV
- LBLOCK
- KITE
- CRASH
- BORED
- ELITE
- HAC
- WWY
- XODEX
- DYP
- VLXPAD
- AZC
- ITMT
- CHEESE
- VCF
- USDC
- TOWER
- ARTFI
- ███
- BLOCX
- SRK
- HEMULE
- NOMNOM
- MOAI
- XMONEY
- NEIRO
- LUNR
- $LOTTO
- DRUGS
- RETH2
- WLKN
- ARTEM
- BEE
- UBXS
- WOZX
- DAN
- SIMMI
- $TOAD
- NICP
- AMKT
- DRIP
- TSHARE
- LLM
- EMP
- MD
- ORNJ
- AVER
- KAP
- MAPS
- 4CHAN
- AVAC
- LIMITLESS
- MBET
- IZE
- SOUL
- VIRGIN
- ZKB
- ANGLERFISH
- JPEG
- LEO
- NEROX
- WUSDN
- SUSX
- SKY
- BABYBNB
- STBU
- USDC
- RACKS
- PEN
- FOX2
- CHELON
- OPXL
- DTIA
- BULL
- NGL
- INCA
- USDC.E
- BB
- SYNTH
- MNRY
- BAMA
- 5IRE
- $THREE
- BSR
- SHY
- IMF
- PIZA
- ZUSDT
- KDAI
- ALOR
- 589
- SPS
- AEG
- ZCN
- CHAD
- SERAPH
- BABYFWOG
- ABYSS
- MIST
- MINEBTC
- ARIA
- AURA
- PLANET
- NEURA
- STYLE
- STAR
- BAI
- DEVAI
- WSTASTR
- CRWNY
- FACT
- SMILE
- AGENT
- TRUMPCOIN
- SHIBOO
- SPICE
- VNXAU
- DEVIN
- CRYSTAL
- SAINT
- HOTKEY
- TALIS
- FCON
- LADYF
- BROCCOLI
- GIB
- CARLO
- BRLA
- TRD
- PDEX
- CPAL
- RSP
- BEFE
- EDN
- SOAR
- GOFX
- TERRA
- BOOSHI
- ANALOS
- TRADE
- RPG
- EBULL
- HLG
- XMON
- JARVIS
- RBLS
- BALLZ
- AIOS
- PYTHETH
- NEOT
- RBT
- GM
- FCTR
- VELAI
- ZPAY
- MATES
- STAR
- STAR10
- GURU
- TEER
- ANDR
- TRUST
- SHIB
- HONK
- USA
- WOM
- TAROT
- RAVEN
- NET
- ZAP
- MTARD
- NVIR
- SLR
- TRENCH
- SEER
- ICOM
- AIRENE
- CKUSDT
- STBL
- ALPHA
- TAOLIE
- FIGHT
- HUSKY
- AVG
- ITHEUM
- ZTG
- TUT
- BGG1
- SDR
- BANX
- BIFI
- BRD
- AGIALPHA
- RECORD
- FEFE
- DATA
- USDC
- $TOAD
- SSG
- PGX
- FALX
- USDT
- XMONEY
- SHR
- SAIL
- PEPE
- ERTHA
- E4C
- CHONK
- THALES
- SB
- GAME
- KEK
- SOLID
- CDOG
- PACA
- BNA
- BONSAI
- JRT
- LA
- GMAC
- AAA
- MENGO
- FROC
- FOLO
- CATBOY
- $PANANA
- NODL
- MAICRO
- UBSN
- BIOFI
- PYTHUSDC
- BONSAICOIN
- U2U
- PUT
- CRTAI
- $PEPE
- TOMO
- XMD
- NEIRO
- HIBER
- FERMA
- OMNI
- WEIRDO
- GYMNET
- JAM
- PEEZY
- HUG
- TRUST
- BABYBROCCO
- XFT
- TST
- IDOGE
- RE7CBBTC
- IRA
- TAXI
- CYI
- C4E
- GAIA
- MND
- KEKE
- MARS4
- FUZZY
- WAM
- SOLENG
- USDC.E
- AM
- GOA
- GRK
- PROPHET
- SYNTH
- FYN
- CHENGU
- ATF
- VAL
- HSUI
- BOOH
- BNBXBT
- ELDA
- HOPE
- HABIBI
- EXD
- SPEEDY
- BOYS
- USDT
- GOZ
- BKOK
- JGN
- MNB
- NGM
- TORCH
- SHIFU
- TRUBGR
- XOXNO
- SHEKEL
- AIT
- BLP
- KAI
- LUCKY
- PHI
- SPORT
- POLK
- NEOS
- DETO
- KOIN
- HONK
- YEC
- UCX
- GSWAP
- $BADCAT
- MUC
- EUROE
- GFI
- NIKO
- WETH
- SAUBER
- PAK
- AYIN
- NABLA
- FAIR
- KNJ
- CCV2
- KOIN
- QWACK
- WAT
- QUARTZ
- WOOF
- NSAI
- WCTC
- KINT
- MIZUKI
- AME
- MINT
- DOSE
- FILTER
- CEP
- ZAP
- GULF
- BGVT
- P3D
- LITH
- DINO
- THC
- KLS
- WBTC
- IGU
- NSFW
- RFL
- $DRIP
- SEUR
- XALPHA
- W3W
- FUJI
- MOO
- AMA
- UNO
- PAJAMAS
- LIT
- QUDEFI
- RET
- MBD
- USDT
- GMB
- SOLMAX
- HBOT
- LBM
- RAIN
- PRX
- HUDI
- UUSDC
- FOR
- AGENT
- EGG
- FORM
- DCN
- ISAACX
- GORA
- NXT
- BTSG
- ATN
- ESTEE
- $CLAP
- LYP
- LSHARE
- DAIGE
- MORE
- P
- EARLY
- MORRA
- IQ50
- UDAO
- NFTB
- RYO
- BCB
- FISH
- NEBO
- MOBY
- KIBBLE
- BRG
- BULLY
- GSTS
- RAZOR
- NICK
- SWP
- NFTL
- DCOIN
- ODIN
- PROOF
- CTI
- HATCHY
- MENDI
- UNV
- ELIZA
- SUSDX
- SCAR
- PUSSY
- $BURN
- CHAI
- WBTC
- WANETH
- BSWAP
- INT
- USDT
- QUANT
- TCC
- CHIDO
- JHH
- AVRK
- ARV
- PEPE
- SAFE
- CZRX
- BERAMO
- RVC
- FWT
- ST
- MELLOW
- MXM
- REVO
- BCUBE
- VOLT
- WEWE
- DERI
- JAIL
- AROK
- FOREST
- WRKX
- DFYN
- SNFT
- ELK
- KROAK
- NOMAI
- CDT
- FUNGI
- HLO
- MTVT
- DAI
- ZAI
- LAMB
- KUMA
- GINNAN
- INFRA
- SOULS
- SHIK
- USDT
- XY
- AURA
- KIBA
- SUGAR
- AVL
- SPHERE
- NUT
- WNK
- DNA
- OAX
- FOFAR
- CHANGE
- MUNCAT
- MIMO
- GNY
- JOK
- RIZZMAS
- DAI
- BABYGROK
- SOLI
- VCG
- $REALKENDO
- FREE
- OPAI
- PANDA
- SOCIAL
- FPS
- ECLD
- AIPUMP
- DOGEFATHER
- ZOO
- CBC
- OCE
- BRIAN
- EVERETH
- DSLA
- OCTO
- VIKITA
- X2Y2
- ZOOMER
- CRPT
- VPS
- BOF
- SKID
- AIPG
- CGT
- REVU
- MOAI
- PLS
- EMR
- STND
- DORITO
- PXP
- STC
- POPDOG
- TST
- SANDY
- GTN
- TRAVA
- MONKEY
- 🟥🟩
- BIAO
- BOBLS
- LAYER
- GST-BSC
- IDRX
- KROM
- $HWTR
- MILLI
- LUMOS
- BOLT
- RAT
- IGNIS
- RMRK
- $JOBSEEK
- WATER
- WOLF
- VAIN
- SALT
- CYPHER
- CBL
- $TRUMPAI
- KAT
- AVENT
- FRTN
- FIGHT
- GEMXBT
- BIS
- SYNDOG
- KFC
- KIT
- STEAK
- $CCC
- BIOHACK
- BETS
- WASSIE
- ZOON
- GLORP
- J3FF
- BTTY
- SSR
- CZ
- EVAL
- DBX
- FLOW
- HNTR
- HORD
- BASED
- MEGA
- NUSA
- CYDX
- NMX
- KEROSENE
- URUS
- AUTO
- LZM
- MOONED
- ◨
- AJNA
- TUA
- BMR
- TTK
- SATX
- CHORUZ
- EQX
- AIT
- CHO
- WAIFU
- X
- SDFXN
- HON
- GRUMPY
- BLEND
- SHITZU
- MAIA
- MOSS
- L8CAP
- PBTC
- BFT
- GROWAI
- SHFT
- QKNTL
- STRUMP
- ROOST
- BENI
- FCL
- PREME
- $HAMI
- TAMA
- BABA
- 21M
- SAGE
- JAIHOZ
- NOOOO
- MAX
- DVY
- CWS
- ITGR
- MBTCS
- MBXN
- GSNAKE
- VIBE
- OXYZ
- CERTAI
- CROW
- INF
- UNQ
- S
- GHOST
- EXCC
- HAN
- LEND
- PLR
- HESTIA
- QCK
- DOG
- CBM
- GASP
- MPS
- BARIO
- AMU
- RONNIE
- BUMP
- BRB
- PICA
- MMPRO
- WALV
- MZERO
- WETH
- BMT
- CROWD
- TOKO
- SQDGN
- WBLT
- BSOP
- BUNKER
- STUPID
- PKR
- PAY
- WANA
- K21
- WHALE
- QMALL
- $IRL
- ATEHUN
- DXD
- FATHA
- PUMPCORN
- AGX
- ASTRL
- CIG
- XAVI
- TOTO
- YAI
- HAKKA
- TURBO
- ABDS
- TURT
- BELT
- VZ
- BURN
- KIRA
- XUSD
- ANON
- VU
- CONVO
- PMX
- CATANA
- AIP
- DOAI
- X
- PEGG
- VSTA
- $SHARBI
- WBS
- POGAI
- $PUCCA
- NORDO
- TITCOIN
- OK
- $ELON
- HEFI
- CUZ
- CLS
- STARSHIP
- OOKI
- LILAI
- KCCPAD
- KICK
- SHOGUN
- MEME
- DSETH
- HBB
- RTIME
- KITTENWIF
- PERQ
- PEN
- LARA
- HEDGY
- BTCBAM
- XET
- APPLE
- GONDOLA
- PTRUMP
- AWS
- NETT
- PRNT
- CYBRO
- BESC
- HYVE
- ANDYMAN
- CLINK
- TUBBI
- EXO
- COOL
- AQUARIUS
- RVST
- MURAD
- DEOD
- MISATO
- YOKO
- JUP
- MUTE
- BSCS
- NEST
- AI
- CHIPPY
- OSEAN
- USDFI
- SOURCE
- DFX
- FEAR
- CIRCLE
- WEALTH
- BED
- TES
- FLSH
- NIZA
- MKUSD
- WNT
- SP
- AKRE
- TROVE
- BCAT
- BOOH
- BRITTO
- RKFI
- QUAD
- ETHO
- LOA
- SAKAI
- NABOX
- GEMINI
- FKR
- CHARLES
- SEVILLA
- DJI
- DUREV
- REGENT
- FOUR
- AMO
- BCDT
- KWANT
- $BROKE
- EGG
- GBCK
- BUILD
- PANO
- PHTR
- RAFT
- KDR
- PEPES
- MUT
- F/ACC
- KEIRO
- SUT
- NORMILIO
- PONCHO
- OMNI
- AUR
- BLINK
- CRGPT
- WOOP
- UNICORN
- POINTS
- OPIUM
- SOONX
- BNBAI
- MARCO
- FREN
- WDOG
- ALPHA
- FIT
- USDT
- USDT
- SUNTRON
- COST
- CND
- FLP
- EZ
- AIM
- MOE
- 8CHAN
- CWAR
- PLENA
- SOLA
- FLU
- JKC
- WDC
- ARC
- CLO
- CPAI
- TAURUS
- MOOMOO
- CATALORIAN
- PRONUT
- WIGL
- COQAI
- SBR
- REV3L
- MTH
- DORA
- MA
- TRENCHAI
- WOMBAT
- EARN
- WEHMND
- BINGUS
- OGSM
- 99BTC
- CURE
- 0XBTC
- ASI
- TDM
- XBLAZE
- PSSYMONSTR
- SOLO
- COME
- DACAT
- KOMET
- $AMEN
- EMILIA
- MELD
- SONE
- HYDRA
- SHIBC
- FAME
- ZMN
- SOLVE
- SOLARIS
- ANDY
- FIRST
- TORSY
- WIFE
- TOOKER
- SECOND
- FLOWER
- KWAII
- CNG
- RIC
- WGR
- MAIV
- SMARTCREDI
- INJX
- AIX
- $GNZ
- PUMPKIN
- FOFAR
- LOAFCAT
- GEKKO
- TSWAP
- SNAIL
- SPERG
- GRLC
- AVIVE
- DEEPAI
- WORK
- MCL
- BCOIN
- BONE
- W3GG
- HERMES
- PSWAP
- GAMI
- HTERM
- SAI
- SAM
- PNDR
- PGOLD
- SUB
- USACOIN
- LINU
- SPARTA
- NFTFI
- YOUSIM
- WNDR
- $CROAK
- FINC
- ROAR
- CHEESE
- BLUESPARRO
- BEENZ
- BIAI
- BEATAI
- ARCA
- LONK
- WONG
- HOGSCOIN
- HIM
- BRO
- TETU
- SPHYNX
- BCCOIN
- OLYN
- BMON
- GORILLA
- IONA
- SHAR
- CIA
- OPTR
- PLQ
- E/ACC
- TRUMPIUS
- CATGPT
- WF
- COINYE
- $SPACE
- AIRI
- KINGSHIB
- IPAD
- ALEPH
- SEED
- PSL
- BTF
- GEKO
- D
- SPIN
- STAM
- SPEX
- COMSWAPWLI
- BTCZ
- TECH
- LEO
- REXBT
- SUNWUKONG
- MYAN
- DFP2
- BHAD
- TKST
- ATRI
- ROCK
- ZACK
- DEFROGS
- MEOW
- BIP
- AICM
- UNISTAKE
- STOIC
- BOP
- LOKY
- YAY
- BITZ
- DUCKAI
- ZYN
- STRONG
- CHAMP
- CLEV
- CELA
- AUTISM
- CNCT
- ROP
- SOLARBA
- CNDY
- PARTY
- ZELIX
- METH
- PAPER
- CNV
- WAI
- $TIMES
- HEDGE
- NIGHT
- CATGIRL
- ASSCOIN
- GEL
- GRAV
- VEGA
- RSN
- CREA
- NEON
- DOGECAST
- KEE
- SPORE
- DEPLOY
- LOON
- MEWC
- MARVIN
- NEMO
- JONES
- $UOS
- MGT
- ROCKY
- HNST
- PURPLE
- HBARK
- OCH
- DMOON
- CHEXBACCA
- CHUCK
- DZOO
- CVAI
- ORDS
- HNC
- WNRG
- INT
- USDT.ETH
- LEND
- PARA
- CADAI
- SCORPIO
- GODL
- SAGIT
- ZIK
- MONAI
- MYST
- ROOK
- CDOGE
- XYZ
- $ACE
- KOVU
- CAPRICORN
- BLAZE
- TENET
- LONG
- ARIES
- XD
- BAG
- GEC
- SENSUS
- CBPAY
- FATAL
- DASHD
- ABOND
- VOLS
- FWB
- PEW
- 🐕
- GARY
- PISCES
- CANCER
- MONSTA
- GUILD
- XPE
- ZOO
- STELAI
- GRV
- OCADA
- NEURAL
- COAI
- BFIC
- PEAK
- PI
- COAL
- YMACH
- SUIYAN
- MUDOL2
- PEPE
- RPK
- GGTK
- GC
- WALTER
- UPTOS
- FCOD
- CLASH
- BIST
- YEETI
- GFT
- BIX
- $BEAT
- BLT
- PIGGY
- PINKM
- RADIO
- WANNA
- VIRGO
- YAM
- ZUSD
- SKICAT
- OVER
- DWEB
- ACS
- SANSHU!
