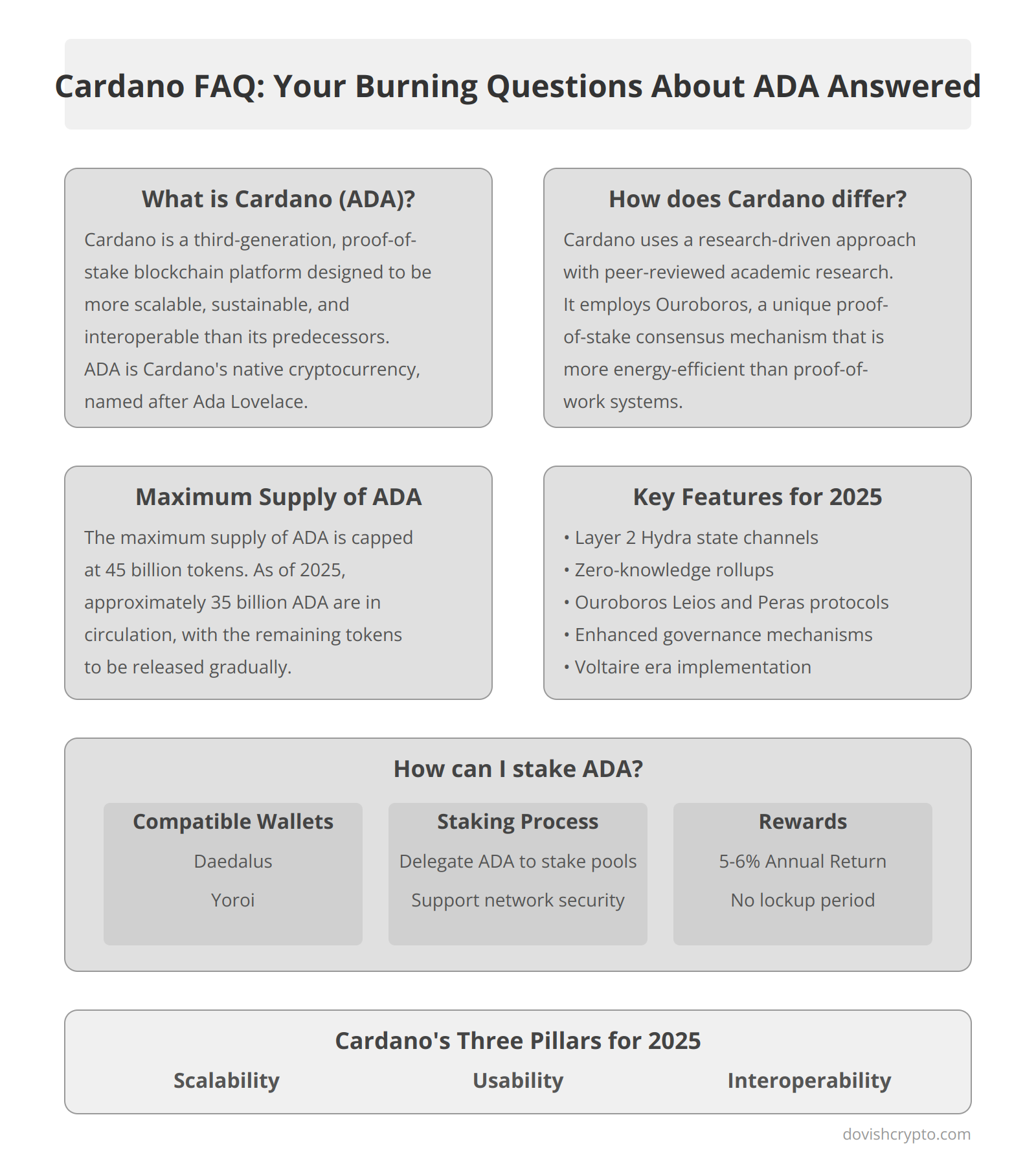
- Zoom
- Type
Table of Contents
Where to buy Cardano?
| # | Source | Pair | Volume | Price | Change | Updated |
|---|
Historical Cardano price
| Date | Open | Close | High | Low | Volume |
|---|
Cardano Calculator
- BTC
- ETH
- USDT
- XRP
- BNB
- SOL
- USDC
- ADA
- DOGE
- TRX
- STETH
- LBTC
- PI
- WBTC
- LEO
- LINK
- HBAR
- USDS
- XLM
- AVAX
- WSTETH
- SHIB
- SUI
- LTC
- BCH
- TON
- OM
- DOT
- USDE
- WETH
- BSC-USD
- BGB
- HYPE
- WBT
- XMR
- WEETH
- UNI
- SUSDS
- DAI
- APT
- NEAR
- PEPE
- ONDO
- ETC
- ICP
- AAVE
- CBBTC
- MNT
- GT
- OKB
- CRO
- TAO
- TKX
- TRUMP
- VET
- FDUSD
- ENA
- TIA
- KAS
- POL
- FIL
- FTN
- ATOM
- ALGO
- IP
- RENDER
- ARB
- S
- USDT
- OP
- JUP
- KCS
- SOLVBTC
- FET
- MOVE
- WETH
- QNT
- RSETH
- NEXO
- XDC
- DEXE
- USD0
- STX
- IMX
- MKR
- RETH
- INJ
- WLD
- FLR
- THETA
- GRT
- SEI
- USDT
- BNSOL
- SOLVBTC.BB
- BONK
- LDO
- EOS
- METH
- XAUT
- GALA
- PYUSD
- XTZ
- USDC.E
- USDC
- WBNB
- BTT
- WBTC
- SAND
- BERA
- IOTA
- BSV
- MONKEYS
- JTO
- JASMY
- KAIA
- USDX
- BUIDL
- FLOW
- PAXG
- MSOL
- EZETH
- FLOKI
- NEO
- ENS
- TEL
- USR
- HONEY
- CRV
- PYTH
- BDX
- HNT
- JUPSOL
- EGLD
- AXS
- RON
- MANA
- TUSD
- WIF
- ZEC
- PUMPBTC
- RAY
- DYDX
- STRK
- KAVA
- USDC.E
- CAKE
- WETH
- XCN
- CMETH
- DOGE
- STBTC
- NFT
- BTC.B
- WETH
- AERO
- CLBTC
- XEC
- CHZ
- RUNE
- APE
- OUSG
- USYC
- USDB
- CORE
- CFX
- AR
- VIRTUAL
- FRAX
- MATIC
- USDY
- IBERA
- KAITO
- EETH
- COMP
- PENGU
- TWT
- OHM
- TBTC
- CGETH.HASH
- AMP
- PENDLE
- AXL
- AKT
- LUNC
- OSETH
- USDT
- BUSD
- GRASS
- VRSC
- GNO
- SPX
- BEAM
- BRETT
- MINA
- GLM
- RSR
- MORPHO
- AIOZ
- BERASTONE
- JST
- FARTCOIN
- CTC
- CBETH
- PLUME
- EIGEN
- SNX
- WETH
- SFP
- 1INCH
- DEUSD
- WBTC
- ETHX
- DASH
- MX
- SNEK
- KSM
- SATS
- TFUEL
- W
- CWBTC
- ZK
- ATH
- EBTC
- SUPEROETHB
- SWETH
- QGOLD
- FRXETH
- LAYER
- ZIL
- ASTR
- BLUR
- SAFE
- CKB
- QTUM
- NOT
- USDD
- ETHDYDX
- BAT
- MASK
- AIC
- USDC.E
- ROSE
- VTHO
- DEEP
- ABTC
- LPT
- ZRX
- CHEX
- GHO
- ZRO
- LSETH
- MEOW
- TOSHI
- SUPER
- PRIME
- USDA
- BABYDOGE
- HOT
- WEMIX
- TRAC
- FLUID
- STG
- AI16Z
- BORG
- CHEEMS
- ARKM
- OSMO
- DCR
- CELO
- GAS
- KET
- WSTUSR
- ACT
- AGENTFUN
- ORDI
- XCH
- RVN
- MWC
- DOG
- SFRXETH
- RLB
- APFC
- TRIP
- SAVAX
- MOG
- ELF
- GOMINING
- XEM
- ANKR
- SC
- MOCA
- YFI
- $RCGE
- RED
- ETH
- T
- AUCTION
- ENJ
- BTSE
- MEW
- VANA
- PNUT
- HONEY
- POPCAT
- TRIBE
- TETH
- CET
- DAG
- SDEUSD
- SUN
- IOTX
- ETHFI
- ZETA
- SKL
- WOO
- CVX
- ETHW
- ACT
- TURBO
- KUB
- DRIFT
- DGB
- XNO
- UXLINK
- FAI
- XYO
- POLYX
- VENOM
- WAVES
- LCX
- ZEN
- WETH
- GMX
- WBETH
- HMSTR
- KOGE
- CSPR
- MPLX
- SOL
- EURC
- ONE
- ME
- BIO
- KAU
- EURS
- WAVAX
- RLUSD
- KDA
- BBSOL
- B3
- MYTH
- LUNA
- GMT
- MAG7.SSI
- WMTX
- USDG
- LRC
- USDC
- FXS
- ONT
- AMAPT
- GAL
- KAG
- GIGA
- GPRO
- GCB
- ZKJ
- DAI
- MMX
- SXP
- NXM
- EUTBL
- IO
- ETH+
- COW
- SUSHI
- BAND
- STPT
- ACH
- NKYC
- PTGC
- COTI
- SWFTC
- USUAL
- HIVE
- SYRUP
- USDC.E
- USDZ
- RPL
- ZIG
- FIDA
- QUBIC
- PROM
- XPR
- BICO
- UXP
- AUDIO
- SOLO
- G
- NEIRO
- REG
- MELANIA
- ICX
- STEAKUSDC
- VVV
- ILV
- AEVO
- METIS
- EUL
- USDF
- RLP
- UMA
- MEME
- VVS
- QUSDT
- ID
- FLUX
- IOST
- AVAIL
- VEE
- IGT
- IAG
- ANIME
- ALEO
- ALT
- CETH
- ECOIN
- MANTA
- SUPRA
- LSK
- FRXUSD
- BOME
- ACX
- SNT
- SPELL
- SAROS
- BORA
- DESO
- AIXBT
- DSOL
- AGLD
- PHA
- ZANO
- CPOOL
- TNSR
- VELO
- BAL
- IQ
- XVS
- GAMA
- ZEUS
- ASBNB
- SSOL
- ORBS
- POWR
- USDT
- OKT
- DF
- RLC
- CTF
- ZRC
- POND
- FRXUSD
- TEMPLE
- SBTC
- REQ
- LON
- SONIC
- CHR
- GLMR
- PAAL
- ONG
- DKA
- FBTC
- GEOD
- METFI
- YGG
- BLAST
- USDT0
- BIGTIME
- WAXP
- ELX
- ZENT
- MVL
- ORCA
- USDP
- BDCA
- SYRUPUSDC
- WETH
- XVG
- PEOPLE
- BMX
- AVL
- WATC
- CVC
- CGPT
- COREUM
- ABT
- WBTC
- STRAX
- HT
- AGI
- DYM
- SGB
- PXT
- USDX
- DOLA
- PUNDIX
- OAS
- LVLUSD
- PEAQ
- ELON
- PUFF
- TRB
- HSK
- MLK
- GFI
- 0X0
- XRD
- KEEP
- SLP
- CRVUSD
- ZBCN
- TAIKO
- JOE
- ARC
- SHELL
- WETH
- SFRAX
- RARE
- XAI
- NOS
- DENT
- SLND
- AGIX
- OMI
- LQTY
- USTBL
- DODO
- NMT
- API3
- KMNO
- BWB
- CLANKER
- ISLM
- PIN
- USTC
- DOGS
- AGETH
- PUNDIAI
- SAAS
- NMR
- SCR
- ANON
- MED
- C98
- STEEM
- ERG
- DAKU
- OETH
- CETUS
- PCI
- CFG
- SOLV
- AMPL
- EZSOL
- GPS
- HEART
- USDF
- CTSI
- MTL
- OBT
- WELL
- ARK
- ACS
- NPC
- BUSD
- MPL
- USDL
- OLAS
- B2M
- CARV
- USUALX
- CORGIAI
- GAME
- QUAI
- OMNI
- ARDR
- TST
- GL-BTC
- WSTETH
- WIN
- SCRT
- MWETH
- ANT
- AAI
- BAN
- COOKIE
- WEETH
- USDC.E
- KNC
- PZETH
- AURORA
- TON
- DEGEN
- M87
- AXGT
- GOAT
- CELR
- MIM
- UFD
- VANRY
- $FARTBOY
- H2O
- AIAT
- BONE
- JET
- DEVVE
- MOVR
- ALCH
- USDT
- BITCOIN
- CTK
- GUSD
- BTG
- FMC
- EWT
- VCNT
- FIUSD
- ERN
- TRUAPT
- SSV
- EKUBO
- PONKE
- WILD
- BANANA
- WETH
- SHX
- TARA
- BOBA
- CAT
- UDS
- LUSD
- QANX
- QKC
- JNFTC
- LOOM
- QI
- SHFL
- ALICE
- HUNT
- USD+
- USDM
- BB
- CBK
- USDC
- DIA
- FORT
- REZ
- OI
- APEX
- WETH
- VELO
- BEL
- USDC
- ORAI
- NYM
- DUSK
- GRIFFAIN
- USDC.E
- PRO
- APU
- ACA
- SUSDA
- MERL
- HIFI
- SUNDOG
- SURE
- EURCV
- FUEL
- TRU
- GNS
- BNT
- CYBER
- SQD
- OCEAN
- COQ
- SWARMS
- PURR
- METAL
- VIC
- HPO
- AITECH
- OXT
- ASM
- EGGS
- AVA
- DBR
- ALU
- RAD
- FWOG
- BFC
- EDU
- WBTC
- OGN
- PEPECOIN
- SKI
- STRIKE
- HIPPO
- DEGO
- EDGE
- UQC
- ANDY
- MAGIC
- AVA
- ZUSDC
- NCT
- TAI
- WBTC
- STORJ
- RIF
- CCD
- ZEDXION
- SFUND
- WXRP
- SN
- ALI
- TMG
- SDEX
- CX
- SB
- BERAETH
- PWEASE
- MBL
- XTER
- SAGA
- SYN
- AZERO
- MBX
- FINVESTA
- RUSD
- STMX
- IOT
- SWEAT
- MOODENG
- ANVL
- D
- AVAX
- SD
- LISUSD
- JETT
- HFT
- SILO
- BRBTC
- BAKE
- KUJI
- ROAM
- SYS
- PLT
- CUSDC
- BADGER
- OSAK
- NTRN
- REACT
- ELA
- XT
- HDX
- RACA
- DAI
- TLOS
- THAPT
- MIN
- MBOX
- BROCCOLI
- SOSO
- GODS
- TRUMATIC
- STONKS
- CUSD
- USD3
- MAV
- MCDULL
- INF
- NKN
- XMW
- SOLVBTC.CO
- MNDE
- BINK
- BIM
- ACE
- A1C
- META
- ALPHA
- FLIP
- BC
- GRND
- VR
- ETN
- REUSDC
- LUMIA
- DEP
- WNXM
- ALPH
- RAIL
- SOC
- CXT
- NFP
- F
- HMT
- PEPU
- HBD
- XION
- PEAS
- PYR
- SLVLUSD
- DAO
- XTUSD
- LOOMOLD
- PNG
- TKP
- CATI
- NEIRO
- WPOL
- GPU
- TT
- MIM
- DEFI
- CRE
- CXO
- HOOK
- HEI
- CLV
- RSC
- USN
- AERGO
- LEVER
- ZEREBRO
- ORDER
- CTXC
- VINE
- WOLF
- PRQ
- SRX
- TJRM
- ATA
- DXI
- CULT
- BTU
- DG
- TLM
- SAUCE
- MARSO
- BNKR
- LISTA
- UNIETH
- LCAT
- UFO
- CUDOS
- USDT.E
- KEYCAT
- RBNT
- FTW
- MFT
- VSC
- MRB
- PIXEL
- SPA
- MOR
- BURN
- KYSOL
- FORTH
- NEON
- NAVX
- XPLA
- GFAL
- PHB
- META
- SLERF
- MIGGLES
- MAPO
- ASUSDF
- MOC
- J
- BOLD
- RDNT
- AQT
- OMIKAMI
- WHITE
- ZCX
- HASHAI
- OMG
- CHILLGUY
- VITA
- VRO
- LAT