- ZCL
- WGC
- BFT
- KIM
- ATOLO
- AGI
- BURT
- FUEGO
- PESTO
- VEIL
- CGAI
- RM9000
- MINIDOGE
- BHAT
- DEGA
- COVN
- WEB3D
- COV
- XMY
- ROOBEE
- $AGENCY
- KIF
- WECO
- $COOK
- DBI
- PEARL
- LIBRA
- POV
- $PLATH
- TWX
- PAC
- MMA
- APU
- SOLANA
- GOVI
- HYDRA
- KTON
- JULD
- MOTOKO
- BEND
- KEK
- RNB
- NAZAREAI
- DGNX
- GLDT
- SLICE
- YOU
- JIM
- RCAT
- ILOCK
- PROTEO
- DOGK
- GMB
- XSEED
- NCTR
- DTX
- XWG
- DAI
- ZEE
- ADASOL
- $SAIKO
- $UPDOG
- FORTKNOX
- DPS
- VERDAO
- THC
- BRIUN
- CARAT
- XENO
- ELAND
- TASTE
- NAILONG
- FORT
- DEGENC
- FIRE
- AIWS
- HOP
- DNA
- CHAOS
- WYNN
- LC
- EOLAS
- IXI
- WILDNOUT
- PINU
- SETAI
- MANE
- FREE
- TKAI
- WN
- MPH
- PLOT
- TRG
- BTN
- UNICE
- VITE
- XUSDT
- $ARKEN
- SUPERCYCLE
- EX
- 🏦
- VAULT
- SATOX
- CGT
- KAT
- DCT
- CHEEMS
- SMI
- LAKKHI
- DONUT
- BARRY
- TRC
- TRAXX
- MEMEAI
- APAD
- NFE
- BIS
- RYOSHI
- HAUS
- $CATS
- CLH
- EXM
- KREX
- SIM
- MONK
- MELON
- BZE
- MANA
- ZRS
- PEPE
- USDX
- ANDY
- FRM
- INETH
- MSR
- BANDIT
- BRLY
- COBY
- Y2K
- UXD
- ELFI
- UNI
- INSUR
- OMEGA
- $KANSTAR
- USDT
- VNST
- THECAT
- ENKI
- KDG
- WAT
- TC
- VERSA
- BOB
- DRINK
- LOOT
- HOLO
- RBTC.B
- KABOSU
- QUIDD
- TIFI
- DOGSHIT2
- TIGRES
- HIT
- MILKBAG
- QRX
- REX
- XEQ
- RIDDLE
- FWT
- LYRA
- NOT
- SHROOM
- RELAY
- FURY
- ENKI
- SMACKM
- GOCHU
- WTFO
- SYLVIAI
- DRAGGY
- POLYPAD
- ARBX
- FLI
- PAC
- MVX
- IVPAY
- FYDE
- SHIBU
- PMON
- IVN
- BANGCHAIN
- $WEEDE
- KLY
- GENI
- ION
- SHEGEN
- CREATE
- VKA
- $RUG
- EKKO
- CMDX
- SATA
- $CHESTER
- BABYBTC
- SYNC
- SHIFT
- METAV
- ASSAI
- FLIPPY
- AGLA
- WOOF
- CIV
- BLOC
- AIEPK
- ADOGE
- TAOSHI
- RATING
- USDV
- SIRIUS
- DUCKIES
- DEFAI
- BROTHER
- TREAT
- AIVIA
- TITAN
- STOG
- PLASTIK
- KSK
- GXT
- ZEN
- DNOW
- DYOR
- CASH
- GYOZA
- DACKIE
- CHONE
- SHROOM
- RAJ
- SWARM
- NEWO
- BTRUMP
- THAT
- BONUS
- B20
- SKITTEN
- NAYM
- KNOT
- CORN
- GM
- SMOL
- YF-DAI
- $DICE
- SUITE
- XBC
- KLEE
- XLA
- VATRENI
- BOPPY
- LABZ
- FWC
- XVN
- ECTE
- CATF
- DFNDR
- CYB
- $SOULS
- LMNL
- AIDA
- POSI
- YES
- INUINU
- DIME
- KEKE
- $LOCKIN
- REGENT
- GOR
- $OTTO
- XNV
- KIRA
- GLDS
- BUILD
- CBX
- AXI
- BORING
- SPX2.0
- ELGATO
- SIMSAI
- L7L
- ODDZ
- SWOP
- XCREDI
- MON
- FOAM
- ETHUSDC
- PYM
- ONC
- EQPAY
- ECLIP
- NSTSTRK
- KONAN
- FREN
- C2H6
- DRX
- VIP
- MEFA
- RAB
- USDT.BSC
- SSSSS
- TGMETRICS
- CGG
- RCN
- WEWE
- REALM
- WAIFU
- SPR
- CPA
- $OZONE
- OCI
- MARO
- ZMT
- LULU
- GLINT
- PINGU
- APED
- COC
- W3F
- MPUP
- DUCK
- TORI
- BIGFACTS
- CHOCTOPUS
- EMBER
- AIMBOT
- PEANUT
- IDNA
- EXA
- SHUI
- TORI
- WSG
- TRUMPSFIGH
- JUICE
- THOL
- CT
- UNIO
- CCX
- USACH
- PVU
- $INTERN
- AUDAI
- SHIELD
- SANI
- HOKK
- WANDER
- TIPS
- NAVAL
- FLIES
- BITCAT
- THE1
- RHUN
- FLAME
- ALPHA
- SHIRYO-INU
- MOON
- H
- KOLZ
- 2DAI
- BLB
- BONKERS
- EDG
- MTS
- BOOJI
- USDC
- RUNNER
- STAPT
- STJUNO
- XPNET
- CHMB
- CHILLGUY
- DNVDA
- PAPERCLIPS
- TOKI
- CENTS
- ETI
- KNIGHT
- PSYOP
- PONCH
- RAMA
- DOOMER
- USDT[HTS]
- TTM
- SOBULL
- TSLT
- USDW
- SEED
- LTD
- H4CK
- CHAD
- ARO
- $QBIT
- OCAI
- R/SNOOFI
- JPOW
- PYRATE
- SUIMON
- ESOL
- ONION
- HARAMBE
- USDT
- NALS
- PFL
- RUM
- WETH
- LOD3
- ARTH
- GIA
- QLIX
- CLEO
- APOLLO
- GOME
- NINA
- KNUT
- ETP
- $MYST
- KM
- INX
- MEOW
- SWPR
- KIRAI
- POCHITA
- DIDID
- $MARU
- BOTON
- SPICE
- DEFAI
- OCC
- NCASH
- ILY
- LINDA
- THUMB
- BWS
- KACY
- DPET
- MAG
- VENT
- VEMP
- FLS
- SATT
- XRP
- ALL
- VES
- DELAY
- MARS
- SUIB
- SILVA
- ZAPO
- DOGAI
- PILL
- NSBT
- PIGU
- FLAT
- STINJ
- SACI
- WIT
- POOKA
- $HOKK
- VASCO
- OKY
- BRIDGE
- HID
- MVD
- EDAT
- GYSR
- $SITCOM
- AIT
- KCH
- XLG
- SAG3
- YDA
- INSC
- KNOX
- CIRUS
- VAR
- BDX
- CONE
- BASKT
- SCC
- QAI
- CATDOG
- DEFAI
- LOT
- GRAI
- USDC
- WHALE
- NEER
- AXIS
- CLND
- O3
- WOLF
- DAWAE
- VSX
- USDT_T
- CYBA
- $PRO
- MFT
- USDT
- PEPO
- BET
- $BOOB
- MANIFEST
- SUWI
- ETH2X-FLI-
- MT
- KORI
- STSEI
- BONECOIN
- FROQ
- FXUSDC
- CHAN
- EVEAI
- GLINK
- NETZ
- TOR
- ZGEN
- VYPER
- AX
- HND
- MRSMIGGLES
- CLOAK
- MYRC
- NDX
- KITTY
- PAD
- LOLCAT
- BBOT
- MONA
- TIME
- BULLIEVE
- BANK
- RIBBIT
- CTT
- EGG
- FELY
- KRA
- CRAPPY
- 🖕
- LRT
- TIMI
- $VAULT
- FATGF
- DRAC
- INBRED
- SHAKEY
- AI
- YGATA
- PEPEC
- SCOTTY
- NFTART
- OVO
- USDT
- CBANK
- LUDWIG
- WICKED
- EPIKO
- FRIN
- LAB
- GOON
- SHIBUSSY
- SHEZMU
- KDAO
- MARVIN
- LUCI
- JETTON
- OGGY
- MANYU
- RISE
- TCAT
- BROT
- KRIPTO
- GLS
- GM
- HOMO
- UME
- RVLT
- SIZE
- PAC
- SOLFUNMEME
- BANJO
- DOGGO
- SHEESHA
- PLEDGE
- REUNI
- NUX
- USDC.E
- CATHEON
- TOPG
- TT-WBTC
- OGME
- BAKKT
- FURY
- CRISPR
- GLCH
- CAT
- PICKLE
- KOY
- TOBI
- ROCK
- NEP
- SAAD
- NR1
- DOG
- GULL
- SPACE
- HMQ
- BLAST
- GOO
- ATD
- CHEYENNE
- KAPPY
- ANARCHY
- GUAN
- ACTUAL
- LDY
- SLOP
- CSW
- KAAI
- IRT
- ZACHXBT
- HYPER
- ALR
- YLD
- ORBIT
- VETME
- MIND
- PROL
- MONK
- WAIT
- BRNX
- MUG
- X
- BLXM
- LOOK
- ZYRO
- QUAIN
- 3P
- BOG
- TAGGR
- PET
- ROCKET
- MOCA
- SUIJAK
- VOID
- EML
- WABBIT
- DND10
- RHYTHM
- BABYSHIB
- WBTC
- SPINDASH
- CS
- MVP
- CHPD
- PEEL
- ELMNT
- CATO
- PLATY
- JELLYFC
- DIP
- FLOCKA
- BMI
- LQDX
- BRO
- BAINANCE
- BUILD
- ATHENA
- CHITAN
- ✖
- WOOF
- AXL-WSTETH
- AX
- UAI
- XRUNE
- CALICO
- LANDWU
- TYRANT
- $LILLO
- WETH
- VAL
- TAX
- TFI
- EBERT
- PTOY
- LPUSS
- OGC
- APR
- USDC.E
- USDC
- OLY
- MOOSK
- AYB
- XKI
- VFOX
- DOUG
- FCO
- BIAO
- SCB
- ETHEREUM
- SCCP
- BCMC
- MAGAA
- PTF
- KT
- SWIFT
- LOS
- SPO
- USDC.E
- KEKIUS
- HOPPY
- L2
- ZWAP
- HUSH
- CAINAM
- CAN
- MIMANY
- FAI
- USDC
- GUA
- SUITRUMP
- TRUTH
- ZHOA
- FFM
- DGH
- $BETH
- RMT
- RICK
- INK
- WELT
- LOOBY
- NOOT
- KAT
- ETHEREUM
- SUIDEPIN
- SANTA
- WIN
- NAI
- BUTTHOLE
- DOGE
- EVAI
- SORA
- MIA
- DEER
- API
- UDOGE
- VIRTU
- SFD
- BLACK
- PICA
- PEPE
- NYAN
- ARA
- EVOLVE
- BANK
- ECOIN
- MOGUL
- NIGELLA
- SHOP
- FLAME
- MF
- REPOALYZE
- ACE
- UGLYDOG
- CNS
- FLASH
- ONTOS
- COK
- USTREAM
- DCHEFSOL
- $LOCG
- ZAI
- CRYORAT
- LNR
- ARCH
- @DOGE
- SHEZETH
- IB
- WBAR
- BLOCK INN
- MFG
- SAINT
- KHEOWZOO
- LOE
- OLT
- METO
- RMT
- ITP
- CABO
- MIHARU
- $RAINI
- USDC
- EOSDAC
- INVITE
- WIK
- LIQ
- CCP
- IETH
- SVMAI
- XWIN
- RODAI
- SL
- WETH
- USDT
- PASTERNAK
- MTRM
- NORA
- PHONON
- CORGI
- FFTB
- CARBON
- CORN
- EUSD
- GEOFF
- SHATS
- MOON
- GROYPER
- TREEINCAT
- SHRED
- DELI
- NAVI
- AIMX
- SPUNK
- RABBIT
- BPT
- RSTK
- BUILD
- ZYGO
- ZKEX
- ZODS
- PYRA
- LEMON
- NAWS
- LYM
- PEANIE
- HLT
- BTCST
- BUNBUN
- SWM
- BAO
- RBW
- CLO
- BORK
- NAIFU
- SOV
- 1ART
- LUIGI
- NOVA
- OOZY•GOOZE
- HUNNY
- NONJA
- MOVE
- ZLK
- PCORN
- VISION
- VIX
- PAINT
- MEOW
- ERN
- $WSB
- PSY
- GOMU
- IAMAI
- SOLCAT
- MERGE
- NOCHA
- TRI
- ERIC
- MILK
- DXY
- WSB
- ENTR
- PBTC35A
- ETH
- XCASH
- $CULTUR
- KASJAK
- SYNO
- MAGICK
- LRS
- BRKL
- KMC
- TSUBA
- MFAM
- ILLUSION
- AICMP
- POTUS
- KWAK
- MEGA
- NSDX
- DAD
- O3
- SHARKI
- DYNA
- CROS
- DNT
- KEN
- LOOT
- ELONIA
- F2C
- USDT
- USDT
- $AIGG
- ∅
- ROT
- MCG
- AISTR
- MATT
- MVRS
- $ICONS
- TRDG
- BLUES
- WMM
- CRODIE
- DTI
- HOL
- IFSCI
- $BLU
- SUNPIG
- NOTI
- TOP
- NEUROS
- DOGMI
- MMF
- ATAI
- SPR
- TOH
- TCT
- RACCOONDOG
- BONK
- DLTA
- AVAX
- BEATS
- TATE
- RAIN
- PRIME
- OCN
- MTG
- SYBTC
- OSIRI
- WIRE
- SEBA
- BASE
- TRAI
- BAT
- DALGO
- ATA
- CLUBMOON
- SCOUT
- BETA
- DRPAL
- DON
- OF
- ARSW
- LOOTER
- CUR
- POD
- GDUPI
- TXN
- FLC
- TIDAL
- NODE
- COMCOIN
- $COFFEE
- MS2
- ZAPCAT
- POODL
- SECT
- NEPT
- NFTBS
- XMX
- PNT
- AGA
- UNEAR
- LEG
- YBO
- KCN
- FTW
- CONV
- PEFI
- LUCHA
- KAGE
- PERI
- HAIR
- INXT
- CAPPY
- NOX
- MONA
- MTRC
- EBYT
- DCI
- CLX
- ZSC
- LUBE
- BBL
- PODGE
- CODE
- SMTY
- ESS
- MEVETH
- WAS
- TOPKEK
- PIPE
- ALF
- DGI
- RE7FRAX
- $BIRDFLU
- ROGEN
- MAHA
- OATH
- WPSG
- OSMI
- BONKEY
- WHACKT
- BEZOGE
- RDX
- PUMLX
- BUU
- RUGGA
- DMND
- TICKL
- $CAT
- SOS
- XMS
- $ONION
- MTR
- RFUEL
- $BABYLONG
- ALLIN
- ANTI
- VOLTX
- PORTX
- BSTY
- FORKY
- BENT
- DYOR
- BTA
- WOG
- ECO
- FOMO
- FAP
- CTR
- CODEX
- BTW
- ARTX
- BAHIA
- NEURONI
- HEC
- TULIP
- ROUGE
- VBELLS
- ARROW
- SPCTRM
- KONO
- $TORO
- CHIB
- GATSBY
- MEAI
- CRP
- OPK
- TZPEPE
- DPLN
- PLANT
- CHEERS
- WHALE
- PARAM
- LION
- MILK
- FODL
- IDEA
- COMFY
- GODEX
- 39A
- RADAR
- AWARE
- MBAG
- CURTIS
- THGUY
- GOAT
- SOH
- $RICH
- RURI
- RADIO
- CORGI
- BSEN
- HSAI
- GMPD
- USDC.BSC
- ODIN
- VOLT
- GAGA
- SPIRIT
- DAW
- CAT
- WJUV
- BUILDX
- AXE
- SANTA
- SU
- REBELZ
- GHSI
- CANDLE
- PIX
- DOGECAST
- SHI
- GSE
- OCEANS
- IONX
- FIRST
- MMAI
- NEW
- DEGENOS
- GKAPPA
- $DAPY
- MORUD
- MOO
- UTS
- BLANK
- TUX
- JEFF
- AAG
- MOON
- ASHA
- PRO
- LEE
- DANCE
- DEEPAI
- UAPT
- CUT
- PRAWN
- ELMO
- ZFI
- QDFI
- CWT
- AEGIS
- WBTC
- HBARBARIAN
- LAD
- URS
- CORE
- CYT
- TTC
- USDT
- PBR
- DEPINS
- MEOW
- MOOSE
- CFI
- SI
- SVTS
- SHIH
- NFTL
- SUUSD
- CSI
- AUDD
- BEEG
- CULT
- BRETT2.0
- DAFI
- KOGIN
- BRO
- MVC
- DRC
- $PIGGY
- PXL
- MINDS
- MOX
- RELIGN
- USDT
- SNAPCAT
- CAI
- AART
- $SHRUB
- AIVA
- APTR
- SPFC
- KUMA
- SOY
- CRYPTIQ
- PAI
- $HORNY
- BNSD
- KANGAL
- $SNIFF
- JAK
- AA
- FECES
- STARGATE
- HAROLD
- APEMAN
- ETHPAD
- IKB
- BD/SOL
- JOI
- CRX
- MAYO
- IMMORTAL
- SBAE
- GRAIN
- LQC
- BNY
- BLADE
- LEXICON
- IFC
- ZAPI
- 42
- PROME
- GOLD
- TALK
- TONE
- QUA
- WATM
- OPM
- SBOY
- BERRY
- AVA
- $DMP
- ARQ
- VRSW
- ORE
- BTM
- MERT
- MERO
- MOB
- LIZA
- GGG
- FEVR
- BOMB
- 1HUB
- NAFT
- VXL
- SHND
- NAOS
- DRU
- WIF
- DFIAT
- WASP
- OBX
- GAIB
- MET
- COOK
- WPR
- LED
- MITHR
- BOSSIE
- BIRDDOG
- DOLLAR
- ARMY
- RIA
- MWD
- HALO
- GREG
- TAI
- YT
- BALTO
- SEN
- INS
- THX
- ETHM
- $CRAMER
- ECHO
- $JANI
- WDOT
- SPIKE
- LILY
- KENDU
- PPAY
- DECHAT
- FLUFFI
- INU
- TURBO
- EFR
- FOMO
- $VOX
- WOWO
- BASEX
- TMSH
- PPBLZ
- ODIN
- CEB
- ZUN
- NFTD
- LUMI
- DOMES
- PAC
- LILB
- GAI
- PWROSE
- BULL
- SOG
- RGEN
- EAGLE
- WORM
- HDAO
- GFY
- CHATTY
- GHFFB47YII
- FREECZ
- PMA
- LINK
- XIDR
- WSPP
- SKAI
- PETER
- HELMET
- SYNC
- $TINYP
- YAP
- IUSD
- MONKEY
- RETRO
- EYE
- POLTER
- CSWAP
- WIF
- BAOS
- YES
- BTCACT
- SPELLFIRE
- DEV
- HANA
- CLAUDE
- BCOIN
- AFC
- LIQQ
- SUIMAN
- MATRIX
- KMON
- DREP
- BABYPEPE
- CKOCT
- ACHI
- RISITA
- EDAS
- NAMI
- GOB
- HER
- PLY
- PING
- PIZZA
- ZER
- SHOPX
- GORPLES
- $RECA
- TIN
- DIGG
- MSMIL
- GOH
- GARY
- VUSD
- GAL
- WEBSIM
- LENDA
- TRUTHFI
- VELA
- MAKE
- AURORA
- SHIT
- USSD
- SWINGBY
- CATBOX
- SQRCAT
- WAWA
- LITT
- XY
- KOBA
- ATM
- AQUA
- SEAL
- BNU
- GOBI
- STX
- NEU
- XNL
- STRNGR
- PLANE
- KOVIN
- KWIF
- DINU
- WOPTIDOGE
- NEZHA
- DBTC
- BRIGHT
- ROGUE
- STA
- JANRO
- MUST
- DAWN
- FARA
- ARG
- GAYCOIN
- CHAD
- BWORM
- DOGECAUCUS
- STV
- DUCKER
- MIST
- GALO
- TRC
- LUFC
- NOWK
- WASR
- TDS
- GIDDY
- ICE
- CALLS
- ZEREPY
- KFT
- COINBT
- DDD
- DMAGA
- CROFAM
- ZILLIONXO
- FINA
- GRAF
- MONKE
- ZAT
- HELIA
- $ITO
- MOLLARS
- FREGO
- STAKE
- LIEN
- $BEFFAI
- MAO
- SPEED
- BANDIT
- NFT
- KAKA
- PEPE
- BETBIG
- RUFF
- QUINT
- GDOG
- INTAI
- BLOCK
- WATCH
- PNUT
- SCR
- SIMON
- PEANUT
- JARVIS
- JAM
- META
- FWOG
- PUPPERS
- BALLZ
- MET
- SPEED
- TXL
- SKILL
- SNAP
- PHX
- WETH
- BLEU
- SAM
- HSC
- DRAGONKING
- CATS
- APU
- CYBER
- GROGGO
- $PULSR
- DORA
- GROKINU
- HYENA
- BASED
- TRACKEDBIO
- ARBI
- LUCHOW
- SWAPZ
- HINAGI
- CLIP
- $GIGAI
- VSG
- NYXC
- XED
- GCOIN
- BABYTRUMP
- MOBY
- DUSD
- MOG
- SKRT
- BSV
- TH
- HOBBES
- MEGALAND
- JARVIS
- MONI
- VCTRAI
- VRX
- SCHRODI
- KABOSU
- WCITY
- OUTIE
- NIOX
- BTX
- CHULO
- WACM
- UFARM
- DCAU
- UTG
- CORN
- BIF
- GDOGE
- YBR
- GNME
- FLUX
- KEYCAT
- DGI
- ZTH
- HPAY
- SBKPT
- PYI
- CUPSEY
- LGTB
- BERF
- XDN
- BRETTGOLD
- CO
- GOOBY
- RFSTETH
- CSAS
- BABYNEIRO
- HOOT
- LOTTY
- GEM
- UTU
- AETHER
- HGT
- RAIDER
- TRIBE
- MUG
- PSM
- SELF
- BIRB
- BKIT
- ACT
- ALICE
- SOLAYA
- CHRONOEFFE
- MOON
- SGT
- SQUAD
- SHEESHA
- IBR
- LIFE
- AVERY
- $BOOTY
- CROGINAL
- BABY
- SIZE
- WETH
- RFR
- GMX
- NOODS
- UPDOG
- FLY
- $BROKIE
- ANIME
- KOAK
- CATEX
- KOAI
- EKTA
- NEVER
- GAMBLE
- D.O.G.E
- COLON
- DOPE
- AFIN
- $KEYDOG
- NIOB
- KING
- HGET
- COIN
- RYIU
- MILTON
- COPE
- UNB
- PINEYE
- USD3
- PFI
- GFT
- HEMPY
- BLOB
- TT-WETH
- WAGMI
- OCAI
- ALL
- SEN
- PLANETS
- BOWSER
- EON
- DYOR
- SASHIMI
- KEIRA
- SACA
- $MRKT
- PROPS
- KALM
- GEM
- KPAW
- FRENS
- ZILPEPE
- SHIKOKU
- ROY
- MVDA25
- DAI[HTS]
- LGNDX
- EEUR
- SOURCE
- HUMO
- BOSHI
- DOCUSOL
- PEPEW
- BANANA
- SOL
- MITH
- PORT
- ADX
- MASS
- MEDUSA
- MER
- $FRANK
- USDT
- SENDOR
- CHEDDA
- KIDEN
- HOP
- NEBL
- TERN
- FORE
- DREAM
- 8PAY
- CAT
- ETF
- LABSV2
- VERSE
- COBE
- THOG
- SDOGE
- UNIX
- MEWING
- MARV
- BAI
- SEDUX
- FROG
- AKITA
- ANTC
- YAWN
- KRIDA
- MGPT
- NICO
- META
- HAWK
- SHDZ
- BOSSU
- MOTH
- MEI
- CB
- BRY
- MVRWA
- SNTR
- PADAWAN
- $SCARF
- SDOGE
- AGORA
- SOLO
- CAKEDOG
- MKAT
- AGB
- NOHAT
- BCRE
- SOLY
- ARBOT
- RB
- PUMPAI
- CHILLAX
- SQR
- LONG
- CHRIST
- DFX
- XCEPT
- BREAKER
- TPAD
- OS
- SLB
- ASTRO
- RUG
- MUSTARD
- PRNT
- JASON
- EDOG
- NCAT
- AIC
- 2077
- PINO
- MEDUSA
- NFTY
- RNA
- FOXGIRL
- SSTR
- NEIREI
- ABX
- OPSYS
- CHWY
- DUCK
- PLOP
- CIRCLE
- ORBK
- POLX
- D2T
- XCT
- FEETCOIN
- ONI
- SCOOP
- MITTENS
- ORACLE
- BUCK
- H1DR4
- SABLE
- RAINBOWTOK
- POPSMILE
- FOMO
- DRIFT
- DRGN
- ROPIRITO
- KTC
- NEONET
- STAB
- MOOVE
- VDT
- OMOCHI
- BEAST
- MEMETIC
- CHICKS
- LVM
- MINIGOUT
- MEARTH
- ONX
- UNLUCKY
- EGG
- SLCL
- CRAFT
- GNRT
- DEFIDO
- VETH
- BABYNEIRO
- SCALE
- OPTION
- LIQ
- YETI
- TOAD
- USEI
- DFY
- ASTRADAO
- PCNT
- GF
- 霞
- GAIM
- SMF
- ALASKA
- SMR
- CHEEMS
- BENJI
- ISLAMI
- NULL
- MYRA
- YOTO
- NEROBOSS
- FIT
- SHORK
- GNX
- SUB
- BRRR
- BALPHA
- AAI
- PLY
- TPU
- DFND
- FARTDADDY
- SAFU
- BCP
- SCRAT
- BISO
- CERES
- ROCK
- SOLAR
- PILLZUMI
- BS
- ASCN
- DATAWITCH
- GINNAN
- ISHI
- TOKITO
- UNVAXSPERM
- ALGT
- MOTA
- KICKS
- EROWAN
- BABYPOES
- SI
- PUSO
- DAI
- MTOS
- HAT
- JOHN
- JASPER
- ARKI
- FBX
- STEAKETH
- MELO
- CUMINU
- CASH
- MVTT10F
- CU
- BABYCATE
- TERMINUS
- INF++
- CRYING
- AUTIST
- IBFK
- TOSHE
- SOL
- SHIBX
- IZZY
- DAWGS
- EYE
- PAC
- AMI
- TRIANGLE
- TINU
- SHITCOIN
- ODDS
- PEPE
- SVD
- ZEBRO
- REAL
- WOKIE
- WHALE
- BTL
- NFAI
- LARRY
- CPL
- CEWBTC
- GOWOKE
- HENAI
- CATWIF
- REM
- MONKE
- NXR
- LBA
- EMC2
- KWT
- GSC
- CORA
- MFI
- BAC
- HAWKTUAH
- NUGGET
- USDT
- SCREAM
- $DCAY
- CHIPI
- HOD
- AEON
- BTO
- SFT
- VCAT
- TAY
- SAVG
- CWH
- DOM
- CRA
- ORION
- CATGF
- BALT
- ZCO
- 32
- POPEYE
- HUAHUA
- DUCKY
- ANDY
- KOI
- LQT
- MFW
- JORGIE
- TWRAE
- 47
- RFT
- NIKITA
- SWRV
- GLP1
- CRUSADER
- GONE
- FORK
- SCF
- MMT
- COR
- DXGM
- LEO
- ESPORT
- OCD
- ZOOMER
- WSPURS
- VPK
- CNC
- BLUE
- IKIGAI
- PEPE
- $ZKITTY
- LILPUMP
- RIZO
- SADMEOW
- SRN
- CHIPS
- BIRD
- OCTO
- DOGIN
- GOAT
- CRE8
- NOAHAI
- LUCY
- ROCKY
- FABS
- SONNE
- COLLAB
- ALP
- GAP
- FRUDO
- BLAZEX
- SADANT
- FORM
- GNOCCHI
- FUNG
- NORD
- CNNS
- MAGAPEPE
- ROBO
- SUNPEPE
- VAULT
- MDS
- MERGE
- ARES
- INTERN
- $DOGE
- HUM
- A16G
- DINU
- BABYSOL
- EGG
- ARX
- BGA
- AGME
- AVN
- STSTARS
- SEED
- FROGS
- HIPP
- FOMOON
- FINS
- TCAT
- WHAT
- GINNAN
- NDAO
- GATTO
- NEXT
- FLURRY
- LMF
- PSEUDO
- ANI
- BIRDDOG
- DAI
- POLI
- PONZIE
- USUALUSDC+
- NIPPY
- PHX
- ARXIV
- GNFTY
- DEGENT
- RCH
- BIAO
- KCAL
- CORTEX
- MCEN
- ONC
- VDL
- EQZ
- CATVAX
- GECKO
- CORSI
- OINK
- PEDRO
- FLAT
- BUSY
- ZZ
- FROG
- SUPERBID
- UNN
- DUK
- HOPPER
- KAPSA
- ALA
- DINO
- STAR
- USDCAT
- BULL
- OMEGA
- DMT
- DTC
- JUNGLE
- GAS
- SSTX
- MISHA
- $CHILL
- MXNE
- MOONY
- BSDX
- BAKSO
- IUS
- GAMEFI
- SOLAPE
- KAMPAY
- MAGNET
- ELEC
- BAZINGA
- RLP
- COT
- GOU
- KINE
- TRIVIA
- QHUB
- DXL
- AGURI
- EMON
- KOL
- AIR
- HAGGIS
- KAMA
- SSNC
- BUTTPLUG
- FA=FO
- DGENAI
- FOXXY
- MIDLE
- DAI
- STICK
- ALETHEIA
- MNST
- BRUME
- ZODI
- GORT
- HANBAO
- SCA
- FXF
- KANDO
- WORKIE
- KOHLER
- VTF
- ARCD
- BLEP
- PWR
- ATS
- DRPXBT
- APES
- SOLX
- NYZO
- PENGY
- SAIL
- BRAZA
- EDX
- GLAM
- OMAGENT
- MEME
- MEAN
- HSM
- STD
- PUFFY
- PACOCA
- PRERICH
- ISAAC
- BOG
- AFFI
- SWAY
- NLC
- FTP
- GWIRE
- BASED
- FUKU
- TYBENG
- LSD
- CTF
- FLUX
- MEMD
- TMANIA
- MSCP
- DXAI
- CAPO
- GAG
- ZINU
- UWU
- PANA
- IDYP
- ITXS
- GENESIS
- EVA
- FNT
- UBTC
- JORKIN
- SINK
- SQUID
- ZORRO
- SPIKE
- STAKELAYER
- BULL
- XYRA
- FIWA
- SAI
- PARADOX
- SOLGOAT
- $RRT
- ARTTO
- BULLA
- BLADE
- TRUST
- FLAVIA
- IF
- SHRIMP
- SPOODY
- LCD
- FINE
- AI69X
- DHV
- AGI
- TURBO
- SHIA
- DYP
- QORBI
- REAP
- MINT
- BASED
- AES
- WAGIEBOT
- GIRLE
- IDV
- OCX
- MOLA
- ERY
- DISCO
- GLFT
- YOURAI
- SNN
- WBTC
- TOSHI
- PANTERAI
- ORBIT
- NINJA
- ARMOR
- FOUR
- GM
- GG
- CITDEL
- SCUBA
- HOG
- YAWN
- RABBIT
- TOGA
- FST
- KWL
- OPEN
- UDO
- CMONK
- CONK
- ANDY
- EARL
- KAKAXA
- DUCK
- TAD
- 🐈
- WAA
- WETH
- TIGRA
- SOB
- DEC
- MATT
- LUCKYSLP
- PRIMAL
- HERIA
- $MOXI
- JFP
- FRF
- FUEL
- FOREXLENS
- WPOR
- AXE
- ROSX
- CZGOAT
- WETH
- COINE
- LAMBOW
- $MUST
- KSTT
- ARB
- MMIT
- POPPY
- 0NE
- DKUMA
- MINU
- DAI
- BULLS
- URD
- SFIL
- TUNA
- ORO
- BONK2.0
- YAKA
- BABYCHEEMS
- WARPER
- WARG
- BOOP
- PUNCH
- PUFF
- OD
- BECOIN
- COIN
- ANDY70B
- GOLDEN
- HULVIN
- STOIC
- RENA
- NITRO
- UNQT
- MCOIN
- SZAR
- ANDY
- PROPEL
- A51
- XWP
- WAVL
- AGTS
- KILLA
- WINTER
- WZRD
- NCASH
- POOLZ
- BASEDGUY
- INCI
- HOOD
- BOG