- TOKEN
- FCT
- SERAPH
- PSP
- CAM
- GEAR
- BRISE
- BMEX
- LBT
- L3
- MIMATIC
- T99
- WFRAGSOL
- RSS3
- EURT
- MATICX
- LYX
- DOGINME
- NEURAL
- PRCL
- MLN
- GRS
- LMWR
- AQUA
- IXS
- IDEX
- LTO
- WHY
- DRV
- SAI
- ARPA
- SVM
- SUSD
- VON
- FIS
- GGP
- OS
- POKT
- USDC
- POLY
- ANYONE
- EUSD
- MATH
- MYRIA
- LADYS
- ICE
- EL
- TORN
- ALEX
- SFM
- QUIL
- X33
- PERP
- WZRD
- SPEC
- CAW
- A8
- ARRR
- CDAI
- SDL
- GME
- RARI
- A47
- PLXY
- TPT
- PROS
- CROWN
- SIREN
- DAI
- REI
- QRL
- ALCX
- SUSD
- GYD
- HOPR
- ANKRETH
- NPXS
- BOUNTY
- COL
- XSGD
- SHDW
- PALM
- ATLAS
- STEP
- $DOGEAI
- NAKA
- AI
- HEGIC
- STRD
- DADDY
- NNN
- VRTX
- HFUN
- OGY
- UM
- BLUE
- MCADE
- AHT
- STTON
- PIKA
- MLC
- XAI
- ELON4AFD
- LIT
- POLS
- PINKSALE
- KMD
- SX
- SEND
- WGBERA
- OHO
- SNAI
- TREE
- PUFFER
- DORA
- APX
- WAN
- OSOL
- SLF
- SHADOW
- SETH
- SBETH
- CKBTC
- NATI
- ULT
- FT
- DMTR
- HTM
- WAGMI
- VARA
- KOMA
- ELG
- ANON
- FUN
- QUICK
- NS
- DEXT
- XUSD
- MNGO
- LAINESOL
- XPRT
- FRONT
- $ADS
- ECOX
- AUKI
- BMT
- GTC
- UOS
- ALOT
- SWELL
- CBAT
- FLM
- TRUNEAR
- GHST
- UNX
- CONX
- BTCPX
- BANANAS31
- QUICK
- ADS
- FLIX
- COS
- MMUI
- BTY
- MNEE
- COCA
- KLV
- BLD
- EURA
- STHYPE
- BOOE
- HARD
- GXC
- REEF
- STRIKE
- STRX
- DNT
- LOFI
- INDY
- GLC
- INV
- PURPE
- ZUSD
- MPT
- TDROP
- BLZ
- LMT
- OPUL
- WCFG
- DIMO
- NFTX
- BEAR
- USDC
- MOOX
- ZND
- CWEB
- SSUI
- BASEDAI
- THE
- USDTE
- COLLAT
- OL
- ADCO
- USDC
- FARTCOIN
- EURE
- PIPPIN
- BFG
- DIONE
- CAW
- ASD
- WUF
- KARRAT
- NST
- RETARDIO
- SPECTRE
- PAIN
- IBGT
- MCOIN
- BXN
- YULI
- PEP
- AVT
- FB
- USDC
- ATR
- BETA
- POLIS
- KISHU
- PUPS
- WOJAK
- FARM
- IDRT
- CHESS
- DAI
- ORN
- LAVA
- MGP
- IDIA
- HAI
- FIRO
- NUM
- NRN
- WXM
- IXT
- SERV
- USDC.E
- FIDU
- CSWAP
- DUCK
- BZZ
- CHEQ
- GEL
- METH
- MSM
- FOX
- BSW
- XBG
- ARMY
- DRGN
- IMO
- WOS
- USDC
- NOW
- $MYRO
- OFT
- VRA
- DRB
- TSWAP
- HANU
- MOZ
- COPI
- VOXEL
- OG
- OX
- SDT
- SCRVUSD
- STRDY
- SANTOS
- SKEY
- $NUMBER
- TOKE
- BENJI
- ALPHA
- LIBRA
- USDC
- CEEK
- USDBC
- CUSDO
- FLEX
- HAIR
- WETH
- WOD
- PSG
- STSOL
- GGAVAX
- $GROK
- AURABAL
- GAME
- KIN
- PHB
- ADX
- BAR
- CTX
- TRIAS
- GHX
- RBTC
- CLOUD
- MDT
- PORK
- OORT
- PORTAL
- USX
- USDX
- ROOT
- LOOKS
- PEPE
- RAMP
- BOSON
- STUFF
- ALUSD
- DINERO
- STATOM
- CRT
- B3TR
- BOBO
- RBN
- WEN
- MERC
- SPC
- USC
- TERA
- QASH
- AKI
- GEMS
- LEASH
- VOLT
- SUKU
- KEKIUS
- UCASH
- XCP
- SEAM
- YNE
- MEMDEX
- TROY
- OXA
- QUACK
- LRDS
- USA
- ENQ
- USDC.E
- NULS
- TKO
- DATA
- JKL
- DEXNET
- SYNT
- AIDOGE
- JOE
- DAI
- BIFI
- BOB
- MOCHI
- PIVX
- PHAR
- XCM
- BTR
- EVER
- TOPIA
- BROCCOLI
- ZKCRO
- GAFI
- WING
- HENLO
- DOGE
- XRETH
- LINA
- FROK
- XEN
- OZO
- SHIRO
- RAI
- MOODENG
- DLC
- CACAO
- AVUSD
- GS
- REKT
- BKN
- CREAM
- FIO
- XDATA
- LYXE
- FXUSD
- OX OLD
- ORA
- ZCHF
- MAX
- ODINDOG
- MONKY
- TRUMP
- $MICHI
- ECET
- OCTA
- VINU
- MASA
- DOG
- USDT
- KRL
- NIM
- JMPT
- ALEPH
- COMBO
- AUSD
- LOCK
- NATIX
- LOKA
- SFLR
- SAMO
- PIRATE
- SWBTC
- ARENA
- DEFI.SSI
- FOXSY
- CLY
- TRYB
- FLAY
- VLX
- KARATE
- PYTHIA
- BTC
- PHNIX
- SVL
- CAST
- 10SET
- RIO
- FARM
- PROPC
- UNION
- EPS
- LOOPIN
- GOLDAO
- WMNT
- HYPERSKIDS
- VERTAI
- FLEXUSD
- ALPACA
- AMO
- MON
- MAG
- FOOM
- WUSD
- PIXL
- IRON
- BGSC
- NTX
- WSTEAMX
- MEOW
- BOTTO
- USSI
- YUSD
- OWN
- WEPE
- AURA
- LCT
- QTCON
- BOMB
- ZEX
- CA
- REE
- STAPT
- BGSOL
- SOV
- BLUB
- FUL
- USDC.E
- EMP
- CLUSTR
- BERT
- USDC.E
- DPI
- UPC
- CLORE
- ODOS
- XPM
- PTU
- ASF
- KASTA
- TRUMP
- MODE
- HTR
- PPC
- ZYPTO
- FPIS
- GUD
- BELLS
- NXRA
- CRTS
- ZKL
- STRONGSOL
- PAID
- SLT
- NOOT
- LAZIO
- PDA
- TREAT
- SETH2
- AGRS
- MOBY
- MERY
- BNBX
- KONET
- INDEX
- XX
- BUTTHOLE
- LWA
- SOVRN
- NVL
- GOG
- SFTMX
- REN
- CGO
- MPC
- OBSR
- STREAM
- GALEON
- FASTUSD
- USDC
- MOBILE
- SEND
- DMAIL
- GST-SOL
- MANEKI
- MONEY
- GAL
- PSTAKE
- LUNA
- GME
- NC
- SPECTRA
- PAI
- TAOBOT
- SIDUS
- VNO
- VCHF
- MIX
- WINK
- THOR
- AVC
- EPENDLE
- SCS
- ARMA
- TIME
- GYEN
- NIBI
- HERO
- KWEEN
- YFII
- CELL
- THL
- ALPINE
- ALB
- BCUT
- JAM
- HIGHKEY
- UFT
- KRD
- PNK
- PIB
- SIGMA
- 42
- EQB
- TET
- VAI
- GRAIL
- JAILSTOOL
- ASTO
- KTA
- SWAP
- RIFT
- LINGO
- FEG
- OPN
- OCT
- WCGUSD
- BUNNI
- MVC
- KAI
- PINTO
- XBT
- PUSS
- EOS
- ZKML
- WETH
- CONAN
- ETHIX
- STTAO
- YNETH
- SSE
- JUV
- DMT
- ZTX
- MEMEFI
- AST
- WINK
- BBB
- PEIPEI
- BROCCOLI
- CERE
- $SIR
- NACHO
- KYVE
- BTCP
- SEDA
- STOS
- PNP
- USDT
- STNK
- WRX
- CAR
- VIDT
- PROPS
- KNDX
- CKP
- CITY
- GOUT
- PKOIN
- BSDETH
- ZUSDT
- EVA
- PLU
- AUTOS
- XAVA
- XSWAP
- FOXY
- ASR
- HAWK
- BTCUSD
- $1
- HGPT
- AE
- OUSDT
- BAD
- STON
- YLAY
- EFI
- PLMC
- WEMIX$
- SQGROW
- UTON
- MFER
- LAI
- EMC
- DEL
- COOK
- $BORGY
- DOGI
- PACK
- USDT
- MIU
- SFRXUSD
- FLX
- $MICRO
- ARCH
- LM
- USDT
- SBD
- PARTY
- AURY
- BBT
- MTLX
- STARDOGE
- PAW
- TONIC
- ATM
- QLC
- TRADE
- BLOK
- PRIMATE
- REI
- STC
- WAGMIGAMES
- KP3R
- VISTA
- REX
- WTN
- VIB
- NPCS
- WALLET
- RYU
- JUNO
- INCO
- EXTRA
- SOUL
- GATSBY
- MEED
- GXA
- $BEAR
- CHAMP
- AXEL
- ZERC
- FNCT
- TXAU
- WBTC
- PKIN
- ROUTE
- TOBY
- COMBO
- MCB
- OUSD
- NEXA
- MUSE
- HOLD
- LAOS
- TORUS
- USDC
- OFN
- DATOM
- LIT
- TALOS
- DEAI
- LNQ
- BDC
- VEIL
- SIPHER
- NAI
- WAMPL
- USDQ
- BEETS
- FACT
- USDT
- NBLU
- GTAI
- XSUSHI
- WFI
- HOPPY
- EEIGEN
- MOXIE
- MOON
- BUZZ
- VALOR
- FPIBANK
- DINGO
- FLOCK
- DBC
- GRIFT
- KENDU
- TGT
- GLQ
- HSUITE
- HBTC
- ORE
- OBT
- SUEDE
- ZYN
- EBET
- ZNN
- LQR
- SHRAP
- CDX
- KIKI
- USDT
- BERRY
- PEPECAT
- HEGE
- KING
- BID
- TMAI
- DVPN
- DOVU
- CLEAR
- KILT
- MYST
- STARS
- CAH
- MAS
- PUNK
- DCK
- FTD
- TYBG
- WEXO
- CEUR
- MEX
- BNC
- MYST
- VADER
- SRM
- AEROBUD
- UFO
- OSMI
- 3ULL
- HERB
- TAROT
- ACM
- BRUSH
- STFLOW
- GGMT
- USDR
- MAX
- ML
- LUCE
- MAVIA
- PAI
- RLY
- EPIC
- METRO
- TIG
- VIVI
- BCD
- MUMU
- SIXP
- DFI
- ACOLYT
- KAI
- AVIA
- EVR
- JEWEL
- THALES
- POZO
- KWENTA
- EAI
- AUDIT
- SMT
- VSTR
- ZAI
- DIVI
- SCA
- DCD
- MBC
- XRT
- PATRIOT
- PIKA
- G7
- WINR
- SAVUSD
- OVR
- ADP
- ARC
- PANDORA
- HPO
- ELYS
- SYMM
- SSLX
- BMX
- GENOME
- SDAO
- PINGO
- EDWIN
- MLG
- DEXTF
- ARTY
- PORT3
- AGRI
- VGX
- BOBAOPPA
- INTER
- MNTA
- KOKO
- LIF3
- LIKE
- WXT
- CANTO
- KATA
- LOCKIN
- VTRADING
- DHT
- PEPE2.0
- ⌘
- PLI
- POLA
- APW
- 1GUY
- ALVA
- KPN
- ARIA20
- FUSE
- HAT
- B4FWX
- XEL
- ASTRA
- SAITO
- MUBI
- XFI
- EXRD
- GSWIFT
- ICETH
- BAC
- TITS
- DNX
- MARS
- YOM
- HUBSOL
- FX
- STOP
- XCAD
- HDRO
- KOIN
- MARS
- SWISE
- LMEOW
- HIGHER
- CAPTAINBNB
- XETA
- MEY
- SWORLD
- WBTC
- CHAIN
- TSOTCHKE
- WRLD