- RZNDE
- SAM
- $LANDLORD
- BOOSEY
- MEME
- ANTT
- PCH
- BELUGA
- MOTION
- ARCONA
- WGAL
- FINA
- KYRO
- D.O.G.C
- PLSPAD
- KEYFI
- KIETH
- ADILLO
- ARGO
- FUND
- BASEY
- FTPXBT
- FOREX
- $BTC25
- GOLDEN
- POPKAT
- SUICY
- INU
- HADES
- DEEBO
- FNX
- WAFC
- EHHH
- FIJI
- WEX
- BMONEY
- LOTUS
- WSG
- PEARL
- SUILAMA
- ENKI
- PAPO
- ZIX
- NORM
- ET
- 42069K
- ALCH
- USDC
- DONTDIE
- DAI
- GOV
- MONKEX
- $GRASS
- SHIP
- SMART
- SLAYER
- LAB-V2
- PEAGUY
- FVT
- RANDOM9
- CPFC
- VGC
- TURT
- FROP
- FXBT
- ZAZU
- PRICK
- ARG
- QQQ
- ANKA
- KZL
- WATERBEAR
- WVG0
- JEOING737
- OFAC
- URQA
- UGG
- TROPPY
- GOOD
- REMILIA
- CROC
- WOOFI
- SPACE
- BABYMARVIN
- PLATA
- TALES
- JENNER
- MEF
- UAP
- MORK
- CATA
- BUMSHAFT
- ANDY
- PAR
- BAE
- ADE
- SHAO
- GBSK
- $STABBY
- POINTS
- ZKID
- LMT
- SHAWK
- STINKCOIN
- ASTEROID
- TRRXITTE
- CATWIF
- MMO
- PFIRE
- CZ
- SLRS
- MIRX
- ALPACA
- $TUSK
- DAFT
- TAMATEST
- DCM
- UNAI
- GFLY
- TIG
- ERGONE
- MOMA
- MBERRY
- OP
- FIN
- AWX
- LODE
- TODD
- $ACAT
- MIN
- TAJ
- BUTTER
- DIS
- FUTURE
- EXMPLR
- COFI
- XOR
- SAKE
- SUMO
- FTX
- BCDN
- MXNBC
- X8X
- MAD
- BRICK
- DG
- DST
- RIN
- JASON
- MSHEESHA
- PSDN
- HELA
- VISION
- SUNNY
- ISTAR
- HOPE
- FARM
- CGO
- ODE
- WSTV
- POPO
- SUPA
- HEC
- OPCT
- JOWNES
- BGCI
- CLU
- ESPR
- NERD
- SFX
- BRAINS
- WALLY
- GOLDEN
- MIR
- SHEERLUCK
- SUCKYP
- SYPHER
- SENT
- CATFROGDOG
- ONDA
- URO
- DAM
- JANET
- HIBS
- CALUM
- MOD
- BLOX
- $KEKIUS
- CAVE
- UFR
- PRINTR
- KLO
- VALUE
- ARCHI
- SCOMP
- BITT
- ZEN
- ILIS
- $SHIBASHOO
- CHOW
- ZB
- LOLA
- DAETA
- BUL
- IB
- PIXI
- MOCHI
- HIVP
- WSAM
- YODE
- BLOB
- BLAP
- DOPE
- APY
- $HOUND
- KOTARO
- WPFL
- PUSSY
- DOGGO
- KS
- FLUF
- BURN
- SUGARB
- USDTSO
- SHARE
- BORPA
- BOBBY
- AMERICA
- AIDP
- SFT
- SONNY
- HEIDRUN
- SHIELD
- CHIKUN
- KIRI
- BUILT
- LUC
- FOXX
- EYE
- DWC
- RETIREMENT
- SIGMA
- HXAI
- STPR
- MRUN
- PETUNIA
- KAKA
- DACKIE
- BWLD
- AVATLY
- DOGEC
- CCOP
- USDC
- QSWAP
- GODS
- $TRUMP
- POCHITA
- INUKO
- KZ
- WTH
- BCOIN
- MEOW
- LESTER
- BAKED
- TENFI
- FRGST
- $FARTMOMMY
- MAD
- KABOSU
- SKU
- $SMACK
- SYDNEY
- DUN
- MAF
- MTN
- TARIFF
- TERRY
- KEKIUS
- WBRGE
- WAIT
- ROCK
- MIYA
- HIPPO
- WAP
- DARK
- SNM
- CTO
- $GENE
- ORB
- TSLA
- STORM
- GAY
- MU
- KTN
- BLUE
- TAB
- MOOO
- CLANKTARDI
- XCAT
- ALPA
- MSPC
- WINTER
- POPO
- MOLECULE
- BULL
- LUCE
- CFT
- USDT
- OISHII
- DAM
- CLANKSTER
- RAPTOR
- HVN
- WYBO
- BZN
- MAO
- PUBLX
- HAT
- DPAD
- SMG
- SC
- N
- BABYHIPPO
- CHAIR
- GOOF
- SPORT
- MILKY
- GREMLINAI
- BURN
- WPERSIB
- SHIB
- XTK
- SABR
- SS
- OCP
- ADANA
- FROTH
- BOBE
- RARE
- OCP404
- SANTA
- WHOREN
- DAWG
- BIO/ACC
- DAI
- SALD
- SUBF
- ROCKI
- USDT
- BANK
- INU
- 4GS
- GOON
- ZAZU
- GLTR
- $PIXE
- SENKU
- 0XMR
- AIDI
- MUGI
- MAGADOGE
- WOKE
- KENJI
- PHMN
- JAI
- SAFU
- UFO
- WCAI
- PINE
- EAR
- SKINUT
- SUISHI
- ME
- HOSHI
- TOPCAT
- HOODRAT
- MXGP
- SUNNED
- HEFE
- CZAR
- HEHEH
- ONGO
- VITAI
- DANA
- PIVN
- SKY
- WBAHIA
- OCTO
- COFI
- BRK
- YNBNB
- BERAFI
- $LOGE
- D/ACC
- IRD
- KPAD
- BLKC
- LUIS
- INCEPT
- LENS
- DRONES
- WODS
- WUFC
- BABYPNUT
- GDAO
- MUNCH
- WTF
- MEGA
- BUN
- HACHI
- SNAP
- TYKE
- SASHA
- IOV
- BORK
- WLEG
- ARIX
- SPUNK
- BOB
- COG/ACC
- MAPE
- MAX
- WNAVI
- XGN
- VICKY
- SNOW
- $JACKY
- PEPEGA
- MAD
- ETF
- MINIDOGE
- COLANA
- OPPIE
- GUS
- EFX
- PIZZA
- $PLPC
- MIHARU
- GINGER
- TRONDOG
- ARIE
- XIO
- ZERO
- ZEEK
- 1ON8
- PIX
- EQUAL
- AUDIT
- ND
- ZENITH
- WVERDAO
- SOCKS
- CELT
- GENIE
- DVINCI
- KPOP
- PRICEAI
- SCOIN
- DVT
- MIS
- ABE
- ALPHA
- W$C
- CMPS
- RIZZ
- SNK
- CORGIB
- FROYO
- WHASHTAG
- CAT
- ELE
- LINQ
- PARRY
- TSUJI
- AEJO
- SHIRO
- ORCL
- EDEN
- PEENO
- CURLY
- OMNI
- SOX
- CHEF
- $MEMES
- DUSTY
- LAPUPU
- YELPE
- LOL
- FIU
- SCAN
- $CRDN
- DUDE
- CRUNCH
- ANON
- FILTER
- SUIDOG
- BLUFF
- WATER
- BHOLE
- HYPU
- WVASCO
- MONA
- PEPEAI
- GECKY
- XP
- PEPE
- SENC
- TORA
- BOYSS
- JEWELS
- LORE
- XSEI
- BABYMIGGLE
- WTIGERS
- BLS
- FIGS
- BUDDHA
- ETHPRINTER
- REM
- SHIMMY
- LET
- BTCAT
- MPX
- PAPU
- KAPPY
- WSARRIES
- FINN
- QGG
- TCP
- WFOR
- FINE
- BOGUS
- FUN
- PHX
- UNIPCS
- VERA
- CUSD
- QUBIT
- LCN
- RAIN
- PMD
- SPQR
- DAM
- CNET
- DAOS
- WSACI
- FKSK
- POG
- DPY
- WBENFICA
- SUNLION
- FLS
- WISTA
- MILK2
- FAPTAX
- WIZARD
- WFLU
- CULO
- MIKO
- DOKY
- LONGEVITY
- FEDJA
- TILLY
- SYNTH
- TONIC
- BPX
- CHINU
- SOLY
- LIQ
- KET
- WSHARKS
- AETHER
- TCAP
- MOON
- CHEESEBALL
- UT
- AZUKI
- $NODE
- MORE
- RS
- DOE
- TUCKER
- FRUG
- CWC
- WTRA
- DOOGLE
- VOLTA
- ALN
- DJCAT
- PEW
- PAWSY
- BLUBIA
- TBFT
- MAGASHIB
- SMILEK
- SAI
- SNIFFS
- THN
- PLEB
- WSFP
- TIRED
- NINJAPUMP
- DOGIUS
- BHC
- BAO
- TNC
- TIME
- HHGTTG
- NEIRO
- AIKA
- BTCW
- BRIDGE
- PRARE
- STORAGENT
- P3NGUIN
- XENO
- DEARBOOK
- FUR
- KFUCAT
- KAIA
- BEING_AI
- EGOLD
- XTT-B20
- QOAT
- GOATX
- WALL
- CHADCAT
- HARAMBE
- LOTION
- صباح الفر
- VERA
- HODL
- GMAT
- PETOSHI
- BALLS
- LFG
- WNAP
- AGV
- PTS
- AAAHHM
- PCHF
- DELAY
- CAT
- DRA
- WAGMI
- GOF
- SONIC
- RIDERS
- SPQR
- HAVA
- UNDEAD
- CHUANPU
- BABYPNUT
- CCTV
- HUHCAT
- BDRM
- ATLAS
- DWA
- SOLPAC
- GIF
- PEPE
- KINGNEIRO
- DOGER
- FDREAM
- NERDY
- LAMA
- BAILEY
- RONDA
- SPEX
- ATH
- ABI
- LUN
- YOBASE
- FUD
- PWAR
- 8008
- APRIL
- SOOTCASE
- PEL
- MILEI
- SANIN
- BOLI
- CHILLGIRL
- ICE
- TMNS
- NDAS
- SPLASH
- KEK
- BRACE
- KOI
- OGGY
- BINARY
- TETHYS
- ROSSCOIN
- GUBERTO
- VIOLET
- BBK
- FX
- CAT
- 69420
- LILA
- ALAN
- $KEK
- LABZ
- BWED
- NSURE
- COCAINE
- LOOPY
- STACY
- 0XDEV
- GAMMA
- FVM
- GARD
- NEIRO
- TRUMPIE
- LONER
- IZUMI
- XMAS
- SAMI1
- ADAX
- SUPAI
- CMST
- BICHO
- N1
- ZOA
- PST
- BOBY
- MAYA
- SPIKE
- WAM
- COPE
- $YUMI
- DND
- BPRIVA
- ONE
- DEGEN
- PAL
- CHEEKS
- ERC-AI
- OKANE
- FMT
- HONKLER
- PDOGE
- EAGLE
- WGFK
- DOGY
- ASTRO
- WMIBR
- SANTINO
- SKULL
- MAN
- NIGI
- SAP
- GINNAN
- REGI
- SOLANA
- PNUT
- POU
- MTK
- PREDICT
- BRUH
- BABYGOAT
- SBET
- YDF
- $CHEUNGUS
- ASTRO
- BUFFI
- $PMW
- BALLS
- WAPL
- POPO
- PRCY
- 1%
- $MAMA
- COOL
- PEPITO
- AGI
- NOTWORK
- NFI
- MATRIX
- ROAD
- WRSO
- OMOCHI
- BTC
- $ROBIE
- SOFAC
- MOFI
- SCHIZO
- JUJU
- FOMO
- DOS
- BOY
- BUB
- CAT
- MWM
- ZYB
- SUNPUMP
- JUSTICE
- CLX
- LUMIO
- MOLLY
- QMIND
- MOCHICAT
- RONOUT
- SQRL
- PNET
- RUSTEE
- SGTV2
- SUYA
- WLEV
- RAZE
- GERTA
- MAMOON
- RINO
- CHANT
- KEN
- LEV
- SOLALA
- COZY
- LAB
- CHOCCY
- WAGMI
- MONGY
- ZOLA
- SANTA
- OASIS
- CRAB
- DONT
- UNO
- BITCAT
- CATFISH
- FOMO
- USAID
- GHNY
- STANDARD
- NWO
- CUFF
- DEGEN
- $BBT
- 1EX
- NAMI
- YANN
- WSAN
- CULTEL
- EXO
- BABYDENG
- WLUFC
- FINKEY
- VISION
- WGOZ
- FUSION
- DNZ
- GUDTEK
- BLAKE
- CAPY
- WJDT
- ROCKETAI
- RUNNER
- ZAAR
- FPFT
- MEE
- RHINO
- TRUMP47
- PDOGE
- GMMF
- CYS
- SHOOT
- PUNK3493
- PTSHP
- 🤡
- WUDI
- WCHVS
- WVCF
- CNTR
- WDZG
- WAIN
- WANNA
- AD
- KRYPT
- POCHITA
- SANTAHAT
- AESOPERATO
- CHILLFAM
- BUNNY
- WBFC
- LOVE
- DABOO
- PEPE
- GENZAI
- CYBORGISM
- SPIZ
- WQUINS
- PISSCOIN
- STENCHCOIN
- CEICAT
- GBOY
- TRUTHS
- GRINGO
- FARTGPT
- UTYAB
- WUCH
- 0KN
- MACKE
- DOGEX
- LEPER
- WITA
- DNXC
- LONG
- MONKEY
- DEGPT
- FTX
- JIN
- KUMA
- HACHI
- ANSOM
- KASBOT
- PUFF
- BAVA
- WROUSH
- REBD
- POLLO
- ENFT
- WVIT
- FEED
- WBUFC
- PSY
- CROW
- POD
- $MAN
- $KOLT
- DOTZ
- YUKIE
- YOUNES
- PFROG
- ∅
- YIELD
- FLEX
- BICOIN
- SOUL
- JADE
- MPRO
- FRA
- CLEG
- VALUE
- SWQUERY
- AIDOGE
- WAWA
- DC
- UCM
- RIKU
- WOTF
- SITY
- ROPE
- BLEPE
- FUKU
- RITO
- WMFC
- WIFI
- PAN
- TREEB
- ANCHOR
- KNIGHT
- PREAI
- SS20
- LESTER
- SHIB
- DUCKY
- RACEX
- LINGYAN
- YSU
- CEUSDT
- SUMMER
- RING
- BURRRD
- POPPY
- PUNCH
- MIVA
- DSM
- BAMBIT
- BULLY
- SNY
- FRED
- QUASAR
- GOOCH COIN
- CATOUR
- DERP
- IDLE
- FTI
- WSCCP
- GINGER
- LMAO
- PHILL
- FLOCKY
- AISCII
- MSWAP
- HTO
- H2W6GM6JZ
- $HUSKY
- RETARDIA
- ARATA
- TRUST
- BUG
- CAF
- MAXWELL
- POPFISH
- GIAC
- STACKS
- FLUXT
- ZORA
- IF
- EARLY
- BUTT
- FIONA
- WAND
- KUSH
- RINA
- DORKL
- $EGG
- URANUS
- DOGEI
- BMS
- HIVE
- OMNI
- OAKS
- ARGON
- KIRBY
- SHIGGA
- DOP
- BUTTCOIN
- WAIFU
- AD
- NODE
- AILIVE
- $FROGS
- GOOMPY
- NEIROH
- $1
- SENTAI
- BOBBY
- $GOODLE
- DONTDIE
- IHT
- JACKPOT
- DRONE
- TRONCHES
- RODOLFO
- MARSK
- BBC
- PE
- MEOW
- MAGAPEPE
- PHTEVE
- KITTY
- DADDYCHILL
- PSOL
- HMX
- GARBAGE
- AITRUMP
- POPDOG
- GIB
- APRT
- CRYPTO
- MOLLY
- AUTISTA
- ISHND
- HANABI
- DWB
- SHILL
- PIZZAGUY
- CORGI
- CHIBI
- WUKONG
- GOOSEPUMPS
- PONK
- PICKLE
- SAD
- H0L0
- DIOM
- TITAN
- PVP
- AII
- CHLOE
- BVM
- MOM
- EFT
- RDOG
- USC
- BWULL
- BILL
- PPDEX
- OTIA
- SULLY
- CHAD
- WOLF
- BABYPURPE
- AITT
- SHARK
- BLITZ
- START
- AINTI
- HYPR∞
- MOON
- QUBE
- JAPAN
- MARS
- LINK
- KRON
- CLAMS
- LIQ
- $MIHARU
- SILLYCAT
- RAGE
- TI
- MOBIC
- HOODRAT
- POI$ON
- POWERAI
- WGALO
- SKULL
- BKN
- CROCDOG
- ESES
- WRACING
- WSEVILLA
- WMENGO
- NEVA
- LSD
- LOLA
- DARK
- BULL
- PMPY
- FARM
- DOGE1
- SOLCAT
- MDEL
- GUM
- LOVECOIN
- CROY
- CNC
- AGENT2025
- APYS
- VBEA
- YIN
- GONESLER
- TAO
- WALA
- DOLA
- WOLFINA
- WENDCEX
- OMN
- SHITCOIN
- SBF
- TIM
- WDAVIS
- PINEOWL
- GRIN
- ALPHR
- USTX
- DLT
- SKM
- REEE
- BOB
- HMMM
- PLANKTON
- BOLLY
- LEGEND
- LOONG
- FOMO
- SWORD
- BUDDY
- SUICAT
- VIDAI
- CHARLIE
- $R3D
- FRYER
- SNEK
- SUIEET
- FRATT
- HAMMER
- EGGY
- WATLAS
- BCPAY
- D.O.G.E
- MMO
- TEST
- DOGE
- AVXT
- POW
- ATO
- UP
- SOLITO
- WEFC
- MEFI
- BEE
- ETHARDIO
- PONKEI
- CA
- ALIENB
- DOGER
- HIGHER
- AUC
- BLES
- TRUMP
- $TRAIMP
- BEE
- REMILIA
- FALCON
- SHIB
- CTO
- CROC
- SION
- GENIE
- CONVICTION
- DOV
- GCAT
- BROWSER
- LONGAI
- BABI
- BOPPY
- ZNZ
- RARE
- DJT
- PONZI
- DESY
- QAI
- MIW
- JENNA
- ENVOY
- CTOAD
- 9TO5
- DEXAI
- $SCOT
- XEN
- WHY
- AM
- UPG
- ATHENA
- DOLAN
- SNOB
- KAMABLA
- TOX
- SEALS
- UPI
- ALINAINTEL
- PEPE
- MALAKAI
- AICRYNODE
- ANIME
- SLAV
- BEZOGE
- DANNY
- $VENKO
- SHIB
- COVE
- TARDI
- $SPACE
- WSPFC
- DAVIDO
- BADGER
- POTATO
- CODERGF
- LOGOS
- SQID
- DHANDS
- DUCK
- FUFU
- SUID
- YOD
- BABY CZHAO
- JRRY
- GFR
- SARAH
- RICH
- WTIGRES
- M7F
- DAK
- KCAT
- AOC
- BUDDY
- PEBLO
- BIBI
- KIT
- BABYLOFI
- $BANE
- PUMPTRUMP
- GMEOW
- STUPIDCOIN
- MAT
- VIVEK
- FROG
- GIGA🧠
- PUMPCAT
- SBTC
- NOFAP
- BOMB
- SUGAR
- OOF
- AVS
- MECHAZILLA
- BOOBS
- CODED
- SHOE
- BRAIN
- KUNDALINI
- BARON
- GATO
- ROXY
- MIND
- UNW
- RYOSHI
- POPGOAT
- BASED
- $PXAI
- MATRIX
- $HONEY
- EPEP
- ZKE
- BSIM
- CSR
- PCT
- GAME
- $LOUIE
- MYB
- RUNEVM
- FARTGUY
- METAIVERSE
- WAGMI
- LKR
- PAT
- $WEN
- CAIRO
- DMLG
- KAFKA
- ALTOID
- BABYGOAT
- POOWEL
- L24AI
- ATHCAT
- SCRL
- WCC
- WAG
- ALIVE
- HUNTBODEN
- GEM
- COIN
- YESBUT
- CRAB
- AQUA
- MST
- WASM
- LUS
- PAUL
- SUNNEIRO
- PULSE
- RAFF
- SOLPOD
- FANX
- SHARDS
- WCPFC
- CEDAR
- MOCK
- MEMEGAME
- DOT
- GUUFY
- INC
- E
- MORRIS
- WEVE
- LORIA
- HAMMY
- CRW
- WOOFER
- SNAKE2025
- X/ACC
- MINJI
- SHUFFLE
- TANGO
- $XAI
- LONG
- TROLLICTO
- ZALPHA
- SDOGE
- JINX
- GRUG
- MENG
- GOP
- $SADDY
- ZOAI
- NERVE
- YOU
- BOB
- AFYON
- MDF
- DEGEN
- MAXX
- HODL
- BTCWIZ
- CRC
- XETRA
- DRX
- TYLER
- SMZAI
- MOONTHAT
- JETCAT
- MULA
- NUT
- FLOWER
- MOON
- IRENE
- KOK
- GLEBE
- BABYMAGA
- KRAMPUS
- SPARTA
- SWIO
- BROTON
- TRUMP
- ACCORD
- DEO
- MRCH
- GNT
- SPELL
- LUV
- CRISP
- MOOCAT
- BOOTS
- CSTR
- ZKGPT
- OBS
- CATJAK
- WSOH
- DOGSHEET
- QUANT
- MOON
- FFF
- POS
- MSTR
- AURA
- TON
- SSF
- BABYDEGEN
- XLN
- CAL
- SIKA
- DEUS
- WSTETH
- HGAI
- X
- $POOKU
- IRO
- BLOCK
- PAWPAW
- GEO
- POPWIF
- JMTAI
- PERA
- ACHI
- FLOOF
- MARIE
- EARN
- SCINET
- AGXBT
- FTS
- XPOW
- OMNIT
- GROOMER
- BITS
- $AIGCR
- PIM
- GRIFT
- FROGIE
- N64
- NXR
- PEPEWIFHAT
- DOPAMINE
- HACHI
- FOMO3D.FUN
- CICADA
- FLOYX
- AURORA
- HAT
- MONDO
- WIBWOB
- TWOCAT
- DMG
- CHANGO
- LCY
- APL
- SNAKES
- LFW
- THL
- FNC
- TUKI
- HMU
- SHRUBIUS
- BKC
- TOMMY
- XMUSK
- BDOGE
- CORE
- WOW
- CHINAU
- DISCIPLINE
- SUPR
- AURI
- GTUSDC
- FROX
- YUNA
- BULLISH
- BUSTER
- KOMA
- GM
- GRUMP
- BABYSHIRO
- BTM
- PWOG
- DOGO
- KOLANA
- GOATSE
- DP
- O3D
- ASAP
- BBANK
- 4WIN
- WIBFK
- QUEEN
- USH
- CATINO
- FAML
- $PACO
- SOAI
- MAGA
- PGEN
- LATENT
- AZIZI
- TAD
- $TRUST
- LOLA
- TDX
- HENTAI
- SOHOT
- OLIVE
- LAPUTA
- MEH
- HAMI
- $VERTEX
- TRUMP47
- TAOTOOLS
- BUENO
- FROG
- ESTEE
- KHA
- MEOW
- DECKO
- SEAT
- WOMEN
- MWH
- NPC
- WSAUBER
- UMI
- BEEP
- CHILLCAPY
- ODIE
- POZI
- CHART
- FUG
- TWURTLE
- BANKSY
- PAUL
- DGOLD
- XENO
- WRT
- MORE
- CFT
- COIN
- DOUG
- WSB
- COPE
- CBK
- RUBY
- CIG
- VAB
- GAISHA
- BITORB
- SEDGE
- MAIN
- PEMDAS
- QUIL
- MAAI
- W
- MDOGAI
- DUEL
- YOWIE
- GIGA
- MIKU
- ESP
- NEURO
- CUB
- KONG
- 2025
- DINO
- RIB
- HOOT
- JONAH
- BTB
- EUROB
- GPUINU
- RETARD
- APE
- YUP
- SWEG69
- ISA
- BOB
- PHNX
- CMFI
- FELICETTE
- THOL
- SHR00M
- $DUB
- ORI
- AKACHI
- KNU
- BRO
- LATTE
- GOBLINTOWN
- DOMO
- PINKY
- CET
- SPECU
- PACATO
- CRYPT
- MCAIFEE
- CAPY
- SCROLLY
- TOGE
- COW
- SLAP
- IMGX2
- $GOLDEN
- GRIDDY
- POOTI
- ALMC
- HORUS
- WOP
- CHONK
- POP
- DRIFTY
- APEDEV
- BL00P
- ROBOCOIN
- TRILLY
- GAPE
- VIORA
- XERAI
- SLIME
- SUMI
- $TALAHON
- KAILY
- RAJU
- DEERMAN
- PTP
- NOOSUM
- MORTI
- SKG888
- CHARM
- $KHAMOO
- CUCK
- GOSPODIN
- WELF
- COC
- NDX
- PC
- POWER
- LOVELY
- BITCORN
- RIZZYEAR
- FOTUS
- MANYU
- TUNE
- KSG
- MAXI
- SAI
- PARROT
- FERG
- WIFMAS
- EGL
- BONSAI
- CHUNK
- Z
- RINTARO
- AICAT
- PUN
- PRAIST
- BCUG
- MORPH
- GNOME
- DOGETHER
- TRUMPED.AI
- DTORO
- NAS
- YUKI
- VDAO
- DATBOI
- JIFF
- SSE
- CAFE
- FLOW
- FLOOF
- FUBB
- AI99X
- SOLPAKA
- BETA
- TUCKER
- CRTB
- UPDOG
- SKULL
- MILO
- GM
- MARS
- IF
- BULLA
- RAINBOW
- SOK
- CATGUY
- KIKI
- KAI
- ONYX
- OTTI
- AVAXMINERA
- SPWN
- MTGRD
- SHSH
- JOSE
- BOLTAI
- GOOFY
- MONKU
- BRC20
- BTL
- SHA
- VS
- CROW
- MANDY
- EYARE
- BAKENEKO
- BITDOG
- MOZ
- MAND
- NIB
- SALTY
- $BULL
- STARRI
- RIA
- $COUCH
- YUGE
- ZEUS
- HOLI
- SEALS
- $DREAM
- KONGZ
- $VENTI
- BUBL
- PUB
- PEPE
- MEOWKA
- DONKEE
- MONKEYAI
- QUANT
- MTC
- PENOSE
- XNF
- AIPETS
- RBIS
- ERSDL
- ENT
- MARE
- SKILL
- CVT
- WAPE
- SIMAI
- OMN
- BULL
- GM
- DOKI
- OJA
- ETHA
- SARCO
- PUPPET
- ALPHADOGE
- BREAK
- GPUL
- DOGB
- ROMEO
- HIM
- SPCTR
- SIBERT
- JU
- CTO
- MBC
- $MANGA
- ISLA
- VIRUS
- MCRN
- CHILLA
- SOLA
- RPG
- WIZ
- CHERRY
- SIN
- $SLCE
- AIGMX
- SOLYMPICS
- SMCT
- DOCTOR
- YDR
- 4TOKEN
- OUTER
- BWOB
- SKYRIM
- STAK
- KAIA
- UP
- $JBM
- CAP
- FUBAO
- TXN
- EARLY
- $ERNIE
- PEPEMAGA
- GIGACAT
- POODL
- ECO
- OGLG
- $BLOOD
- KING
- WIZZIE
- PUPPET
- 3D3D
- BNOM
- PIPO
- LILCAT
- BUIO
- CRAFT
- CORTEXZERO
- DMTC
- ITA
- BROOD
- ERMINE
- PNG
- BOOF
- PRESS
- WIZARD
- UARB
- NUKEY
- EDM
- CHAD
- FAPCOIN
- HERMY
- WOS
- UMINT
- FATCAT
- MEMECUP
- JRIT
- WNETZ
- GLAZE
- SOAI
- PEG
- SAI
- DASH
- CSUN
- PUMP
- LIMON
- ACTP
- CROCHET
- LEMON
- DCC
- WOME
- GSLAM
- SED
- JACK
- PIPI
- KUMA
- FREAK
- JACK
- BIO
- 4547
- 1984
- BOL
- TOCO
- ETF
- PET
- PSYCAT
- TISM
- AIDAOVC
- WHISPY
- CHADY
- 777
- CAVIAR
- ORCL
- VRTX
- MOMO V2
- NEWERA
- EDSE
- ITX
- MIKI
- SKIBIDI
- SERALPHA
- ECO
- POP
- SUDO
- CASH
- KING
- ASCIA
- ZAZA
- BETA
- GEM
- KABAL
- DEGEN
- ORA
- VERTEX
- AAAI
- FIRA
- POPNUT
- SLURP
- WIFEAR
- POSHI
- EGG
- FROSTY
- BALD
- CANGURO
- FREG
- HODL
- HAPPYDOG
- SUKI
- MURTIS
- CONOR
- KACY
- $LUMI
- ONLYUP
- SOLYCAT
- ROCK
- UNREAL
- APED
- AMPLY
- PING
- EYZ
- VIVEK
- SKATECAT
- HORNT
- $CROCO
- ALOT
- $ROFL
- CLICK
- CNB
- XP
- $SHEESH
- BURNT
- JET
- PEPIG
- GOLDN
- FINDME
- WINSTON
- NOSE
- DUCKEY
- SMORE
- KRPZA
- VTRA
- ANGRYGUY
- BSOV
- TESOURO
- OP
- ECT
- WARS
- CUTE
- MOJI
- WOLT
- LS
- FUKUROU
- COOL
- HOTDOGE
- TYPEN
- $ILENCE
- SBABE
- EQU
- LAWN
- CHI
- ATROFA
- $WIF2
- GTM
- TYLER
- INFC
- GFN
- BAOLONG
- PCAT
- $MAX
- ERB
- PEW
- PLUTO
- WILLY
- BXNF
- MGOD
- LGCY
- KAPI
- MOON
- LEONAI
- WTC
- PONZIO
- FLY
- XTE
- SASHA
- LIDYA
- IAI
- KEK
- MOZART
- ROSIE
- KOZUE
- CHAT
- KURO
- METADOGE
- $WAIFU
- TRONARMY
- LOLCAT
- K
- MOFI
- HCAT
- NOAI
- HABI
- TGPU
- $HOPE
- MATRIX
- ISKY
- SQUARES
- EGGY
- PLN
- EMOTI
- $GODFATHER
- RETARD
- QRK
- $CATA
- GIZMO
- MNTA
- VOID
- HAZEL
- MCBROKEN
- CHED
- DISKNEE
- ETHFAI
- CHARLIE
- BRUCE
- DIF
- MM
- REIKO
- OPRV
- BBYDEV
- COCO
- GOLC
- DOGGO
- BARK
- BAOBAO
- SHAKE
- CHILLA
- NUM
- $PIVOT
- ORB
- DFAI
- HUB
- LICKER
- TOKI
- MOVEZ
- KOL
- JOOPS
- $INSORA
- WENIS
- IUX
- DWAKE
- LONG
- BG
- LENNI
- SIGHT
- GVR
- 0XP
- WORK
- SOON
- WADU
- GACHA
- STRESSGUY
- PEEP
- MOJO
- PHILLIP
- BOLGUR
- FEG
- NEXEA
- GEN
- POLAR
- TARO
- $VIBE
- LAIFU
- KITTEN
- RIVUS
- KYRA
- PITTY
- FLAME
- PUNGU
- YUNKI
- PWOT
- CRY
- TMFT
- NEBULA
- RICE
- DANK
- SMH
- GUGU
- $LOLA
- SGLY
- $ωMσGA
- FAT
- DEKOPON
- STARS
- DONK
- RPG
- MIGRAINE
- MINTYGIRL
- TRIANGLE
- DIGGAI
- BONG
- MOSHI
- $BUN
- MARSHALL
- NRC
- $OCCER
- AG
- URMOM
- NOO
- ODIN
- CYCE
- GENESIS
- KGC
- CERBER
- UFIL
- ACTII
- APED
- ALMAN
- WIMPO
- FROP
- DCT
- SNARC
- NFTS
- AIRENA
- IRS
- KIMCHI
- LTT
- TOLYCAT
- L
- SPIX
- ONIGCHI
- JILLBODEN
- EPOCH
- TODD
- WAGIE
- WEN
- BOB
- BITARD
- SWAN
- BONKEY
- CUMS
- PJ
- BCI
- BURGIIR
- $BLK
- BILLI
- NOTDOG
- PAMP
- APOW
- $BIRDIE
- SHNJ
- GLUB
- SHADOAI
- CZOL
- ZECK
- MIMAS
- MOOTUN
- NORM
- GLOOM
- $SQUISH
- ZERESCAN
- SENDR
- CHRYSTAL
- GDOG