- KAR
- FLOCK
- SLIM
- FRIC
- DMD
- BRAT
- RENBTC
- ZGD
- CROID
- KLIMA
- BAMBOO
- DOLZ
- FLT
- SNSY
- SIX
- XDB
- USDF
- SLOTH
- LZUSDC
- GDP
- CATE
- BIZA
- GENE
- ROA
- USDC
- USDT
- BEAM
- ABSTER
- TRAC
- GBYTE
- RCH
- AKUMA
- WCO
- OXY
- UCJL
- USDH
- TADA
- BST
- CLAY
- OWC
- BNUSD
- VVAIFU
- UNCX
- HNS
- VIRAL
- JESUS
- SCF
- MOTHER
- DCB
- ANT
- ASIA
- INFRA
- STOSMO
- HELLO
- SWELL
- EVERY
- BLOCK
- XZK
- ROCK
- SNK
- JOULE
- STTIA
- BEETS
- WHALE
- MAGA
- USDC.E
- OIIAOIIA
- RVF
- WIFI
- BUBBLES
- STARL
- 00
- MXC
- SFG
- BLUB
- USDC
- LEA
- ASK
- HUSD
- DIGITS
- NECT
- CULT
- METAV
- COT
- LAIKA
- RGOAT
- RE7WETH
- MNW
- XCHNG
- AFR
- $NAP
- STAT
- MOD
- EGP
- WISE
- BBONK
- SDN
- ASM
- XEP
- FORWARD
- SEN
- SWASH
- CUNI
- LOAN
- PDT
- WIKEN
- NAVI
- FP
- TRT
- VAI
- APL
- MINIMA
- BCN
- HANDY
- JELLYJELLY
- SINGULARRY
- SNPAD
- TROLL
- XOT
- MAN
- CREO
- ASTRO
- BOTIFY
- PASG
- 888
- CHAD
- SWPX
- HARAMBEAI
- LL
- USDT
- EMAID
- DKP
- MAD
- CAGA
- DC
- BXX
- SHD
- OPCAT
- GHUB
- WETH
- XAND
- ISLAND
- ETUS
- REP
- PPT
- KIMA
- APP
- CELL
- PAL
- GRAB
- MEMES
- QMV
- MEUSD
- MG8
- ABEL
- MINT
- SCFX
- TEVA
- FARM
- L1
- GOGLZ
- RONKE
- BMC
- SLN
- OXEN
- DNA
- GIKO
- RAIN
- PLAY
- AINTI
- ICHI
- SKEB
- AVINOC
- SOIL
- $KEKEC
- SHIDO
- RADAR
- NEX
- KOLIN
- DIVER
- BOA
- HI
- WELSH
- 7007
- XDAG
- SAN
- $PURGE
- AIUS
- LIMBO
- MOE
- PAI
- CVR
- TRIO
- SHOGGOTH
- CUBE
- $BILLY
- O
- FITFI
- POOLX
- KNCL
- GOAL
- ORBT
- VITA-FAST
- BRETT
- BOB
- POLYDOGE
- NUB
- DJED
- ETH2X-FLI
- WETH
- UW3S
- AMETA
- ATS
- BTCMT
- CSIX
- LORDS
- AVB
- BIG
- PTS
- HDN
- M3M3
- SQT
- ESE
- HMND
- ISK
- HOGE
- WOOF
- CUMMIES
- SEED
- DMC
- AIPAD
- NWC
- DOME
- THRUST
- USDT
- FURM
- SOFI
- JEFF
- CAPS
- ASTRAFER
- TOMI
- WELF
- QBX
- LOGX
- SHI
- LISTEN
- MBS
- SNFTS
- LAUNCH
- VUSD
- AIR
- MNTC
- FLUXB
- KANGO
- VEUR
- TYPUS
- EDGESOL
- TRISIG
- SIS
- MIAO
- NATIVE
- ARCA
- DEGENAI
- BLENDR
- SUAI
- LLD
- DAY
- AGIXT
- HYUSD
- TVK
- ABX
- OMZ
- TRVL
- FRED
- N3
- EBTC
- AIT
- BIDZ
- GPCX
- HYPER
- TOP
- WOW
- THT
- KIP
- WETH
- VC
- LVN
- HARAMBE
- NHT
- PLN
- LTX
- OPUS
- XNA
- $EVA
- AVI
- PRISMA
- CRAI
- HXD
- NAVI
- SPURS
- KAN
- VAL
- MCRT
- PUSH
- ALD
- MOVE
- TRUF
- GPT
- MYSTERY
- SAI
- NAP
- MINI
- PREMIA
- IRIS
- DIP
- MAK
- LEDGER
- BAX
- NSASTR
- USDT
- YEET
- GMEE
- IMGNAI
- BLK
- CEL
- HAROLD
- AURA
- LANA
- CRU
- LYA
- BEER
- NYA
- KOMPETE
- ARG
- " "
- SEKOIA
- USDC
- CFGI
- CHOMP
- WITCH
- AZIT
- USDGLO
- LAND
- NOCHILL
- DERO
- CPH
- EEFI
- FIRE
- XPACK
- ATH
- TRA
- WUSDM
- UBU
- REGEN
- ZKP
- TN100X
- FIVE
- NRS
- GOVAI
- HAPPY
- EUSD
- KIBSHI
- CARROT
- LEOX
- ETF500
- BULL
- KNS
- HENLO
- HOLD
- ASIX
- SCOT
- MOEW
- DUKO
- WHINE
- PNDC
- RJV
- PZM
- PINO
- WINNIE
- AKIDS
- REF
- HERA
- BIGJIM
- BAN
- LQDR
- QORPO
- DUEL
- KLEVA
- ISP
- SNC
- EFL
- WBTC
- USDC.E
- BRYAN
- BCT
- ICBX
- IVT
- 🦝
- NRG
- LUMO
- NETVR
- LUSH
- DKING
- SWITCH
- YAYSTONE
- BTM
- EQUAL
- IBEX
- LCS
- FEI
- TITAN
- BTCB
- RE7WBTC
- STIMA
- BTC2X-FLI
- MINT
- ITHACA
- ANLOG
- DOP
- WOM
- HMX
- SOLNIC
- CAMEL
- ADX
- MAHA
- $SIGMA
- VY
- FUD
- BUT
- KEY
- BAAS
- OMAX
- EVMOS
- MZR
- PPKAS
- TAKI
- YAYAGETH
- RISE
- STFX
- MUSKIT
- USDN
- AGVE
- QUEEN2
- IMG
- DOLAN
- LTAI
- NEURON
- NSTR
- SOCKS
- SBR
- DEMI
- LMCSWAP
- USDC
- DROP
- USDT
- TOKEN
- NLS
- IMPT
- PIKA
- MSTR
- BUY
- AFC
- $CATBAL
- REWARD
- BARSIK
- SOLID
- AZUR
- GLEEC
- $POM
- JUICY
- EZEIGEN
- SPARKLET
- ZEPH
- TREMP
- APRS
- SPS
- REDO
- GUI
- VITARNA
- WEL
- FROG
- GMM
- LMR
- SPE
- SBR
- PUNDU
- SNS
- EMT
- TAOCAT
- PRE
- $SYMP
- YAK
- RWA
- Y2K
- PSPS
- MUSD
- ZARP
- FUTURE
- WANBTC
- BONGO
- RBX
- STRP
- CYG
- SCHIZO
- $CWIF
- W3S
- FARTGIRL
- MV
- NYAN
- VTC
- ELIZA
- GRIN
- 1000X
- OPSEC
- BUDDY
- USDC
- CREDI
- STORM
- RBC
- KCT
- SYLO
- SOON
- EPIK
- ANGLE
- WAFFLES
- BTS
- MASQ
- CGX
- LKY
- DIKO
- POR
- FURI
- NEUR
- ROCO
- WHISP
- PIP
- TSUKA
- QVRS
- OMNOM
- TANK
- $SCRATCH
- AGIXBT
- CNHT
- BEEPER
- MEDIA
- REV
- PERRY
- AIXCB
- NTMPI
- TNQ
- XTN
- AIKEK
- BODEGA
- ADM
- GOD
- UNIBOT
- USDC.E
- POOL
- CAIR
- $SMH
- MDX
- PMT
- SEXY
- RIKO
- BOOP
- BOO
- USDC
- BOZO
- YUSD
- TGC
- MYT
- TLX
- WEFI
- COCO
- MTRG
- FAR
- WARPED
- SWAN
- U
- KIZUNA
- AREA
- BRAINLET
- FREYA
- SOL
- XCB
- ION
- SWCH
- X314
- AIMONICA
- AGENT
- DOBO
- USDC
- DG
- POWER
- MINIDOGE
- FLRETH
- ASCAKE
- IQ
- WAAC
- KPOP
- STARS
- EPIK
- ANDY
- ADO
- X
- FJO
- ALL
- SAFEMARS
- JAM
- AA
- CTN
- USDC
- CONVO
- HAPI
- RAI
- APX
- LIQUIDIUM
- SLC
- TTG
- PIDOG
- Q*
- BABYSHARK
- SG
- ORT
- OXI
- FRIEND
- BROCK
- BALN
- SHRUB
- KASPY
- AUDF
- LAKE
- WOOLLY
- SAN
- UPT
- TXT
- RATS
- WIBE
- THC
- TANGO
- DOMI
- CHAT
- $KIT
- TWIN
- G3
- MAJOR
- DEFX
- TIRED
- BLND
- MAZZE
- CABAL
- DAI
- RAMEN
- PHIL
- HUAHUA
- DREAMS
- DOJO
- GIZMO
- BSX
- BITCI
- BENDOG
- RXD
- MTD
- UNFI
- MIR
- CTRL
- BRO
- COMAI
- CAT
- BYTE
- BOND
- STRIKE
- NEXT
- WIT
- 0XGAS
- GARI
- WACME
- GNON
- NEST
- BFT
- INTX
- EDUM
- WBTC
- WHALE
- CTG
- VOI
- TON
- CAT
- DREAM
- USOL
- KEX
- GET
- MDAO
- SPORE
- PAR
- TAG
- BILLY
- PERC
- RSAVAX
- BXBT
- GRELF
- GTCBBTCC
- PAPPLE
- WUD
- SMURFCAT
- LMY
- EVAN
- MDEX
- DUCX
- RIZ
- TALK
- TUSD
- BRN
- JAV
- CNG
- USDT
- XNET
- MCONTENT
- OOE
- ZJOE
- LI
- SSDX
- AION
- RIZO
- ARCAS
- SATORI
- IBEUR
- DVI
- SERO
- FAN
- RFD
- BTC2
- PEPPER
- ZERO
- ANDY
- TRKX
- FLY
- ECS
- TPRO
- SCP
- TBULL
- VIA
- ROKO
- VPAD
- COR
- M
- SCI
- BABY
- TERMINUS
- HXRO
- BIB
- DOGEGF
- CYB
- PLSR
- GAU
- MAXETH
- NXS
- USDT
- WSDM
- USUI
- HSUSDC
- CLARITY
- PRD
- NINJA
- LUFFY
- LIXX
- NAV
- MKL
- FACTR
- NFD
- KRAV
- RWA
- ARGO
- REALIS
- MINTME
- FP
- BLOCK
- XAR
- HENLO
- NUTS
- TURBOS
- UCO
- LKI
- RKEY
- NX
- SCIHUB
- AIV
- PONGO
- GRPH
- BRAINERS
- $ROAR
- SCPT
- SOLAMA
- DAI
- DAI
- WHISKEY
- LIQD
- SKOP
- BRLN
- AIN
- GNUS
- LYNK
- ((=ↀωↀ=))
- GO
- TOLY
- PEP
- AIAGENT
- NILE
- DTRXBT
- FU
- WART
- SAMA
- SEAMANIA
- SXETH
- METAL
- SILK
- DOGC
- KOTO
- DEPAY
- OGV
- ISC
- JYAI
- FAYA
- GROW
- SCLP
- RDPX
- BEPRO
- FXN
- SDT
- SILLY
- CARR
- MUSD
- VEX
- SUDO
- ZOO
- IBTC
- NYX
- SAGE
- IPOR
- ZBIT
- GRC
- CHATOSHI
- BUTTCOIN
- POGS
- FOMO
- CKETH
- USDT
- $MONKO
- APES
- AXOL
- KEKE
- WQOM
- LOULOU
- GOATSEUS
- HODL
- ONI
- SWTH
- DIO
- TNT
- LUCA
- MVI
- STABLE
- IOUSDT
- LAUGH
- ETH
- RING
- UP
- EXA
- AI23T
- CAT
- MACHI
- HEU
- SLAP
- USDC
- ETHOS
- JOY
- UXRP
- WLTH
- LNDX
- CATBAT
- KNIGHT
- POOH
- GOODBOY
- WOLF
- RNT
- LBR
- COFE
- GEEQ
- HEHE
- $WOLF
- SCUSD
- BMP
- BM
- MARSH
- UNIT0
- ARI
- GAMMA
- USDT
- CAI
- SFI
- PHRZ