- TWINNY
- BSPT
- CHADAI
- CHILLWHALE
- PELICAN
- VAI
- GOOSE
- AMAI
- PEWPEW
- MAGIC
- GIC
- VOTEDOGE
- ROK
- NOM
- FUG
- IF
- FCAT
- PEPCAT
- CROAK
- ALDIN
- SHARP
- SQRB
- AST
- FITT
- SWAGGY
- CANCER
- SFAI
- MOLLY
- ISEC
- TENDIE
- IUSDC
- HACK
- ORION
- MOON
- POLY
- KRATOM
- MOON
- RAINBOW
- XTCASH
- BLOOP
- BIC
- PKIN
- FUM
- CROISSANT
- ASTA
- BIAO
- MEEB
- FREEDOM
- CRINGE
- TOOT
- UWU
- LOAF
- LBW
- BABYP
- PEPEK
- CHOLO
- CRAZY
- DWOG
- BOT
- CHECKR
- CGF
- BLUE
- CTAX
- LOAF
- GIRLS
- GM
- MOB
- MAGIC
- NOD
- OIACAT
- JUMP4EVER
- BLUE
- RYNO
- HCAT
- SPURDO
- KLEIN
- DAIO
- PIGGA
- KINI
- DGEN
- ASAFE
- BOP
- FROGGY
- DECATS
- AGSYS
- GGAINS
- HAKU
- WHC
- GARGOYLE
- OGAI
- 2025
- PEPEWFPORK
- DWOLF
- CLAUDE 2
- MOO
- NODEV
- GBTC
- TITAN
- BULLCAT
- GONG
- UHOSU
- PRTCLE
- TRM
- POU
- FINE
- MEN
- SPOON
- BOBA
- NML
- MOON
- DOCTOR
- POPFROG
- MGGA
- YURO
- PEPINU
- LPP
- TDT
- TWOOD
- EVIN
- PUSH
- $NUKUMUTU
- PEPEZ
- FSC
- SASHA
- FIRA
- DRAKO
- PUMP
- SAF
- YEET
- DCA
- FINDER
- YOOMI
- $BITB
- KAKA
- ALPACA
- FRKT
- $COST
- RUNNER
- TETHER
- CORX
- IWBTC
- BUBBLU
- VRN
- BBAXOL
- RIZZMASEVE
- CRX
- ADEL
- BOOK
- FORKY
- MICU
- MX
- KAPSEL
- RAT
- CHENG
- NEB
- RGP
- SLOW
- MONKIE
- WEEBS
- BELUGA
- DUKIE
- LIFE
- DERMO
- ONAI
- DOX
- RUGRAT
- REGRET
- GRACIE
- BAND
- LFDOG
- GINGER
- AINAL
- ACM
- ABCDE
- SMOL
- TSU
- DWOG
- $SCANNING
- MLNR
- ROLLIE
- LARPAI
- SCALEX
- KOOKY
- CTT
- $SPOT
- AXIAL
- SANTAPEPE
- CT100
- NAME
- HOMELESS
- UPX
- STANK
- PIZA
- RE7USDC
- TOBY
- SOR
- $LILY
- TUB
- HYRAX
- APET
- APE
- MD
- GG
- AFEN
- BRRRIAN
- SPACE
- FLYCAT
- NYANDOGE
- CHUMP
- DEPIN
- SFX
- ELE
- AVI
- WRINKLE
- DOGM
- NIPZ
- AVA
- $HACK
- BSL
- ICE
- SAGEL
- FFROG
- ARGY
- MONET
- LOST
- GOLEM
- N.E.R.D
- RBT
- MIRAI
- MSI
- TUNP
- KICHI
- DOGGY
- MONKE
- CAESAR
- MAGNUS
- WOOF
- HYP
- SOLP
- FIBER
- SVN
- EGS
- LUI
- YNBTCK
- HELLO
- TRIP
- STI
- WQT
- SKYH
- USDT.B
- TURBO
- 1FLR
- JES
- OLUMPC
- MCAI
- ZOID
- PUGGY
- SUZAN
- MUSK
- REBEL
- TROOP
- BLACKY
- PSI
- MC
- UCRO
- YARD
- LOADING
- AOK
- TPCAT
- SSOL
- FRANK
- TECH
- PEPECAT
- JAW
- GRWV
- DDIM
- BUDDY
- MAWA
- NOLE
- WORMS
- DOGNUS
- SMAS
- SNV
- UBE
- TRX
- GARY
- WIWI
- CHOWIE
- SAO
- RIZZO
- $WANTED
- CRIP
- WERK
- SAIKO
- ARAI
- SWC
- NUBDOG
- BIR
- CLOWN
- BUNDL
- BRINT
- PEKO
- CRIPPL
- LOS
- TRUFF
- VIPER
- MOLECULAR
- INVIFY
- WAG
- SEAI
- ORO
- EYE
- CDR
- TRN
- $STICKY
- WRAP
- $SODA
- $CLUB
- S
- $🧲6900
- BATYA
- MEVR
- RPD
- APE
- ULTRAETHS
- CHILLMAS
- FOOKER
- MPAD
- DEG
- MTK
- SEX
- GORILLA
- MSHARE
- SOLOTH
- TXA
- EZETH
- TME
- MSHIBA
- AIS
- ARIA
- INME
- MOOND
- META
- APEDOG
- RUBY
- M
- UFET
- LEMON
- EGGP
- DOE
- NRFB
- NANA
- NON
- SXS
- COSMIC
- CRYSTL
- NEXIS
- SING
- RUN
- WIRTUAL
- KINQ
- DEXSHARE
- ROULETTE
- HAPPY
- KUNCI
- AGS
- ALEXIS
- STON
- TRANQ
- MN2
- TSAI
- FIRE
- COW
- NUTZ
- JOSH
- NYANTE
- ROOM
- R1
- ALAI
- WOOLY
- CPOO
- GRASS
- NET
- BB
- OPX
- $DUCKY
- KLAP
- LANA
- IME
- XHV
- LORDZ
- ONI
- BABY
- VST
- CPO
- TRY
- PRMX
- PNUTS
- W3KT
- SWINE
- KURO
- DIAMOND
- BRTR
- BITS
- V
- TOON
- HERB
- DRACE
- PALG
- DDD
- DEGENUSDC
- IDAI
- MC.USD0
- MILK
- PANIC
- VIBE
- DCNT
- FOTA
- FAB
- SHEZUSD
- GMICHI
- UADA
- SLX
- CATT
- USDT
- CRX
- BANANA
- HUSL
- ZM
- ARTR
- RNBW
- SHILL
- 1EARTH
- KFN
- HASBULL
- BABY NEIRO
- FROGEX
- MFTU
- AFN
- AED
- ALL
- AMD
- ANG
- AOA
- ARS
- AUD
- AWG
- AZN
- BAM
- BBD
- BDT
- BGN
- BHD
- BIF
- BMD
- BND
- BOB
- BRL
- BSD
- BYN
- BYR
- BTC
- CLF
- BTN
- BZD
- CHF
- CUC
- CAD
- CRC
- CLP
- DKK
- CUP
- CNY
- DJF
- ETB
- DOP
- CVE
- ERN
- GEL
- EUR
- GBP
- GBX
- DZD
- GNF
- GMD
- GGP
- FJD
- HRK
- HNL
- GTQ
- IMP
- GHS
- ILS
- ILA
- HTG
- JEP
- ISK
- INR
- KGS
- GYD
- KES
- BWP
- JMD
- HUF
- KRW
- KWD
- KHR
- LKR
- LBP
- IQD
- CDF
- KYD
- LYD
- LVL
- COP
- MMK
- JOD
- LRD
- MKD
- KMF
- MVR
- CZK
- MAD
- MUR
- KZT
- MNT
- EGP
- MZN
- NAD
- LSL
- FKP
- MWK
- NPR
- NZD
- GIP
- MDL
- NGN
- PHP
- HKD
- MOP
- OMR
- PGK
- RON
- IDR
- PKR
- MXN
- SBD
- QAR
- NIO
- RSD
- IRR
- SAR
- SHP
- SCR
- JPY
- PAB
- SLL
- SGD
- SVC
- PLN
- KPW
- SYP
- STD
- TMT
- RUB
- LAK
- TND
- TJS
- TWD
- SDG
- LTL
- TZS
- TTD
- UYU
- SOS
- USD
- USX
- UZS
- MGA
- WST
- VUV
- XAF
- MRO
- XDR
- SZL
- XCD
- TOP
- MYR
- ZMK
- UAH
- ZAR
- ZAc
- XOF
- NOK
- VEF
- ZMW
- XAG
- PEN
- XPF
- PYG
- ZWL
- RWF
- SEK
- SRD
- THB
- TRY
- UGX
- VND
- XAU
- YER
- SLE
- VES
- SSP
- MRU
- CNH
What is Ethereum? The Revolutionary Blockchain Platform Explained
Ethereum, launched in 2015, is a decentralized, open-source blockchain platform that enables the creation of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). Founded by Vitalik Buterin, Gavin Wood, and other contributors, Ethereum’s core purpose is to serve as a global, programmable blockchain network. Unlike Bitcoin, which primarily functions as a digital currency, Ethereum provides a robust platform for developers to build and deploy various applications on its blockchain.Key Features of Ethereum
Ethereum introduced several groundbreaking concepts to the cryptocurrency world:- Smart Contracts: Self-executing contracts with the terms directly written into code
- Decentralized Applications (dApps): Applications that run on a peer-to-peer network of computers
- Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM): A Turing-complete software that runs on the Ethereum network
- Ether (ETH): The native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network
Ethereum vs. Bitcoin
While Bitcoin focuses on peer-to-peer electronic cash transactions, Ethereum expands blockchain technology’s potential by providing a platform for complex computational tasks. This versatility has led to Ethereum’s widespread adoption in various sectors, including decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).Technical Differences
| Feature | Ethereum | Bitcoin |
|---|---|---|
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof-of-Stake (PoS) | Proof-of-Work (PoW) |
| Block Time | ~12 seconds | ~10 minutes |
| Smart Contract Capability | Yes | Limited |
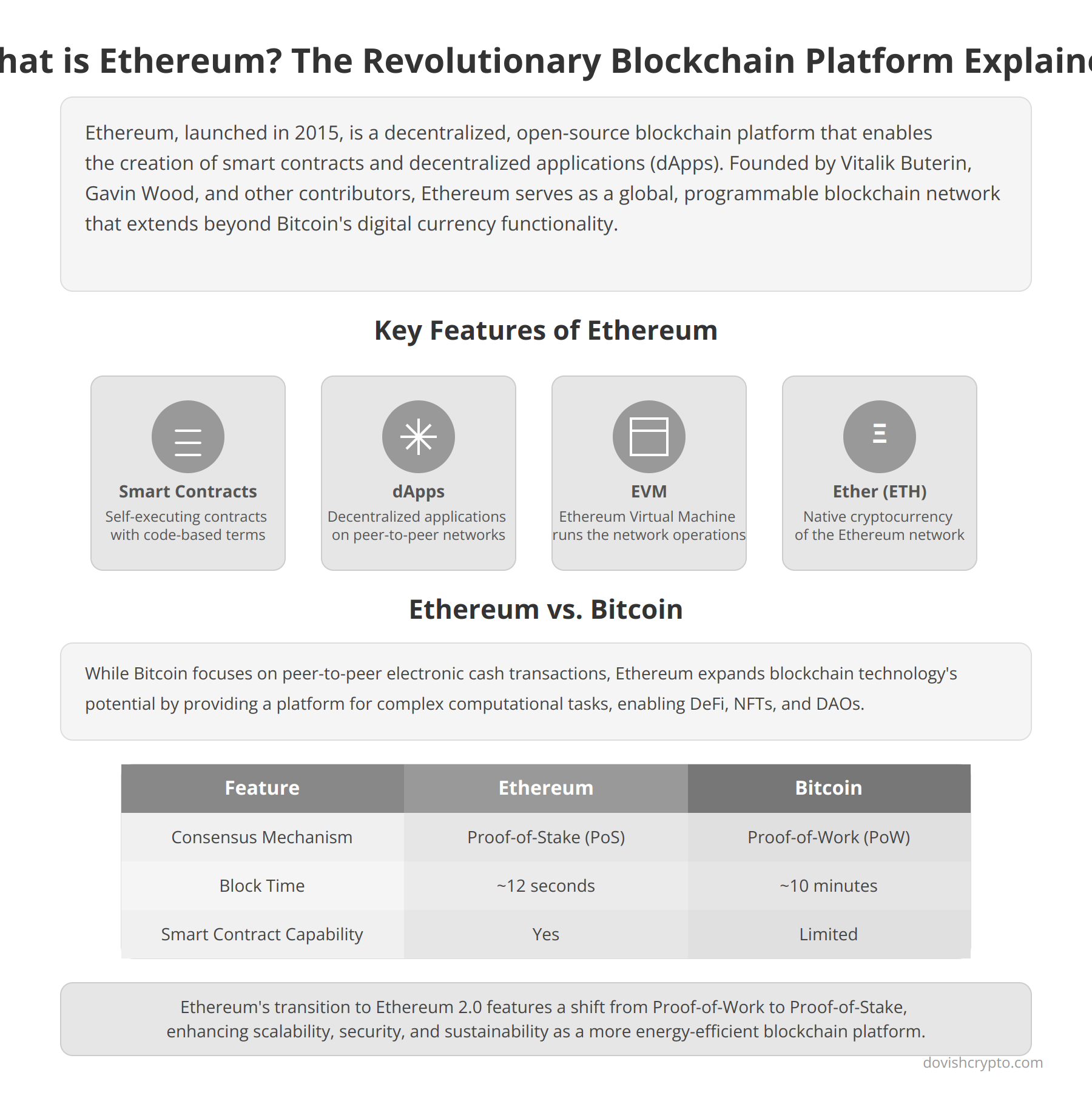
The Ethereum Ecosystem: Smart Contracts, DApps, and More
The Ethereum ecosystem represents a revolutionary blockchain platform that extends far beyond simple cryptocurrency transactions. At its core, Ethereum leverages smart contracts, self-executing agreements with predefined conditions encoded directly into blockchain-based software. These contracts enable the creation of decentralized applications (DApps), which operate on a peer-to-peer network rather than centralized servers. The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) serves as the runtime environment for these smart contracts, executing code consistently across all network nodes. As of 2025, Ethereum’s Layer 2 solutions have significantly enhanced scalability, with total value locked exceeding $55 billion across various rollups and sidechains. The platform’s native programming language, Solidity, allows developers to write complex smart contracts, while the EVM’s stack-based architecture processes transactions and updates Ethereum’s global state. Notable DApps built on Ethereum span diverse sectors, including decentralized finance (DeFi), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). The ecosystem continues to evolve with upgrades like EIP-7692 and EIP-7594, focusing on improving smart contract execution and Layer 2 efficiency. Ethereum’s modular approach to scaling and its vibrant developer community have positioned it as a leading platform for blockchain innovation, despite facing competition from newer protocols.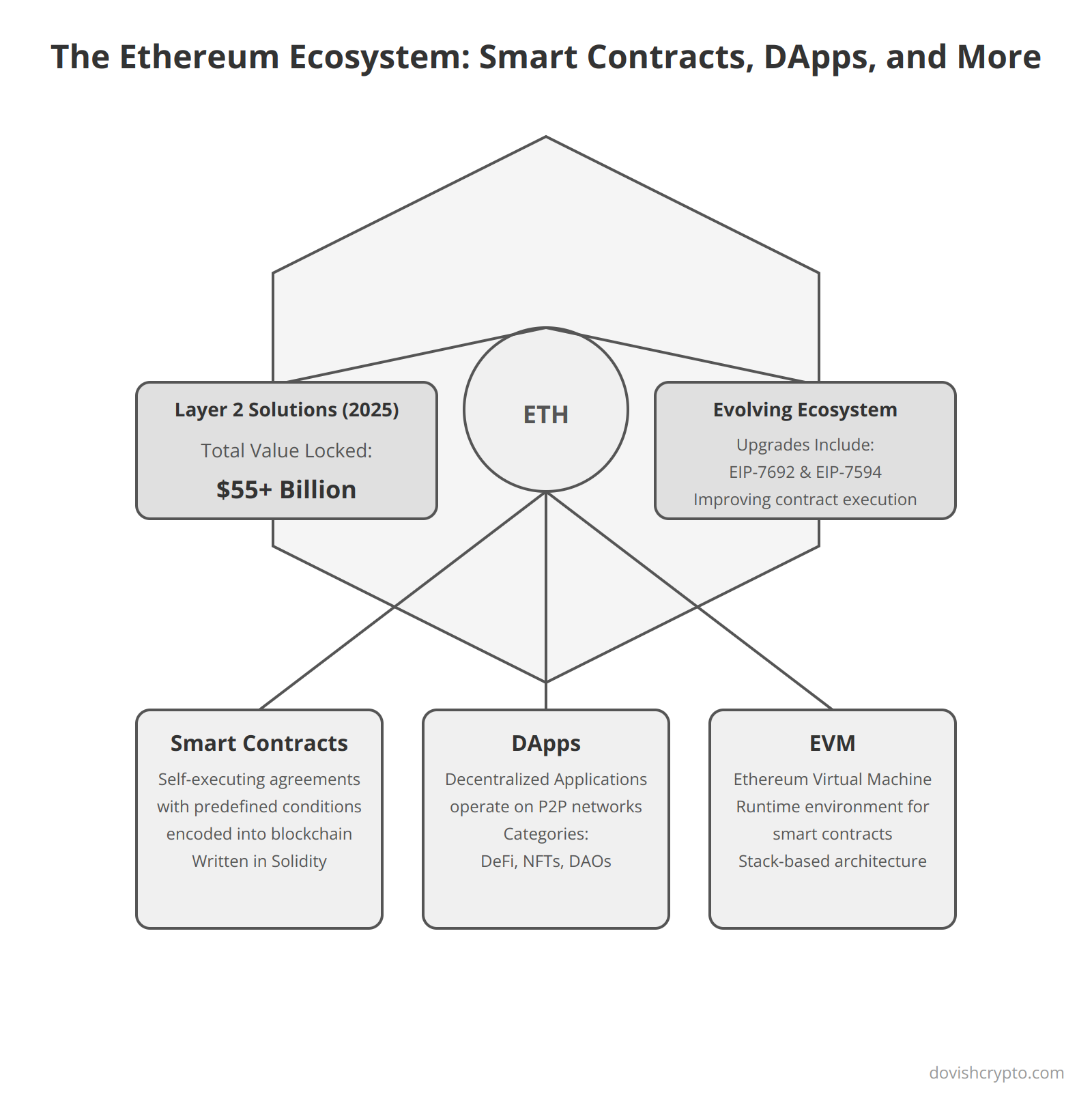
Ether (ETH): The Fuel that Powers the Ethereum Network
Ether (ETH) is the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum blockchain, serving as the lifeblood of the entire ecosystem. As the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, ETH plays a crucial role in facilitating transactions, executing smart contracts, and powering decentralized applications (dApps) on the Ethereum network. Unlike Bitcoin, which primarily functions as a store of value and medium of exchange, Ether’s utility extends far beyond simple transfers of value.The Role of Ether in the Ethereum Ecosystem
Ether serves multiple functions within the Ethereum network:- Gas Fees: ETH is used to pay for computational resources and transaction fees, known as “gas,” which are required to execute operations on the network.