- JURIS
- LAVA
- THE DOGEFA
- ITA
- PENG
- RDT
- NOVA
- SIGNA
- RFOX
- SEAL
- USDC
- SKR
- WMC
- SERSH
- VMANTA
- XPX
- XOXO
- LQNA
- TRACY
- CRASHOUT
- SHU
- THUSD
- SDM
- YOSHI
- FLORK
- NUUM
- RWA
- UBT
- OTK
- GYAT
- IVFUN
- WEPC
- AIR
- WARS
- RUSSELL
- DEDI
- TIME
- PBX
- VSP
- DARK
- SHIBDOGE
- MONG
- FAKEAI
- KASPER
- ARTHERA
- GAINS
- KUDAI
- MONOPOLY
- NEOX
- SMOL
- SABAI
- TDE
- LOU
- FOUR
- SKBDI
- MUSIC
- BABYBONK
- INSP
- GZIL
- GCR
- WSM
- PUMPIT
- TSUKI
- ONE
- XTT
- VAPOR
- GALAXIS
- TABOO
- FRA
- PEPO
- QI
- CLXY
- VERSE
- BREW
- BOB
- RTM
- EMC
- CTA
- FER
- CBY
- AIFUN
- ROME
- FILM
- TARDI
- RDD
- CONWAI
- SPACE
- HINT
- GOATS
- YUSD
- UFI
- WBTC
- KBL
- HTS
- SQR
- DEFI
- OOKS
- NAV
- FARTY
- SC
- $RIF
- LPETH
- ORX
- LIKE
- CHKN
- EURR
- PZP
- BRAIN
- HVH
- MBTC
- HELIO
- RAKE
- OPTI
- XPI
- MTO
- MET
- RC
- BZRX
- KOS
- STEAKUSDC
- DOGA
- MUSIC
- DUST
- TOKE
- POX
- TETSUO
- AMORE
- AWR
- $H2
- DOK
- WCHI
- 4EVER
- SLAM
- DOR
- HYDRA
- UMJA
- PACE
- STS
- MPS
- GOOFY
- LYRA
- RMNER
- DYOR
- FXN
- GZONE
- QUNT
- BSCPAD
- DEPIN
- ANC
- SOMM
- FLD
- CATS
- XER
- WIGO
- NBT
- AIINU
- IOUSDC
- AKA
- WATER
- FLX
- STASH
- $NMKR
- MOBI
- SPH
- CONDO
- UX
- KIMBO
- BODEN
- CHAPZ
- TDC
- PEEZY
- DICKBUTT
- MDAI
- LEGIT
- HOA
- CITADAIL
- SP
- ENQAI
- DUSD
- WSI
- KDX
- CHADETTE
- SPHYNX
- WOLF
- XDEFI
- PNIC
- CRYO
- STAVAIL
- XELS
- TROG
- 21BTC
- ENF
- DBR
- TNSR
- WETH
- BREW
- VETH
- XIDO
- SENATE
- DFL
- CHRP
- USDT.E
- PIP
- TAPT
- BVM
- ZF
- LFT
- RWN
- NCR
- XCFX
- SONIC
- $ANTY
- PLEB
- FU
- CAI
- USDC
- MORI
- DDX
- VCX
- AAX
- BOX
- $URO
- SEND
- EYWA
- ABR
- GBEX
- KHAI
- YAPSTER
- ALTT
- RTB
- HST
- BTRFLY
- FAFO
- DCI
- USDT
- BOOMER
- SAY
- SSWP
- PTC
- SIMP
- LBL
- PART
- NCDT
- LSS
- ZAI
- BOOT
- RGT
- NVT
- KOI
- EGO
- ASKJ
- DOGE
- UNO
- KALIS
- EURQ
- OBOT
- BIT
- FULLSEND
- RSVETH
- KM
- IXC
- BLACKDRAGO
- CKUSDC
- STEAM
- BLUSD
- MAIAR
- LOC
- GRG
- FOX
- MTA
- DEFIT
- MANC
- $WELL
- GUSDC
- DEUS
- MLT
- POLC
- BRRR
- NASDAQ420
- GG
- RMV
- ELU
- FLX
- DDBAM
- $OG
- SELFIE
- ICE
- OMNIA
- WPAY
- XR
- AIYP
- $UNFK
- VEXT
- MEME.SSI
- GOTTI
- YUKO
- MORPHAI
- CGV
- SYL
- XNK
- JBX
- DMAGA
- PIKA
- BERRY
- DOP
- GRP
- WING
- SUIP
- USV
- YEL
- XTM
- IST
- HACD
- CLANKFUN
- BIRDDOG
- TOMB
- BULLY
- XFUND
- PUPPIES
- TRONKEY
- DOOM
- TREB
- RWAX
- IDO
- PROJECT89
- BDOGITO
- MNT
- BABYNEIRO
- C3
- HUND
- BUZ
- BCAT
- NGL
- SEIYAN
- NITRO
- SYK
- CHUD
- BTX
- OBI
- PEUSD
- USK
- VIS
- FOLD
- TYPE
- MAMA
- LCC
- KOL
- BOOK
- DOGL
- UPO
- IOL
- TALENT
- LUNAR
- REV
- MEMESAI
- BNX
- EGC
- FDX
- CLUTCH
- FLNCHY
- SUNCAT
- SHA
- CHONKY
- LYNX
- DSRUN
- HELP
- ATETH
- VPT
- INTOS
- STELLA
- CATCH
- BONZO
- SIN
- KARAT
- RPLS
- BPT
- UBC
- GMRT
- HEEHEE
- $BLS
- CNFI
- ID
- MBP
- EMYC
- HART
- RBD
- PIRATE
- ADAPAD
- SAGE
- OKI
- GHOAD
- ZKF
- DYAD
- WHALES
- ANZ
- $FATCAT
- SKYA
- TEMA
- VIDYA
- BUBBLE
- EQUAD
- REVV
- NOTE
- LUX
- RST
- ZULU
- CAG
- TONY
- SUIAI
- PKF
- UMB
- NAMI
- SOBULL
- PROB
- BAG
- VELAR
- MCHC
- LIBRE
- PURSE
- SAL
- QOM
- TUT
- PXC
- ASH
- AI9000
- PER
- COVAL
- ORC
- SKH
- DITH
- FMC
- DETF
- FREN
- BWEN
- FEENIX
- MTV
- PSY
- SATOSHI
- CLOUDY
- WANUSDT
- SHROOMY
- MARS
- VBNC
- USDT
- HOTCROSS
- PRISM
- FLOPPA
- BDP
- KNINE
- MINX
- CAS
- SMT
- CVP
- COSA
- PND
- OSCAR
- USDC
- $JIM
- MNTL
- MNFT
- MELD
- NATO
- KOM
- TAONU
- SUGAR
- MIND
- USTRY
- EDEN
- PEAR
- BRWL
- WETH
- FUZN
- DIME
- BSX
- PIPO
- INDI
- UFC
- CJPY
- BIGSB
- HZN
- BENFICA
- SAVM
- QBIO
- NOTAI
- SKAI
- $KOKU
- USDC[HTS]
- BANANA
- RUGPULL
- CALVIN
- LUM
- CHIRP
- EJS
- AIW
- SPACEM
- FTC
- EDOGE
- CARD
- LEV
- GQ
- RE7USDT
- SNS
- VOYAGE
- IXO
- DTF
- WBTC
- SPLASH
- PLYR
- VSYS
- PIG
- CPT
- ORAIX
- NFTXBT
- TRCL
- SENSI
- VDA
- FSN
- ASX
- VEE
- GMTO
- JEST
- USDT
- DINO
- KRO
- HVLO
- WAR
- GUMMY
- SEILOR
- AMB
- SYNK
- WAVE
- HAMMY
- CRAZE
- IVY
- RITE
- USDS
- DISTRIBUTE
- USDC.E
- GUAC
- SOPH
- STGWETH
- BSKT
- ZARA
- POT
- MIM
- WYAC
- MM
- DORKY
- LVL
- STDYDX
- VTX
- GLUTEU
- NORMIE
- MC
- TIA
- SENTAI
- QST
- STATE
- BONDLY
- RIDE
- OKAYEG
- IBIT
- ASYM
- PKT
- AXV
- RTBL
- DTEC
- PANDA
- RAM
- SOBA
- USDC.ETH
- VMINT
- ART
- YBTC
- XKR
- ACQ
- XI
- CHAMPZ
- XFI
- DESCI
- APY
- KAON
- MZC
- EFC
- DESU
- ELONRWA
- AIX9
- BABYPEPE
- NOTE
- FROGE
- AI
- RING
- BTORO
- ANTIRUG
- STEPSOL
- MP
- TRONPAD
- RAMON
- QAI
- KLAUS
- RICH
- ROCK
- ASM
- LESTER
- SBX
- NIBBLES
- MK
- GST-ETH
- NAV
- HLN
- FUKU
- USDT
- MUNDI
- GURU
- XSP
- APM
- POWSCHE
- BAZED
- OUSDC
- ENG
- NGC
- NOBL
- YAKU
- GRRR
- RETIRE
- XYRO
- T3AI
- INTR
- LOL
- MOOV
- FLUT
- SNIFT
- EXPERT
- TERMINAL
- FA
- WECAN
- PUPS
- NSTK
- XENCAT
- TEN
- WANUSDC
- BLEND
- POLY
- PIRB
- OMIRA
- BRICK
- SHR0
- JUSDT
- XGC
- PPCOIN
- MUMU
- CAU
- TOONA
- GIV
- LBLOCK
- KITE
- CRASH
- BORED
- ELITE
- HAC
- WWY
- XODEX
- DYP
- VLXPAD
- AZC
- ITMT
- CHEESE
- VCF
- USDC
- TOWER
- ARTFI
- ███
- BLOCX
- SRK
- HEMULE
- NOMNOM
- MOAI
- XMONEY
- NEIRO
- LUNR
- $LOTTO
- DRUGS
- RETH2
- WLKN
- ARTEM
- BEE
- UBXS
- WOZX
- DAN
- SIMMI
- $TOAD
- NICP
- AMKT
- DRIP
- TSHARE
- LLM
- EMP
- MD
- ORNJ
- AVER
- KAP
- MAPS
- 4CHAN
- AVAC
- LIMITLESS
- MBET
- IZE
- SOUL
- VIRGIN
- ZKB
- ANGLERFISH
- JPEG
- LEO
- NEROX
- WUSDN
- SUSX
- SKY
- BABYBNB
- STBU
- USDC
- RACKS
- PEN
- FOX2
- CHELON
- OPXL
- DTIA
- BULL
- NGL
- INCA
- USDC.E
- BB
- SYNTH
- MNRY
- BAMA
- 5IRE
- $THREE
- BSR
- SHY
- IMF
- PIZA
- ZUSDT
- KDAI
- ALOR
- 589
- SPS
- AEG
- ZCN
- CHAD
- SERAPH
- BABYFWOG
- ABYSS
- MIST
- MINEBTC
- ARIA
- AURA
- PLANET
- NEURA
- STYLE
- STAR
- BAI
- DEVAI
- WSTASTR
- CRWNY
- FACT
- SMILE
- AGENT
- TRUMPCOIN
- SHIBOO
- SPICE
- VNXAU
- DEVIN
- CRYSTAL
- SAINT
- HOTKEY
- TALIS
- FCON
- LADYF
- BROCCOLI
- GIB
- CARLO
- BRLA
- TRD
- PDEX
- CPAL
- RSP
- BEFE
- EDN
- SOAR
- GOFX
- TERRA
- BOOSHI
- ANALOS
- TRADE
- RPG
- EBULL
- HLG
- XMON
- JARVIS
- RBLS
- BALLZ
- AIOS
- PYTHETH
- NEOT
- RBT
- GM
- FCTR
- VELAI
- ZPAY
- MATES
- STAR
- STAR10
- GURU
- TEER
- ANDR
- TRUST
- SHIB
- HONK
- USA
- WOM
- TAROT
- RAVEN
- NET
- ZAP
- MTARD
- NVIR
- SLR
- TRENCH
- SEER
- ICOM
- AIRENE
- CKUSDT
- STBL
- ALPHA
- TAOLIE
- FIGHT
- HUSKY
- AVG
- ITHEUM
- ZTG
- TUT
- BGG1
- SDR
- BANX
- BIFI
- BRD
- AGIALPHA
- RECORD
- FEFE
- DATA
- USDC
- $TOAD
- SSG
- PGX
- FALX
- USDT
- XMONEY
- SHR
- SAIL
- PEPE
- ERTHA
- E4C
- CHONK
- THALES
- SB
- GAME
- KEK
- SOLID
- CDOG
- PACA
- BNA
- BONSAI
- JRT
- LA
- GMAC
- AAA
- MENGO
- FROC
- FOLO
- CATBOY
- $PANANA
- NODL
- MAICRO
- UBSN
- BIOFI
- PYTHUSDC
- BONSAICOIN
- U2U
- PUT
- CRTAI
- $PEPE
- TOMO
- XMD
- NEIRO
- HIBER
- FERMA
- OMNI
- WEIRDO
- GYMNET
- JAM
- PEEZY
- HUG
- TRUST
- BABYBROCCO
- XFT
- TST
- IDOGE
- RE7CBBTC
- IRA
- TAXI
- CYI
- C4E
- GAIA
- MND
- KEKE
- MARS4
- FUZZY
- WAM
- SOLENG
- USDC.E
- AM
- GOA
- GRK
- PROPHET
- SYNTH
- FYN
- CHENGU
- ATF
- VAL
- HSUI
- BOOH
- BNBXBT
- ELDA
- HOPE
- HABIBI
- EXD
- SPEEDY
- BOYS
- USDT
- GOZ
- BKOK
- JGN
- MNB
- NGM
- TORCH
- SHIFU
- TRUBGR
- XOXNO
- SHEKEL
- AIT
- BLP
- KAI
- LUCKY
- PHI
- SPORT
- POLK
- NEOS
- DETO
- KOIN
- HONK
- YEC
- UCX
- GSWAP
- $BADCAT
- MUC
- EUROE
- GFI
- NIKO
- WETH
- SAUBER
- PAK
- AYIN
- NABLA
- FAIR
- KNJ
- CCV2
- KOIN
- QWACK
- WAT
- QUARTZ
- WOOF
- NSAI
- WCTC
- KINT
- MIZUKI
- AME
- MINT
- DOSE
- FILTER
- CEP
- ZAP
- GULF
- BGVT
- P3D
- LITH
- DINO
- THC
- KLS
- WBTC
- IGU
- NSFW
- RFL
- $DRIP
- SEUR
- XALPHA
- W3W
- FUJI
- MOO
- AMA
- UNO
- PAJAMAS
- LIT
- QUDEFI
- RET
- MBD
- USDT
- GMB
- SOLMAX
- HBOT
- LBM
- RAIN
- PRX
- HUDI
- UUSDC
- FOR
- AGENT
- EGG
- FORM
- DCN
- ISAACX
- GORA
- NXT
- BTSG
- ATN
- ESTEE
- $CLAP
- LYP
- LSHARE
- DAIGE
- MORE
- P
- EARLY
- MORRA
- IQ50
- UDAO
- NFTB
- RYO
- BCB
- FISH
- NEBO
- MOBY
- KIBBLE
- BRG
- BULLY
- GSTS
- RAZOR
- NICK
- SWP
- NFTL
- DCOIN
- ODIN
- PROOF
- CTI
- HATCHY
- MENDI
- UNV
- ELIZA
- SUSDX
- SCAR
- PUSSY
- $BURN
- CHAI
- WBTC
- WANETH
- BSWAP
- INT
- USDT
- QUANT
- TCC
- CHIDO
- JHH
- AVRK
- ARV
- PEPE
- SAFE
- CZRX
- BERAMO
- RVC
- FWT
- ST
- MELLOW
- MXM
- REVO
- BCUBE
- VOLT
- WEWE
- DERI
- JAIL
- AROK
- FOREST
- WRKX
- DFYN
- SNFT
- ELK
- KROAK
- NOMAI
- CDT
- FUNGI
- HLO
- MTVT
- DAI
- ZAI
- LAMB
- KUMA
- GINNAN
- INFRA
- SOULS
- SHIK
- USDT
- XY
- AURA
- KIBA
- SUGAR
- AVL
- SPHERE
- NUT
- WNK
- DNA
- OAX
- FOFAR
- CHANGE
- MUNCAT
- MIMO
- GNY
- JOK
- RIZZMAS
- DAI
- BABYGROK
- SOLI
- VCG
- $REALKENDO
- FREE
- OPAI
- PANDA
- SOCIAL
- FPS
- ECLD
- AIPUMP
- DOGEFATHER
- ZOO
- CBC
- OCE
- BRIAN
- EVERETH
- DSLA
- OCTO
- VIKITA
- X2Y2
- ZOOMER
- CRPT
- VPS
- BOF
- SKID
- AIPG
- CGT
- REVU
- MOAI
- PLS
- EMR
- STND
- DORITO
- PXP
- STC
- POPDOG
- TST
- SANDY
- GTN
- TRAVA
- MONKEY
- 🟥🟩
- BIAO
- BOBLS
- LAYER
- GST-BSC
- IDRX
- KROM
- $HWTR
- MILLI
- LUMOS
- BOLT
- RAT
- IGNIS
- RMRK
- $JOBSEEK
- WATER
- WOLF
- VAIN
- SALT
- CYPHER
- CBL
- $TRUMPAI
- KAT
- AVENT
- FRTN
- FIGHT
- GEMXBT
- BIS
- SYNDOG
- KFC
- KIT
- STEAK
- $CCC
- BIOHACK
- BETS
- WASSIE
- ZOON
- GLORP
- J3FF
- BTTY
- SSR
- CZ
- EVAL
- DBX
- FLOW
- HNTR
- HORD
- BASED
- MEGA
- NUSA
- CYDX
- NMX
- KEROSENE
- URUS
- AUTO
- LZM
- MOONED
- ◨
- AJNA
- TUA
- BMR
- TTK
- SATX
- CHORUZ
- EQX
- AIT
- CHO
- WAIFU
- X
- SDFXN
- HON
- GRUMPY
- BLEND
- SHITZU
- MAIA
- MOSS
- L8CAP
- PBTC
- BFT
- GROWAI
- SHFT
- QKNTL
- STRUMP
- ROOST
- BENI
- FCL
- PREME
- $HAMI
- TAMA
- BABA
- 21M
- SAGE
- JAIHOZ
- NOOOO
- MAX
- DVY
- CWS
- ITGR
- MBTCS
- MBXN
- GSNAKE
- VIBE
- OXYZ
- CERTAI
- CROW
- INF
- UNQ
- S
- GHOST
- EXCC
- HAN
- LEND
- PLR
- HESTIA
- QCK
- DOG
- CBM
- GASP
- MPS
- BARIO
- AMU
- RONNIE
- BUMP
- BRB
- PICA
- MMPRO
- WALV
- MZERO
- WETH
- BMT
- CROWD
- TOKO
- SQDGN
- WBLT
- BSOP
- BUNKER
- STUPID
- PKR
- PAY
- WANA
- K21
- WHALE
- QMALL
- $IRL
- ATEHUN
- DXD
- FATHA
- PUMPCORN
- AGX
- ASTRL
- CIG
- XAVI
- TOTO
- YAI
- HAKKA
- TURBO
- ABDS
- TURT
- BELT
- VZ
- BURN
- KIRA
- XUSD
- ANON
- VU
- CONVO
- PMX
- CATANA
- AIP
- DOAI
- X
- PEGG
- VSTA
- $SHARBI
- WBS
- POGAI
- $PUCCA
- NORDO
- TITCOIN
- OK
- $ELON
- HEFI
- CUZ
- CLS
- STARSHIP
- OOKI
- LILAI
- KCCPAD
- KICK
- SHOGUN
- MEME
- DSETH
- HBB
- RTIME
- KITTENWIF
- PERQ
- PEN
- LARA
- HEDGY
- BTCBAM
- XET
- APPLE
- GONDOLA
- PTRUMP
- AWS
- NETT
- PRNT
- CYBRO
- BESC
- HYVE
- ANDYMAN
- CLINK
- TUBBI
- EXO
- COOL
- AQUARIUS
- RVST
- MURAD
- DEOD
- MISATO
- YOKO
- JUP
- MUTE
- BSCS
- NEST
- AI
- CHIPPY
- OSEAN
- USDFI
- SOURCE
- DFX
- FEAR
- CIRCLE
- WEALTH
- BED
- TES
- FLSH
- NIZA
- MKUSD
- WNT
- SP
- AKRE
- TROVE
- BCAT
- BOOH
- BRITTO
- RKFI
- QUAD
- ETHO
- LOA
- SAKAI
- NABOX
- GEMINI
- FKR
- CHARLES
- SEVILLA
- DJI
- DUREV
- REGENT
- FOUR
- AMO
- BCDT
- KWANT
- $BROKE
- EGG
- GBCK
- BUILD
- PANO
- PHTR
- RAFT
- KDR
- PEPES
- MUT
- F/ACC
- KEIRO
- SUT
- NORMILIO
- PONCHO
- OMNI
- AUR
- BLINK
- CRGPT
- WOOP
- UNICORN
- POINTS
- OPIUM
- SOONX
- BNBAI
- MARCO
- FREN
- WDOG
- ALPHA
- FIT
- USDT
- USDT
- SUNTRON
- COST
- CND
- FLP
- EZ
- AIM
- MOE
- 8CHAN
- CWAR
- PLENA
- SOLA
- FLU
- JKC
- WDC
- ARC
- CLO
- CPAI
- TAURUS
- MOOMOO
- CATALORIAN
- PRONUT
- WIGL
- COQAI
- SBR
- REV3L
- MTH
- DORA
- MA
- TRENCHAI
- WOMBAT
- EARN
- WEHMND
- BINGUS
- OGSM
- 99BTC
- CURE
- 0XBTC
- ASI
- TDM
- XBLAZE
- PSSYMONSTR
- SOLO
- COME
- DACAT
- KOMET
- $AMEN
- EMILIA
- MELD
- SONE
- HYDRA
- SHIBC
- FAME
- ZMN
- SOLVE
- SOLARIS
- ANDY
- FIRST
- TORSY
- WIFE
- TOOKER
- SECOND
- FLOWER
- KWAII
- CNG
- RIC
- WGR
- MAIV
- SMARTCREDI
- INJX
- AIX
- $GNZ
- PUMPKIN
- FOFAR
- LOAFCAT
- GEKKO
- TSWAP
- SNAIL
- SPERG
- GRLC
- AVIVE
- DEEPAI
- WORK
- MCL
- BCOIN
- BONE
- W3GG
- HERMES
- PSWAP
- GAMI
- HTERM
- SAI
- SAM
- PNDR
- PGOLD
- SUB
- USACOIN
- LINU
- SPARTA
- NFTFI
- YOUSIM
- WNDR
- $CROAK
- FINC
- ROAR
- CHEESE
- BLUESPARRO
- BEENZ
- BIAI
- BEATAI
- ARCA
- LONK
- WONG
- HOGSCOIN
- HIM
- BRO
- TETU
- SPHYNX
- BCCOIN
- OLYN
- BMON
- GORILLA
- IONA
- SHAR
- CIA
- OPTR
- PLQ
- E/ACC
- TRUMPIUS
- CATGPT
- WF
- COINYE
- $SPACE
- AIRI
- KINGSHIB
- IPAD
- ALEPH
- SEED
- PSL
- BTF
- GEKO
- D
- SPIN
- STAM
- SPEX
- COMSWAPWLI
- BTCZ
- TECH
- LEO
- REXBT
- SUNWUKONG
- MYAN
- DFP2
- BHAD
- TKST
- ATRI
- ROCK
- ZACK
- DEFROGS
- MEOW
- BIP
- AICM
- UNISTAKE
- STOIC
- BOP
- LOKY
- YAY
- BITZ
- DUCKAI
- ZYN
- STRONG
- CHAMP
- CLEV
- CELA
- AUTISM
- CNCT
- ROP
- SOLARBA
- CNDY
- PARTY
- ZELIX
- METH
- PAPER
- CNV
- WAI
- $TIMES
- HEDGE
- NIGHT
- CATGIRL
- ASSCOIN
- GEL
- GRAV
- VEGA
- RSN
- CREA
- NEON
- DOGECAST
- KEE
- SPORE
- DEPLOY
- LOON
- MEWC
- MARVIN
- NEMO
- JONES
- $UOS
- MGT
- ROCKY
- HNST
- PURPLE
- HBARK
- OCH
- DMOON
- CHEXBACCA
- CHUCK
- DZOO
- CVAI
- ORDS
- HNC
- WNRG
- INT
- USDT.ETH
- LEND
- PARA
- CADAI
- SCORPIO
- GODL
- SAGIT
- ZIK
- MONAI
- MYST
- ROOK
- CDOGE
- XYZ
- $ACE
- KOVU
- CAPRICORN
- BLAZE
- TENET
- LONG
- ARIES
- XD
- BAG
- GEC
- SENSUS
- CBPAY
- FATAL
- DASHD
- ABOND
- VOLS
- FWB
- PEW
- 🐕
- GARY
- PISCES
- CANCER
- MONSTA
- GUILD
- XPE
- ZOO
- STELAI
- GRV
- OCADA
- NEURAL
- COAI
- BFIC
- PEAK
- PI
- COAL
- YMACH
- SUIYAN
- MUDOL2
- PEPE
- RPK
- GGTK
- GC
- WALTER
- UPTOS
- FCOD
- CLASH
- BIST
- YEETI
- GFT
- BIX
- $BEAT
- BLT
- PIGGY
- PINKM
- RADIO
- WANNA
- VIRGO
- YAM
- ZUSD
- SKICAT
- OVER
- DWEB
- ACS
- SANSHU!