- Smart Contract Execution: Developers utilize ETH to deploy and interact with smart contracts, self-executing agreements with predefined conditions.
- Staking: With Ethereum’s transition to Proof-of-Stake (PoS), ETH holders can stake their tokens to become validators and earn rewards for securing the network.
- Collateral: In decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, ETH often serves as collateral for loans and other financial instruments.
Transaction Processing and Gas Fees
Every transaction on the Ethereum network requires a certain amount of computational power, measured in units of gas. The cost of this gas is paid in ETH, with the price fluctuating based on network demand. As of May 2024, the average transaction fee on Ethereum is approximately 0.0015 ETH, or $3.50 USD. During periods of high network congestion, these fees can spike significantly, sometimes reaching hundreds of dollars for complex smart contract interactions.EIP-1559 and Fee Burning
In August 2021, Ethereum implemented the London Hard Fork, which included EIP-1559. This upgrade introduced a base fee that is burned (permanently removed from circulation) with every transaction, potentially making ETH deflationary over time. Since its implementation, over 3 million ETH have been burned, reducing the overall supply and potentially increasing the scarcity and value of the remaining tokens.| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Total ETH Supply | ~120 million |
| ETH Burned (since EIP-1559) | ~3 million |
| Average Daily Transactions | ~1.2 million |
| Average Gas Price (May 2024) | 30 Gwei |

Ethereum’s Consensus Mechanism: From Proof-of-Work to Proof-of-Stake
Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, underwent a significant transformation in September 2022 with its transition from a Proof-of-Work (PoW) to a Proof-of-Stake (PoS) consensus mechanism. This upgrade, known as “The Merge,” marked a pivotal moment in Ethereum’s evolution, addressing critical issues of energy consumption, scalability, and network efficiency. Under the previous PoW system, miners competed to solve complex mathematical puzzles, consuming vast amounts of electricity in the process. The new PoS model replaces miners with validators who stake their Ether (ETH) to secure the network, dramatically reducing energy usage by an estimated 99.95%.Reasons for the Transition
The shift to PoS was driven by several factors:- Energy Efficiency: PoS significantly reduces Ethereum’s carbon footprint, aligning with global sustainability goals.
- Scalability: The new mechanism lays the groundwork for future upgrades, including sharding, which promises to increase transaction throughput exponentially.
- Security: PoS introduces economic penalties for malicious behavior, enhancing network security.
- Decentralization: Lower barriers to entry for network participation promote a more diverse set of validators.
Implications for Network Efficiency and Scalability
The transition to PoS has far-reaching implications for Ethereum’s performance and future development:Enhanced Transaction Processing
While The Merge itself did not immediately increase network capacity, it set the stage for future upgrades that could potentially allow Ethereum to process up to 100,000 transactions per second, a significant improvement from its previous capacity of about 15-30 transactions per second.Reduced Energy Consumption
The move to PoS has drastically cut Ethereum’s energy usage, addressing one of the main criticisms of cryptocurrency networks. This reduction in energy consumption not only improves Ethereum’s public image but also makes it more attractive for institutional adoption and environmentally conscious users.Improved Tokenomics
The PoS model has introduced deflationary pressure on ETH through reduced issuance and the burning of transaction fees, potentially leading to increased scarcity and value over time.| Aspect | Proof-of-Work | Proof-of-Stake |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | High | Low |
| Validator Selection | Computational Power | Staked ETH |
| Network Security | 51% Attack | Economic Penalties |
| Scalability Potential | Limited | High |
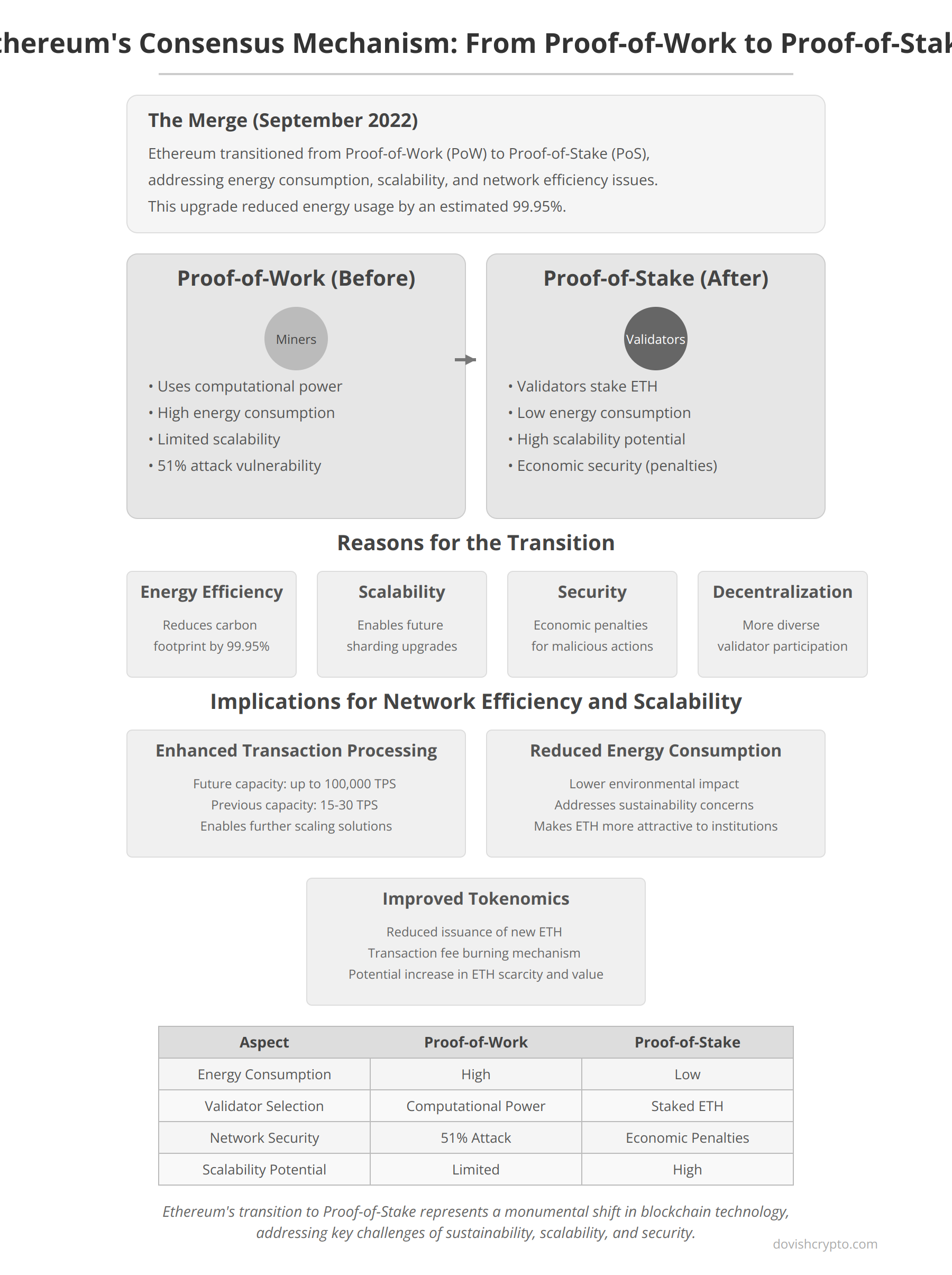
The Ethereum 2.0 Upgrade: Scalability, Security, and Sustainability
The Ethereum 2.0 upgrade, also known as Serenity, represents a significant evolution of the Ethereum blockchain, addressing critical issues of scalability, security, and sustainability. This comprehensive overhaul transitions the network from a proof-of-work (PoW) to a proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism, dramatically reducing energy consumption by approximately 99.95%. The upgrade introduces sharding, a method of partitioning the blockchain into 64 separate chains, enabling parallel transaction processing and significantly increasing throughput from the current 15-30 transactions per second to a potential 100,000 transactions per second. Ethereum 2.0 is being implemented in phases, with the Beacon Chain launch in December 2020 marking the first step. The Merge, completed in September 2022, unified the original Ethereum mainnet with the Beacon Chain’s PoS system. Subsequent phases will introduce sharding and further optimizations, enhancing the network’s capacity to support decentralized applications (dApps) and smart contracts at scale.Key Improvements in Ethereum 2.0
Scalability: Through sharding and layer-2 solutions, Ethereum 2.0 aims to overcome network congestion and high gas fees, making the platform more accessible for developers and users alike. Security: The PoS mechanism introduces economic incentives for validators to act honestly, reducing the risk of 51% attacks and enhancing overall network security. Sustainability: By eliminating energy-intensive mining, Ethereum 2.0 aligns with global sustainability goals, potentially attracting environmentally conscious investors and users.Impact on the Ethereum Ecosystem
The Ethereum 2.0 upgrade is poised to revolutionize the blockchain landscape, enabling more efficient decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and enterprise blockchain solutions. By addressing scalability and sustainability concerns, Ethereum 2.0 strengthens its position as a leading smart contract platform, potentially accelerating mainstream adoption of blockchain technology across various industries.| Feature | Ethereum 1.0 | Ethereum 2.0 |
|---|---|---|
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof of Work | Proof of Stake |
| Transactions per Second | 15-30 | Up to 100,000 |
| Energy Consumption | High | Reduced by ~99.95% |
| Sharding | No | Yes (64 shard chains) |

Decentralized Finance (DeFi) on Ethereum: Revolutionizing Financial Services
Ethereum’s blockchain has become the epicenter of a financial revolution, hosting a thriving ecosystem of Decentralized Finance (DeFi) applications that are reshaping traditional financial services. As of 2025, the total value locked (TVL) in Ethereum-based DeFi protocols has surged to $165 billion, representing a 450% increase from 2021 levels. This exponential growth is driven by innovative platforms that offer a wide array of financial products without intermediaries. Lending protocols such as Aave and Compound have disrupted traditional banking by allowing users to borrow and lend cryptocurrencies directly, with over $50 billion in loans outstanding. Decentralized exchanges (DEXs) like Uniswap and SushiSwap have processed more than $2 trillion in trading volume annually, challenging centralized counterparts with their permissionless and transparent operations. The concept of yield farming has introduced novel ways for crypto holders to maximize returns, with some strategies yielding annualized returns exceeding 100% during peak periods.Key DeFi Metrics on Ethereum (2025)
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Total Value Locked (TVL) | $165 billion |
| Annual DEX Trading Volume | $2+ trillion |
| Outstanding DeFi Loans | $50+ billion |
| Unique DeFi Users | 15 million |
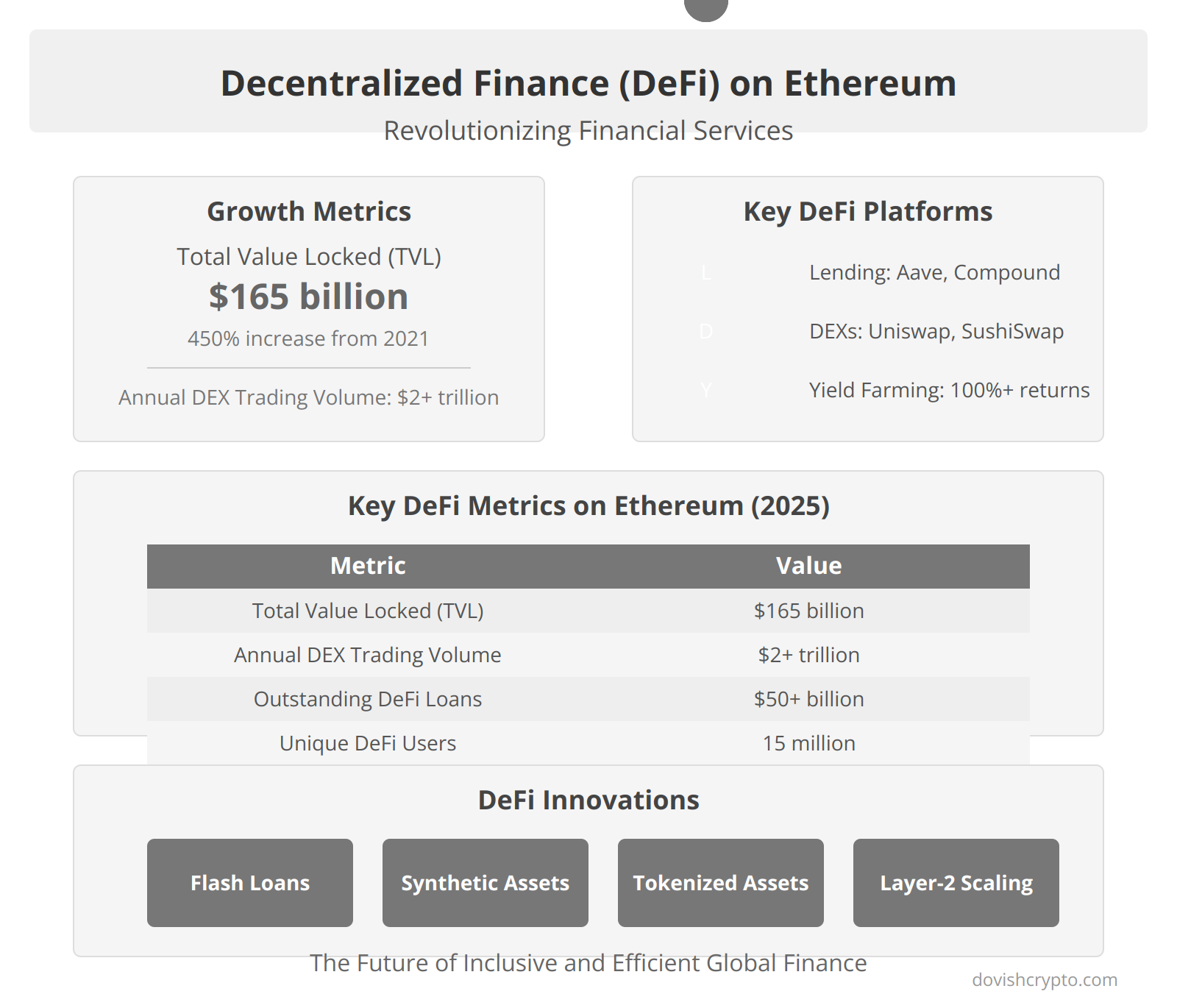
NFTs and Ethereum: The Digital Art and Collectibles Revolution
Ethereum has played a pivotal role in catalyzing the Non-Fungible Token (NFT) boom, revolutionizing digital ownership and creativity. As the primary blockchain platform for NFT creation and trading, Ethereum’s smart contract functionality has enabled the development of unique digital assets with verifiable scarcity and authenticity. The ERC-721 and ERC-1155 token standards, native to Ethereum, have become the foundation for most NFTs, facilitating the tokenization of digital art, collectibles, and virtual real estate.Popular NFT Platforms on Ethereum
Several prominent NFT marketplaces have emerged on the Ethereum blockchain, including:- OpenSea: The largest NFT marketplace, with over $25 billion in all-time sales volume
- Rarible: A community-owned platform featuring a wide range of digital assets
- SuperRare: A curated marketplace focusing on high-quality digital art
- Nifty Gateway: Known for exclusive drops from renowned artists and brands
Impact on Digital Ownership and Creativity
The Ethereum-powered NFT ecosystem has transformed digital ownership by providing:- Verifiable scarcity and uniqueness for digital assets
- Transparent ownership records on the blockchain
- Programmable royalties for creators on secondary sales
- New revenue streams for artists and content creators
Challenges and Future Prospects
Despite its success, the Ethereum NFT ecosystem faces challenges such as high gas fees and scalability issues. Layer-2 solutions and the transition to Ethereum 2.0 aim to address these concerns, potentially unlocking further growth in the NFT space. As the technology matures, NFTs are expected to expand beyond digital art into areas like gaming, virtual real estate, and decentralized finance, further solidifying Ethereum’s position as the backbone of the digital ownership revolution.| Year | Ethereum NFT Sales Volume | Unique Buyers |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | $94 million | 75,000 |