- ZCL
- WGC
- BFT
- KIM
- ATOLO
- AGI
- BURT
- FUEGO
- PESTO
- VEIL
- CGAI
- RM9000
- MINIDOGE
- BHAT
- DEGA
- COVN
- WEB3D
- COV
- XMY
- ROOBEE
- $AGENCY
- KIF
- WECO
- $COOK
- DBI
- PEARL
- LIBRA
- POV
- $PLATH
- TWX
- PAC
- MMA
- APU
- SOLANA
- GOVI
- HYDRA
- KTON
- JULD
- MOTOKO
- BEND
- KEK
- RNB
- NAZAREAI
- DGNX
- GLDT
- SLICE
- YOU
- JIM
- RCAT
- ILOCK
- PROTEO
- DOGK
- GMB
- XSEED
- NCTR
- DTX
- XWG
- DAI
- ZEE
- ADASOL
- $SAIKO
- $UPDOG
- FORTKNOX
- DPS
- VERDAO
- THC
- BRIUN
- CARAT
- XENO
- ELAND
- TASTE
- NAILONG
- FORT
- DEGENC
- FIRE
- AIWS
- HOP
- DNA
- CHAOS
- WYNN
- LC
- EOLAS
- IXI
- WILDNOUT
- PINU
- SETAI
- MANE
- FREE
- TKAI
- WN
- MPH
- PLOT
- TRG
- BTN
- UNICE
- VITE
- XUSDT
- $ARKEN
- SUPERCYCLE
- EX
- 🏦
- VAULT
- SATOX
- CGT
- KAT
- DCT
- CHEEMS
- SMI
- LAKKHI
- DONUT
- BARRY
- TRC
- TRAXX
- MEMEAI
- APAD
- NFE
- BIS
- RYOSHI
- HAUS
- $CATS
- CLH
- EXM
- KREX
- SIM
- MONK
- MELON
- BZE
- MANA
- ZRS
- PEPE
- USDX
- ANDY
- FRM
- INETH
- MSR
- BANDIT
- BRLY
- COBY
- Y2K
- UXD
- ELFI
- UNI
- INSUR
- OMEGA
- $KANSTAR
- USDT
- VNST
- THECAT
- ENKI
- KDG
- WAT
- TC
- VERSA
- BOB
- DRINK
- LOOT
- HOLO
- RBTC.B
- KABOSU
- QUIDD
- TIFI
- DOGSHIT2
- TIGRES
- HIT
- MILKBAG
- QRX
- REX
- XEQ
- RIDDLE
- FWT
- LYRA
- NOT
- SHROOM
- RELAY
- FURY
- ENKI
- SMACKM
- GOCHU
- WTFO
- SYLVIAI
- DRAGGY
- POLYPAD
- ARBX
- FLI
- PAC
- MVX
- IVPAY
- FYDE
- SHIBU
- PMON
- IVN
- BANGCHAIN
- $WEEDE
- KLY
- GENI
- ION
- SHEGEN
- CREATE
- VKA
- $RUG
- EKKO
- CMDX
- SATA
- $CHESTER
- BABYBTC
- SYNC
- SHIFT
- METAV
- ASSAI
- FLIPPY
- AGLA
- WOOF
- CIV
- BLOC
- AIEPK
- ADOGE
- TAOSHI
- RATING
- USDV
- SIRIUS
- DUCKIES
- DEFAI
- BROTHER
- TREAT
- AIVIA
- TITAN
- STOG
- PLASTIK
- KSK
- GXT
- ZEN
- DNOW
- DYOR
- CASH
- GYOZA
- DACKIE
- CHONE
- SHROOM
- RAJ
- SWARM
- NEWO
- BTRUMP
- THAT
- BONUS
- B20
- SKITTEN
- NAYM
- KNOT
- CORN
- GM
- SMOL
- YF-DAI
- $DICE
- SUITE
- XBC
- KLEE
- XLA
- VATRENI
- BOPPY
- LABZ
- FWC
- XVN
- ECTE
- CATF
- DFNDR
- CYB
- $SOULS
- LMNL
- AIDA
- POSI
- YES
- INUINU
- DIME
- KEKE
- $LOCKIN
- REGENT
- GOR
- $OTTO
- XNV
- KIRA
- GLDS
- BUILD
- CBX
- AXI
- BORING
- SPX2.0
- ELGATO
- SIMSAI
- L7L
- ODDZ
- SWOP
- XCREDI
- MON
- FOAM
- ETHUSDC
- PYM
- ONC
- EQPAY
- ECLIP
- NSTSTRK
- KONAN
- FREN
- C2H6
- DRX
- VIP
- MEFA
- RAB
- USDT.BSC
- SSSSS
- TGMETRICS
- CGG
- RCN
- WEWE
- REALM
- WAIFU
- SPR
- CPA
- $OZONE
- OCI
- MARO
- ZMT
- LULU
- GLINT
- PINGU
- APED
- COC
- W3F
- MPUP
- DUCK
- TORI
- $DAPY
- BIGFACTS
- CHOCTOPUS
- EMBER
- AIMBOT
- PEANUT
- IDNA
- EXA
- SHUI
- TORI
- WSG
- TRUMPSFIGH
- JUICE
- THOL
- CT
- UNIO
- CCX
- USACH
- PVU
- $INTERN
- AUDAI
- SHIELD
- SANI
- HOKK
- WANDER
- TIPS
- NAVAL
- FLIES
- BITCAT
- THE1
- RHUN
- FLAME
- ALPHA
- SHIRYO-INU
- MOON
- H
- KOLZ
- 2DAI
- BLB
- BONKERS
- EDG
- MTS
- BOOJI
- USDC
- RUNNER
- STAPT
- STJUNO
- XPNET
- CHMB
- CHILLGUY
- DNVDA
- PAPERCLIPS
- TOKI
- CENTS
- ETI
- KNIGHT
- PSYOP
- PONCH
- RAMA
- DOOMER
- USDT[HTS]
- TTM
- SOBULL
- TSLT
- USDW
- SEED
- LTD
- H4CK
- CHAD
- ARO
- $QBIT
- OCAI
- R/SNOOFI
- JPOW
- PYRATE
- SUIMON
- ESOL
- ONION
- HARAMBE
- USDT
- NALS
- PFL
- RUM
- WETH
- LOD3
- ARTH
- GIA
- QLIX
- CLEO
- APOLLO
- GOME
- NINA
- KNUT
- ETP
- $MYST
- KM
- INX
- MEOW
- SWPR
- KIRAI
- POCHITA
- DIDID
- $MARU
- BOTON
- SPICE
- DEFAI
- OCC
- NCASH
- ILY
- LINDA
- THUMB
- BWS
- KACY
- DPET
- MAG
- VENT
- VEMP
- FLS
- SATT
- XRP
- ALL
- VES
- DELAY
- MARS
- SUIB
- SILVA
- ZAPO
- DOGAI
- PILL
- NSBT
- PIGU
- FLAT
- STINJ
- SACI
- WIT
- POOKA
- $HOKK
- VASCO
- OKY
- BRIDGE
- HID
- MVD
- EDAT
- GYSR
- $SITCOM
- AIT
- KCH
- XLG
- SAG3
- YDA
- INSC
- KNOX
- CIRUS
- VAR
- BDX
- CONE
- BASKT
- SCC
- QAI
- CATDOG
- DEFAI
- LOT
- GRAI
- USDC
- WHALE
- NEER
- AXIS
- CLND
- O3
- WOLF
- DAWAE
- VSX
- USDT_T
- CYBA
- $PRO
- MFT
- USDT
- PEPO
- BET
- $BOOB
- MANIFEST
- SUWI
- ETH2X-FLI-
- MT
- KORI
- STSEI
- BONECOIN
- FROQ
- FXUSDC
- CHAN
- EVEAI
- GLINK
- NETZ
- TOR
- ZGEN
- VYPER
- AX
- HND
- MRSMIGGLES
- CLOAK
- MYRC
- NDX
- KITTY
- PAD
- LOLCAT
- BBOT
- MONA
- TIME
- BULLIEVE
- BANK
- RIBBIT
- CTT
- EGG
- FELY
- KRA
- CRAPPY
- 🖕
- LRT
- TIMI
- $VAULT
- FATGF
- DRAC
- INBRED
- SHAKEY
- AI
- YGATA
- PEPEC
- SCOTTY
- NFTART
- OVO
- USDT
- CBANK
- LUDWIG
- WICKED
- EPIKO
- FRIN
- LAB
- GOON
- SHIBUSSY
- SHEZMU
- KDAO
- MARVIN
- LUCI
- JETTON
- OGGY
- MANYU
- RISE
- TCAT
- BROT
- KRIPTO
- GLS
- GM
- HOMO
- UME
- RVLT
- SIZE
- PAC
- SOLFUNMEME
- BANJO
- DOGGO
- SHEESHA
- PLEDGE
- REUNI
- NUX
- USDC.E
- CATHEON
- TOPG
- TT-WBTC
- OGME
- BAKKT
- FURY
- CRISPR
- GLCH
- CAT
- PICKLE
- KOY
- TOBI
- ROCK
- NEP
- SAAD
- NR1
- DOG
- GULL
- SPACE
- HMQ
- BLAST
- GOO
- ATD
- CHEYENNE
- KAPPY
- ANARCHY
- GUAN
- ACTUAL
- LDY
- SLOP
- CSW
- KAAI
- IRT
- ZACHXBT
- HYPER
- ALR
- YLD
- ORBIT
- VETME
- MIND
- PROL
- MONK
- WAIT
- BRNX
- MUG
- X
- BLXM
- LOOK
- ZYRO
- QUAIN
- 3P
- BOG
- TAGGR
- PET
- ROCKET
- MOCA
- SUIJAK
- VOID
- EML
- WABBIT
- DND10
- RHYTHM
- BABYSHIB
- WBTC
- SPINDASH
- CS
- MVP
- CHPD
- PEEL
- ELMNT
- CATO
- PLATY
- JELLYFC
- DIP
- FLOCKA
- BMI
- LQDX
- BRO
- BAINANCE
- BUILD
- ATHENA
- CHITAN
- ✖
- WOOF
- AXL-WSTETH
- AX
- UAI
- XRUNE
- CALICO
- LANDWU
- TYRANT
- $LILLO
- WETH
- VAL
- TAX
- TFI
- EBERT
- PTOY
- LPUSS
- OGC
- APR
- USDC.E
- USDC
- OLY
- MOOSK
- AYB
- XKI
- VFOX
- DOUG
- FCO
- BIAO
- SCB
- ETHEREUM
- SCCP
- BCMC
- MAGAA
- PTF
- KT
- SWIFT
- LOS
- SPO
- USDC.E
- KEKIUS
- HOPPY
- L2
- ZWAP
- HUSH
- CAINAM
- CAN
- MIMANY
- FAI
- USDC
- GUA
- SUITRUMP
- TRUTH
- ZHOA
- FFM
- DGH
- $BETH
- RMT
- RICK
- INK
- WELT
- LOOBY
- NOOT
- KAT
- ETHEREUM
- SUIDEPIN
- SANTA
- WIN
- NAI
- BUTTHOLE
- DOGE
- EVAI
- SORA
- MIA
- DEER
- API
- UDOGE
- VIRTU
- SFD
- BLACK
- PICA
- PEPE
- NYAN
- ARA
- EVOLVE
- BANK
- ECOIN
- MOGUL
- NIGELLA
- SHOP
- FLAME
- MF
- REPOALYZE
- ACE
- UGLYDOG
- CNS
- FLASH
- ONTOS
- COK
- USTREAM
- DCHEFSOL
- $LOCG
- ZAI
- CRYORAT
- LNR
- ARCH
- @DOGE
- SHEZETH
- IB
- WBAR
- BLOCK INN
- MFG
- SAINT
- KHEOWZOO
- LOE
- OLT
- METO
- RMT
- ITP
- CABO
- MIHARU
- $RAINI
- USDC
- EOSDAC
- INVITE
- WIK
- LIQ
- CCP
- IETH
- SVMAI
- XWIN
- RODAI
- SL
- WETH
- USDT
- PASTERNAK
- MTRM
- NORA
- PHONON
- CORGI
- FFTB
- CARBON
- CORN
- EUSD
- GEOFF
- SHATS
- MOON
- GROYPER
- TREEINCAT
- SHRED
- DELI
- NAVI
- AIMX
- SPUNK
- RABBIT
- BPT
- RSTK
- BUILD
- ZYGO
- ZKEX
- ZODS
- PYRA
- LEMON
- NAWS
- LYM
- PEANIE
- HLT
- BTCST
- BUNBUN
- SWM
- BAO
- RBW
- CLO
- BORK
- NAIFU
- SOV
- 1ART
- LUIGI
- NOVA
- OOZY•GOOZE
- HUNNY
- NONJA
- MOVE
- ZLK
- PCORN
- VISION
- VIX
- PAINT
- MEOW
- ERN
- $WSB
- PSY
- GOMU
- IAMAI
- SOLCAT
- MERGE
- NOCHA
- TRI
- ERIC
- MILK
- DXY
- WSB
- ENTR
- PBTC35A
- ETH
- XCASH
- $CULTUR
- KASJAK
- SYNO
- MAGICK
- LRS
- BRKL
- KMC
- TSUBA
- MFAM
- ILLUSION
- AICMP
- POTUS
- KWAK
- MEGA
- NSDX
- DAD
- O3
- SHARKI
- DYNA
- CROS
- DNT
- KEN
- LOOT
- ELONIA
- F2C
- USDT
- USDT
- $AIGG
- ∅
- ROT
- MCG
- AISTR
- MATT
- MVRS
- $ICONS
- TRDG
- BLUES
- WMM
- CRODIE
- DTI
- HOL
- IFSCI
- $BLU
- SUNPIG
- NOTI
- TOP
- NEUROS
- DOGMI
- MMF
- ATAI
- SPR
- TOH
- TCT
- RACCOONDOG
- BONK
- DLTA
- AVAX
- BEATS
- TATE
- RAIN
- PRIME
- OCN
- MTG
- SYBTC
- OSIRI
- WIRE
- SEBA
- BASE
- TRAI
- BAT
- DALGO
- ATA
- CLUBMOON
- SCOUT
- BETA
- DRPAL
- DON
- OF
- ARSW
- LOOTER
- CAT
- CUR
- POD
- GDUPI
- TXN
- FLC
- TIDAL
- NODE
- COMCOIN
- $COFFEE
- MS2
- ZAPCAT
- POODL
- SECT
- NEPT
- NFTBS
- XMX
- PNT
- AGA
- UNEAR
- LEG
- YBO
- KCN
- FTW
- SOS
- CONV
- PEFI
- LUCHA
- KAGE
- PERI
- HAIR
- INXT
- 39A
- CAPPY
- NOX
- MONA
- MTRC
- EBYT
- DCI
- CLX
- ZSC
- SHIH
- LUBE
- BBL
- PODGE
- CODE
- SMTY
- ESS
- MEVETH
- WAS
- TOPKEK
- PIPE
- ALF
- DGI
- WHACKT
- RE7FRAX
- $BIRDFLU
- ROGEN
- MAHA
- OATH
- WPSG
- OSMI
- BONKEY
- BEZOGE
- RDX
- PUMLX
- BUU
- $CAT
- DMND
- RFUEL
- $ONION
- RUGGA
- TICKL
- ALLIN
- VOLTX
- ANTI
- BENT
- ECO
- PORTX
- BSTY
- BTA
- FORKY
- XMS
- FAP
- MTR
- CTR
- FOMO
- $BABYLONG
- HEC
- CODEX
- BAHIA
- ROUGE
- ARTX
- NEURONI
- DYOR
- TULIP
- $TORO
- KONO
- VBELLS
- SPCTRM
- CHIB
- MEAI
- WOG
- GATSBY
- CRP
- DPLN
- OPK
- TZPEPE
- PLANT
- ARROW
- BTW
- CHEERS
- WHALE
- LION
- PARAM
- FODL
- GODEX
- MILK
- CURTIS
- COMFY
- BUILDX
- MBAG
- THGUY
- SOH
- GOAT
- AWARE
- RURI
- $RICH
- SPIRIT
- DEPINS
- HSAI
- RADIO
- CORGI
- RADAR
- USDC.BSC
- IDEA
- GMPD
- BSEN
- SU
- ODIN
- GAGA
- DAW
- AXE
- CANDLE
- PIX
- BLANK
- VOLT
- IONX
- WJUV
- DOGECAST
- REBELZ
- GHSI
- NEW
- GSE
- OCEANS
- DEGENOS
- MOO
- GKAPPA
- SANTA
- FIRST
- MMAI
- MORUD
- SHI
- TUX
- UTS
- ASHA
- MOON
- LEE
- ELMO
- DEEPAI
- PRAWN
- JEFF
- UAPT
- PRO
- DANCE
- HBARBARIAN
- CWT
- CUT
- AEGIS
- ZFI
- QDFI
- WBTC
- URS
- CORE
- CFI
- TTC
- CULT
- USDT
- SI
- MEOW
- MOOSE
- AUDD
- CYT
- PXL
- SVTS
- PBR
- NFTL
- KUMA
- $SNIFF
- SUUSD
- BRO
- SNAPCAT
- DAFI
- AART
- MVC
- RELIGN
- $PIGGY
- MINDS
- MOX
- AA
- USDT
- KENDU
- LAD
- CAI
- $SHRUB
- KOGIN
- BRETT2.0
- HAROLD
- AIVA
- SOY
- APTR
- BNSD
- $HORNY
- GARY
- CRYPTIQ
- STARGATE
- PAI
- FECES
- JAK
- APEMAN
- BD/SOL
- CRX
- SPFC
- MAYO
- IKB
- LILY
- PROME
- 1HUB
- LEXICON
- ZUN
- KANGAL
- IMMORTAL
- BNY
- GRAIN
- SBAE
- ZAPI
- ETHPAD
- BLADE
- LQC
- TONE
- IFC
- TALK
- JOI
- 42
- WATM
- GOLD
- QUA
- OPM
- BERRY
- SBOY
- MERT
- $DMP
- BTM
- AVA
- VRSW
- ARQ
- ORE
- MOB
- AAG
- MERO
- LIZA
- FEVR
- BOMB
- SHND
- GGG
- VXL
- WIF
- COOK
- DFIAT
- WASP
- GAIB
- MITHR
- DRU
- ARMY
- MET
- BIRDDOG
- WPR
- NAOS
- GREG
- LED
- BOSSIE
- DOLLAR
- BALTO
- YT
- RIA
- MWD
- TAI
- WDOT
- NAFT
- INS
- HALO
- SPIKE
- THX
- $CRAMER
- ECHO
- FOMO
- OBX
- TURBO
- FLUFFI
- PPAY
- DECHAT
- SEN
- $VOX
- INU
- EFR
- DOMES
- LILB
- BASEX
- TMSH
- WOWO
- PPBLZ
- ODIN
- LUMI
- GAI
- PWROSE
- $JANI
- PAC
- SOG
- CHATTY
- BEEG
- NFTD
- CEB
- BULL
- EAGLE
- RGEN
- GHFFB47YII
- HDAO
- LINK
- FREECZ
- PMA
- YAP
- XIDR
- SKAI
- MONKEY
- WIF
- WORM
- MATRIX
- BAOS
- PETER
- BTCACT
- $TINYP
- CSI
- RETRO
- EYE
- POLTER
- IUSD
- WSPP
- CLAUDE
- YES
- SUIMAN
- HELMET
- DEV
- SPELLFIRE
- BCOIN
- CSWAP
- HANA
- LIQQ
- KMON
- ACHI
- AFC
- DREP
- CKOCT
- EDAS
- GORPLES
- NAMI
- DRC
- PING
- RISITA
- GOB
- PLY
- $RECA
- HER
- DIGG
- PIZZA
- BABYPEPE
- ZER
- MSMIL
- SHOPX
- GOH
- GFY
- ATM
- LENDA
- VUSD
- WEBSIM
- GAL
- SHIT
- USSD
- MAKE
- AURORA
- SQRCAT
- CATBOX
- WAWA
- XY
- NEU
- KOBA
- GOBI
- NEZHA
- STRNGR
- BNU
- STX
- PLANE
- WOPTIDOGE
- XNL
- SWINGBY
- AQUA
- STA
- KOVIN
- KWIF
- DINU
- DBTC
- TRUTHFI
- SEAL
- BRIGHT
- ROGUE
- DAWN
- ARG
- JANRO
- CHAD
- MUST
- FARA
- GAYCOIN
- DOGECAUCUS
- LUFC
- STV
- TRC
- BWORM
- DUCKER
- VELA
- CALLS
- GALO
- ZEREPY
- NOWK
- TDS
- COINBT
- GIDDY
- ICE
- CROFAM
- FREGO
- WASR
- MIST
- KFT
- GRAF
- MONKE
- ZILLIONXO
- MOLLARS
- $ITO
- TIN
- ZAT
- OUTIE
- HELIA
- FINA
- DMAGA
- SPEED
- STAKE
- VSG
- LIEN
- BETBIG
- PEPE
- MAO
- BANDIT
- $BEFFAI
- NFT
- PNUT
- SIMON
- GDOG
- INTAI
- RUFF
- BLOCK
- SCR
- FWOG
- PEANUT
- KAKA
- META
- JARVIS
- JAM
- PUPPERS
- BALLZ
- MET
- SPEED
- WATCH
- QUINT
- SNAP
- BLEU
- WETH
- PHX
- SAM
- TXL
- HSC
- GROGGO
- SYNC
- SKILL
- CYBER
- DRAGONKING
- APU
- $PULSR
- COBE
- BASED
- LUCHOW
- DORA
- CATS
- $GIGAI
- TRACKEDBIO
- HYENA
- ARBI
- DDD
- SWAPZ
- CLIP
- HINAGI
- GCOIN
- GROKINU
- NYXC
- MOBY
- BABYTRUMP
- JARVIS
- MOG
- KABOSU
- SKRT
- MEGALAND
- HOBBES
- BSV
- TH
- SCHRODI
- LITT
- VCTRAI
- MONI
- VRX
- XED
- NIOX
- WCITY
- CORN
- CHULO
- DUSD
- IBR
- UFARM
- UTG
- BIF
- DCAU
- WACM
- DGI
- GDOGE
- FLUX
- YBR
- GNME
- BERF
- ZTH
- CUPSEY
- HPAY
- PYI
- SBKPT
- LGTB
- XDN
- KEYCAT
- BRETTGOLD
- BKIT
- RFSTETH
- CO
- BABYNEIRO
- BTX
- GOOBY
- CSAS
- BIRB
- GEM
- UTU
- LOTTY
- CHRONOEFFE
- GFT
- RAIDER
- KOAI
- HGT
- AETHER
- PSM
- SELF
- ALICE
- ACT
- TRIBE
- SHEESHA
- SOLAYA
- MOON
- SGT
- SQUAD
- CROGINAL
- BABY
- SIZE
- $BOOTY
- LIFE
- $BROKIE
- WETH
- RFR
- AVERY
- $KEYDOG
- NOODS
- UPDOG
- GAMBLE
- FLY
- COLON
- ANIME
- GMX
- KOAK
- D.O.G.E
- DOPE
- AFIN
- INF++
- KING
- COIN
- NIOB
- CATEX
- MILTON
- HGET
- UNB
- RYIU
- COPE
- WAGMI
- EKTA
- TT-WETH
- PLANETS
- USD3
- MUG
- PFI
- HEMPY
- OCAI
- PINEYE
- ALL
- NEVER
- BLOB
- SEN
- EON
- $MRKT
- SASHIMI
- KEIRA
- BOWSER
- SACA
- DYOR
- KPAW
- PROPS
- SHIKOKU
- GEM
- MVDA25
- ZILPEPE
- LGNDX
- ROY
- SOURCE
- FRENS
- DAI[HTS]
- EEUR
- HUMO
- DOCUSOL
- KALM
- BANANA
- SOL
- BOSHI
- PEPEW
- MITH
- CHEDDA
- HOP
- MASS
- ADX
- TERN
- PORT
- MEDUSA
- $FRANK
- USDT
- MER
- NEBL
- KIDEN
- MARV
- THOG
- VERSE
- DREAM
- FORE
- SEDUX
- CAT
- FORK
- UNIX
- SDOGE
- MEWING
- YAWN
- MOTH
- BAI
- FROG
- BOSSU
- 8PAY
- ANTC
- ETF
- KRIDA
- $SCARF
- NICO
- MGPT
- SHDZ
- META
- MVRWA
- HAWK
- MEI
- AKITA
- CB
- PADAWAN
- TRUMP47
- CAKEDOG
- SNTR
- SOLO
- AGORA
- SDOGE
- MKAT
- SOLY
- PUMPAI
- BRY
- AGB
- NOHAT
- LONG
- DFX
- SENDOR
- BCRE
- ARBOT
- RUG
- RB
- CHILLAX
- SQR
- BREAKER
- CHRIST
- SLB
- XCEPT
- 2077
- MEDUSA
- JASON
- OS
- ASTRO
- AIC
- NCAT
- PRNT
- NEIREI
- RNA
- EDOG
- SSTR
- OPSYS
- MUSTARD
- PINO
- PLOP
- FEETCOIN
- NFTY
- CIRCLE
- CHWY
- POLX
- TPAD
- DUCK
- FOXGIRL
- ORBK
- D2T
- SCOOP
- XCT
- ORACLE
- ABX
- NEONET
- MITTENS
- ONI
- FOMO
- BUCK
- H1DR4
- POPSMILE
- SABLE
- RAINBOWTOK
- ROPIRITO
- DRIFT
- KTC
- DRGN
- STAB
- BEAST
- VDT
- LVM
- MEMETIC
- CRAFT
- EGG
- ROCK
- CHICKS
- GNRT
- UNLUCKY
- MOOVE
- MEARTH
- MINIGOUT
- ONX
- LIQ