| 2021 | $17 billion | 2.3 million |
| 2022 | $8.4 billion | 2.7 million |

Investing in Ethereum: Strategies, Risks, and Potential Returns
Ethereum (ETH) has emerged as a prominent investment opportunity in the cryptocurrency market, offering diverse strategies for potential returns. Investors can employ various approaches, including long-term holding, dollar-cost averaging, and staking to capitalize on ETH’s growth potential. The 70/20/10 rule suggests allocating 70% to stable assets like ETH, 20% to growth opportunities, and 10% to high-risk ventures. ETH’s price, currently at $2,628.99 with a market cap of $316.6 billion, is influenced by factors such as network upgrades, institutional adoption, and regulatory developments. The upcoming Pectra upgrade in March 2025 is expected to enhance transaction capacity and introduce gas sponsorship, potentially driving ETH’s value higher.Investment Strategies
Investors can consider the following strategies:- Direct purchase on cryptocurrency exchanges
- Ethereum-focused ETFs for traditional brokerage exposure
- Futures contracts for speculative trading
- Staking for passive income generation
Risks and Challenges
Despite its potential, Ethereum faces several risks:- Scalability issues and competition from other blockchains
- Declining transaction fees impacting network economics
- Regulatory uncertainties in the DeFi space
- Technological vulnerabilities and potential software flaws
Factors Affecting Ethereum’s Value
ETH’s price is influenced by:- Supply and demand dynamics
- Technological developments and network upgrades
- Adoption rates in DeFi, NFTs, and enterprise applications
- Macroeconomic factors and correlation with traditional markets
Potential Returns
Analysts project varying price targets for Ethereum:| Year | Projected Price Range |
|---|---|
| 2025 | $5,554 – $12,000 |
| 2026 | $10,112 – $14,580 |
| 2030 | $20,958 – $25,006 |

Ethereum vs. Competitors: How Does It Stack Up?
Ethereum, the pioneering smart contract platform, faces stiff competition from emerging blockchain networks like Cardano, Solana, and Polkadot. While Ethereum maintains its position as the dominant smart contract ecosystem, each competitor offers unique advantages that challenge its supremacy.Ethereum’s Strengths
Ethereum’s primary strength lies in its first-mover advantage and extensive developer ecosystem. With over 4,000 active developers and a robust network of decentralized applications (dApps), Ethereum boasts unparalleled network effects. The platform’s transition to Ethereum 2.0 and the implementation of proof-of-stake consensus aim to address scalability issues and reduce energy consumption.Cardano: The Academic Approach
Cardano distinguishes itself through its research-driven approach and formal verification methods. While its development has been slower, Cardano’s Ouroboros consensus protocol offers enhanced security and energy efficiency. The platform’s recent addition of smart contract functionality positions it as a potential Ethereum competitor, particularly in areas requiring high assurance and regulatory compliance.Solana: Speed and Scalability
Solana has gained significant traction due to its high throughput and low transaction costs. With a theoretical capacity of 65,000 transactions per second (TPS), Solana outpaces Ethereum’s current capabilities. However, concerns about centralization and network stability have emerged, as evidenced by several outages in 2021 and 2022.Polkadot: Interoperability Focus
Polkadot’s unique selling proposition is its interoperability and parachain architecture. By enabling cross-chain communication and shared security, Polkadot aims to create a network of interconnected blockchains. This approach offers flexibility for developers but faces challenges in terms of complexity and adoption rates.Comparative Analysis
| Platform | TPS | Consensus | Smart Contract Language |
|---|---|---|---|
| Ethereum | 15-30 | PoS (ETH 2.0) | Solidity |
| Cardano | 250 | Ouroboros | Plutus |
| Solana | 65,000 | PoH + PoS | Rust |
| Polkadot | 1,000 | NPoS | Ink! |
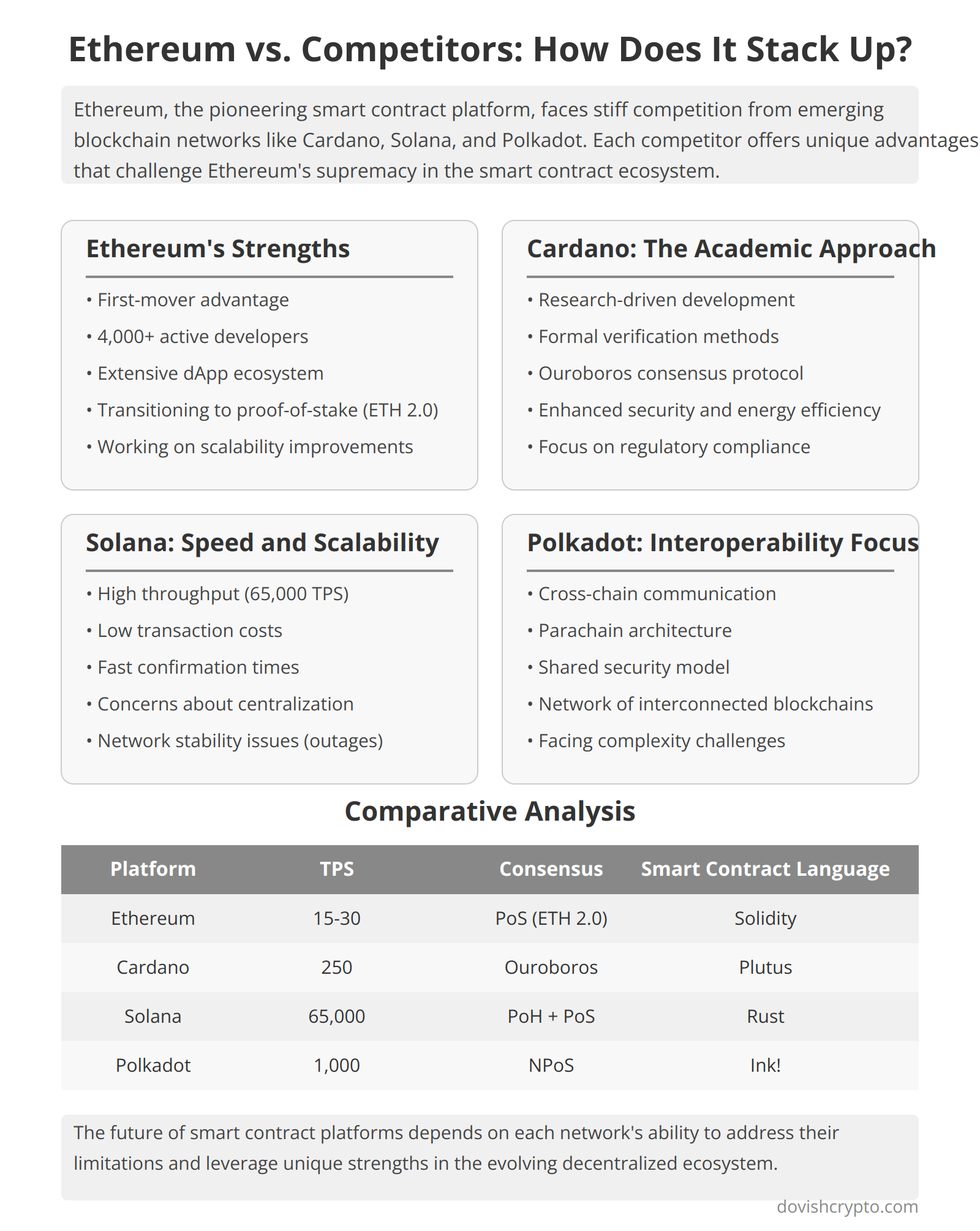
The Future of Ethereum: Upcoming Developments and Potential Impact
Ethereum, the pioneering smart contract platform, is poised for significant advancements in the coming years. The highly anticipated Pectra upgrade, scheduled for March 2025, promises to enhance the network’s efficiency and usability through a series of Ethereum Improvement Proposals (EIPs). Key features include EIP-7702, which will enable programmable user wallets, and EIP-7251, increasing the maximum validator stake from 32 to 2,048 ETH. These improvements aim to streamline user experience and bolster network security.Scalability Solutions
Ethereum’s roadmap emphasizes scalability through innovations like sharding and layer 2 solutions. Danksharding, expected to be fully implemented by late 2025, will dramatically increase the network’s data availability, potentially reducing transaction costs on layer 2 networks by 10-100 times. This development is crucial for supporting the growing ecosystem of decentralized applications (dApps) and accommodating increased user adoption.Expanding Use Cases
As Ethereum evolves, its potential applications continue to diversify:- Decentralized Finance (DeFi): Ethereum remains the backbone of the DeFi ecosystem, with innovations in lending, derivatives, and decentralized exchanges expected to flourish.
- Non-Fungible Tokens (NFTs): The platform continues to drive innovation in digital ownership and creative economies.
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs): Ethereum’s smart contract capabilities enable new forms of decentralized governance and collaboration.
- Enterprise Solutions: Major corporations are increasingly exploring Ethereum for supply chain management, identity verification, and tokenization of real-world assets.
Environmental Sustainability
Following the successful transition to Proof-of-Stake in 2022, Ethereum has reduced its energy consumption by 99.95%. This shift positions Ethereum as a more sustainable blockchain platform, aligning with global environmental concerns and potentially attracting environmentally conscious investors and users.Interoperability and Cross-Chain Solutions
Ethereum’s developers are actively working on improving interoperability with other blockchain networks. Projects like the Beacon Chain and advancements in cross-chain communication protocols aim to create a more interconnected blockchain ecosystem, with Ethereum at its center. As Ethereum continues to evolve, its role in shaping the future of blockchain technology and the decentralized internet becomes increasingly significant. The platform’s ongoing developments in scalability, security, and functionality position it as a cornerstone of Web3 infrastructure, potentially revolutionizing industries ranging from finance and gaming to governance and digital identity.
Ethereum FAQ: Your Burning Questions Answered
Ethereum, the second-largest cryptocurrency by market capitalization, has revolutionized the blockchain landscape with its smart contract functionality. To address the most common inquiries about this innovative platform, we have compiled a comprehensive FAQ section with schema.org microdata for enhanced SEO:Frequently Asked Questions about Ethereum
What is Ethereum?
Ethereum is a decentralized, open-source blockchain platform that enables the creation and execution of smart contracts and decentralized applications (dApps). Founded by Vitalik Buterin in 2015, Ethereum has become the foundation for numerous blockchain-based projects and decentralized finance (DeFi) applications.
How does Ethereum differ from Bitcoin?
While Bitcoin primarily functions as a digital currency, Ethereum’s blockchain is designed to support programmable smart contracts and dApps. Ethereum uses a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, whereas Bitcoin relies on proof-of-work. Additionally, Ethereum has no fixed supply cap, unlike Bitcoin’s 21 million coin limit.
What are smart contracts?
Smart contracts are self-executing agreements with the terms directly written into code. They automatically enforce and execute the terms of a contract when predefined conditions are met, without the need for intermediaries. This technology enables trustless, transparent, and efficient transactions across various industries.
What is Ether (ETH)?
Ether (ETH) is the native cryptocurrency of the Ethereum network. It serves as the fuel for executing smart contracts and transactions on the Ethereum blockchain. ETH is used to pay for computational services, transaction fees (gas), and can be traded on cryptocurrency exchanges.
What is the Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM)?
The Ethereum Virtual Machine (EVM) is a Turing-complete software environment that runs on the Ethereum network. It executes smart contracts and computes the state of the Ethereum network for every new block added to the blockchain. The EVM enables developers to create complex, decentralized applications using various programming languages.
What is Ethereum 2.0?
Ethereum 2.0, also known as Eth2 or Serenity, is a major upgrade to the Ethereum network aimed at improving scalability, security, and sustainability. It introduces a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, shard chains for parallel processing, and a new Ethereum Virtual Machine (eWASM). The transition to Ethereum 2.0 is expected to significantly increase transaction throughput and reduce energy consumption.
How can I invest in Ethereum?
Investors can purchase Ether (ETH) on various cryptocurrency exchanges, through ETH-based exchange-traded funds (ETFs), or by participating in Ethereum-based projects. Additionally, users can stake ETH to earn rewards by validating transactions on the Ethereum 2.0 network. It is crucial to conduct thorough research and consider the volatile nature of cryptocurrency investments before committing funds.