- BABYNEIRO
- SLCL
- HOOT
- USEI
- SCALE
- TOAD
- CASH
- VETH
- DEFIDO
- OPTION
- GF
- SMR
- YETI
- DFY
- ALASKA
- PCNT
- BENJI
- ASTRADAO
- 霞
- CHEEMS
- MYRA
- GAIM
- YOTO
- SMF
- FIT
- ISLAMI
- NEROBOSS
- SUB
- GNX
- FARTDADDY
- NULL
- PLY
- BRRR
- BALPHA
- AAI
- TPU
- SOLAR
- DFND
- SAFU
- BABYPOES
- BAC
- CERES
- BS
- DATAWITCH
- SCRAT
- BCP
- SFT
- TOKITO
- BISO
- PILLZUMI
- GINNAN
- ASCN
- SI
- ALGT
- EROWAN
- ISHI
- MOTA
- JOHN
- UNVAXSPERM
- MELO
- PUSO
- KICKS
- DAI
- FBX
- HAT
- STEAKETH
- MVTT10F
- ARKI
- JASPER
- TERMINUS
- CRYING
- CUMINU
- SOL
- TOSHE
- CU
- IZZY
- DAWGS
- SHIBX
- LABSV2
- AMI
- IBFK
- PAC
- WOKIE
- AUTIST
- EYE
- TRIANGLE
- TINU
- SHITCOIN
- BABYCATE
- PEPE
- ODDS
- MTOS
- SVD
- ZEBRO
- REAL
- CEWBTC
- WHALE
- NFAI
- LBA
- GOWOKE
- MONKE
- LARRY
- NXR
- CATWIF
- HENAI
- REM
- SCREAM
- CORA
- BTL
- EMC2
- MFI
- CPL
- KWT
- $DCAY
- CHIPI
- VCAT
- NUGGET
- USDT
- CWH
- HAWKTUAH
- RFT
- BTO
- HUAHUA
- TAY
- ANDY
- CATGF
- DOM
- 32
- CRA
- SAVG
- ORION
- BALT
- ZCO
- MFW
- POPEYE
- HOD
- TWRAE
- OMOCHI
- KOI
- AEON
- NIKITA
- LQT
- 47
- SHORK
- CRE8
- SWRV
- GONE
- GLP1
- CRUSADER
- JORGIE
- ESPORT
- SCF
- MMT
- COR
- DXGM
- ZOOMER
- LEO
- OCD
- GSC
- PEPE
- BLUE
- RIZO
- VPK
- SADMEOW
- CNC
- FABS
- LILPUMP
- $ZKITTY
- SRN
- NOAHAI
- UDO
- GOAT
- CHIPS
- DOGIN
- OCTO
- BIRD
- WSPURS
- ALP
- IKIGAI
- LUCY
- ROCKY
- HIPP
- SONNE
- COLLAB
- GAP
- GNOCCHI
- FRUDO
- VDL
- MAGAPEPE
- BLAZEX
- SADANT
- FORM
- FUNG
- NORD
- CNNS
- VAULT
- ROBO
- MERGE
- SUNPEPE
- MDS
- ARES
- A16G
- $DOGE
- BABYSOL
- AGME
- INTERN
- EGG
- HUM
- FROGS
- ARX
- SEED
- NDAO
- STSTARS
- AVN
- GINNAN
- BGA
- FOMOON
- PSEUDO
- LMF
- TCAT
- WHAT
- GATTO
- NEXT
- FINS
- FLURRY
- DAI
- POLI
- BIRDDOG
- ARXIV
- PONZIE
- ANI
- USUALUSDC+
- NIPPY
- PHX
- GNFTY
- MCEN
- RCH
- BIAO
- DUK
- KCAL
- DEGENT
- CORTEX
- OINK
- ONC
- GECKO
- EQZ
- CATVAX
- FROG
- CORSI
- PEDRO
- FLAT
- BUSY
- DINO
- HOPPER
- BULL
- ZZ
- SUPERBID
- UNN
- GAS
- USDCAT
- KAPSA
- ALA
- OMEGA
- STAR
- MISHA
- DMT
- JUNGLE
- $CHILL
- SSTX
- MOONY
- MXNE
- BSDX
- DUCKY
- BAKSO
- SOLAPE
- COT
- RLP
- GOU
- IUS
- GAMEFI
- BAZINGA
- KAMPAY
- AGURI
- ELEC
- DXL
- KINE
- TRIVIA
- MAGNET
- QHUB
- EMON
- DTC
- KOL
- AIR
- FA=FO
- MIDLE
- HAGGIS
- BUTTPLUG
- KAMA
- DGENAI
- SSNC
- BLEP
- FOXXY
- STICK
- DAI
- ALETHEIA
- HANBAO
- D.O.G.C
- MNST
- GORT
- KOHLER
- BRUME
- ZODI
- FXF
- SCA
- WORKIE
- PUFFY
- KANDO
- ARCD
- DRPXBT
- PWR
- MEME
- ATS
- STD
- VTF
- BRAZA
- FUKU
- NYZO
- PENGY
- APES
- OMAGENT
- PRERICH
- GLAM
- SAIL
- SOLX
- ISAAC
- EDX
- COINE
- HSM
- MEAN
- GWIRE
- FTP
- BOG
- AFFI
- SWAY
- CTF
- PACOCA
- MEMD
- BASED
- LSD
- CAPO
- TMANIA
- TYBENG
- DXAI
- FLUX
- ITXS
- GAG
- NLC
- ZINU
- UBTC
- UWU
- EVA
- JORKIN
- GENESIS
- SQUID
- FNT
- ZORRO
- MSCP
- SPIKE
- BULL
- PANA
- PARADOX
- STAKELAYER
- XYRA
- SAI
- FIWA
- ARTTO
- SOLGOAT
- $RRT
- DYP
- BULLA
- BLADE
- SPOODY
- FLAVIA
- TRUST
- SHRIMP
- FINE
- LCD
- SHIA
- IF
- TURBO
- SMART
- DHV
- AGI
- MINT
- BASED
- GIRLE
- REAP
- AES
- WAGIEBOT
- IDV
- OCX
- MOLA
- ERY
- TOSHI
- DISCO
- YOURAI
- SNN
- NINJA
- PANTERAI
- ORBIT
- WINTER
- WBTC
- QORBI
- HOG
- CITDEL
- AI69X
- GG
- ARMOR
- FOUR
- GM
- TOGA
- KWL
- YAWN
- GLFT
- FST
- OPEN
- EARL
- RABBIT
- CMONK
- CONK
- 🐈
- KAKAXA
- TAD
- DUCK
- WAA
- HERIA
- ANDY
- WETH
- FROP
- PRIMAL
- DEC
- ETHM
- WPOR
- TIGRA
- SOB
- MATT
- FOREXLENS
- LUCKYSLP
- SCUBA
- $MOXI
- FRF
- ROSX
- FUEL
- $MUST
- POPPY
- WETH
- AXE
- ARB
- LAMBOW
- IDYP
- 0NE
- DKUMA
- SINK
- PUNCH
- CZGOAT
- BONK2.0
- DAI
- BOOP
- MMIT
- URD
- BULLS
- SFIL
- ORO
- SZAR
- WARPER
- BABYCHEEMS
- ANDY70B
- TUNA
- PUFF
- OD
- ANTT
- STOIC
- COIN
- MINU
- BECOIN
- GOLDEN
- KSTT
- HULVIN
- UNQT
- WARG
- KILLA
- RENA
- YAKA
- ANDY
- PROPEL
- A51
- XWP
- AGTS
- BASEDGUY
- WAVL
- BOOSEY
- POOLZ
- INCI
- HOOD
- BELUGA
- BOG
- RZNDE
- SAM
- $LANDLORD
- NITRO
- WZRD
- PCH
- MEME
- MOTION
- KYRO
- FINA
- ARCONA
- KIETH
- BASEY
- ADILLO
- WGAL
- ARGO
- FUND
- $BTC25
- PLSPAD
- FOREX
- KEYFI
- DEEBO
- HADES
- FNX
- INU
- MCOIN
- SUICY
- ZIX
- ENKI
- FTPXBT
- FIJI
- WAFC
- GOLDEN
- PEARL
- NORM
- ET
- BMONEY
- 42069K
- SUILAMA
- DONTDIE
- XOR
- LOTUS
- ALCH
- USDC
- PAPO
- DAI
- WEX
- CPFC
- $GRASS
- WSG
- GOV
- JFP
- MONKEX
- TROPPY
- EHHH
- KZL
- FVT
- RANDOM9
- SHIP
- ZAZU
- PRICK
- LAB-V2
- PEAGUY
- VGC
- TURT
- QQQ
- ARG
- JEOING737
- UGG
- ANKA
- WVG0
- WOOFI
- URQA
- FXBT
- CROC
- WATERBEAR
- OFAC
- CATA
- GOOD
- MEF
- SPACE
- REMILIA
- PLATA
- UAP
- STINKCOIN
- BABYMARVIN
- SLAYER
- TALES
- POPKAT
- ASTEROID
- JENNER
- SHAO
- BAE
- BUMSHAFT
- PAR
- MORK
- DAFT
- ADE
- $STABBY
- POINTS
- CATWIF
- ANDY
- GBSK
- ZKID
- LMT
- SHAWK
- $TUSK
- TRRXITTE
- MMO
- TAMATEST
- CZ
- MBERRY
- ALPACA
- SLRS
- UNAI
- DCM
- PFIRE
- GFLY
- ERGONE
- TIG
- AWX
- MOMA
- OP
- TODD
- MIN
- FIN
- $ACAT
- MXNBC
- MIRX
- EXMPLR
- SAKE
- TAJ
- BUTTER
- DIS
- FUTURE
- COFI
- FTX
- DINU
- SUMO
- X8X
- LODE
- JASON
- BCDN
- MAD
- BRICK
- DST
- DG
- RIN
- HELA
- MSHEESHA
- PSDN
- VISION
- SUNNY
- ISTAR
- CGO
- HOPE
- FARM
- WSTV
- SUPA
- ODE
- HEC
- POPO
- JOWNES
- OPCT
- GOLDEN
- BGCI
- DAM
- CLU
- SHEERLUCK
- BRAINS
- ESPR
- $KEKIUS
- UFR
- NERD
- WALLY
- PRINTR
- SUCKYP
- CATFROGDOG
- SYPHER
- ONDA
- SENT
- CALUM
- URO
- SFX
- JANET
- HIBS
- KLO
- MOD
- NCASH
- MIR
- BLOX
- CAVE
- ZB
- VALUE
- $SHIBASHOO
- ZEN
- DAETA
- SCOMP
- ARCHI
- MOCHI
- BITT
- LOLA
- BUL
- ILIS
- IB
- PIXI
- BLOB
- HIVP
- CHOW
- BLAP
- PUSSY
- APY
- WSAM
- KS
- $HOUND
- YODE
- DOGGO
- KOTARO
- USDTSO
- BORPA
- AMERICA
- RETIREMENT
- WPFL
- FLUF
- BURN
- SONNY
- SUGARB
- SHARE
- HEIDRUN
- BOBBY
- CHIKUN
- SFT
- AIDP
- KIRI
- BUILT
- SHIELD
- LUC
- FOXX
- DWC
- SIGMA
- HXAI
- EYE
- STPR
- MRUN
- PETUNIA
- KAKA
- MAF
- BWLD
- DOGEC
- CCOP
- WAIT
- AVATLY
- POCHITA
- DACKIE
- USDC
- GODS
- QSWAP
- DOPE
- MEOW
- $TRUMP
- KZ
- INUKO
- $FARTMOMMY
- MAD
- TENFI
- LESTER
- BCOIN
- BAKED
- WTH
- FRGST
- KEKIUS
- KABOSU
- TERRY
- DUN
- $SMACK
- SKU
- SYDNEY
- SC
- DARK
- TARIFF
- ROCK
- MTN
- WBRGE
- GAY
- MIYA
- KTN
- HIPPO
- WAP
- TAB
- TSLA
- CTO
- SNM
- $GENE
- MU
- ORB
- BLUE
- MOOO
- MOLECULE
- CLANKTARDI
- POPO
- XCAT
- SMG
- LUCE
- OISHII
- MSPC
- RAPTOR
- BULL
- CFT
- CLANKSTER
- USDT
- BZN
- PUBLX
- DAM
- WINTER
- ALPA
- HAT
- HVN
- MAO
- WYBO
- GREMLINAI
- N
- CHAIR
- DPAD
- GOOF
- MILKY
- SPORT
- BOBE
- BURN
- SHIB
- XTK
- BABYHIPPO
- SS
- WHOREN
- ROCKI
- SABR
- WPERSIB
- ADANA
- FROTH
- BIO/ACC
- OCP404
- SANTA
- RARE
- SALD
- OCP
- COFI
- DAWG
- SUBF
- DAI
- USDT
- KENJI
- BANK
- INU
- GOON
- 4GS
- ZAZU
- GLTR
- $PIXE
- SENKU
- WOKE
- PHMN
- MAGADOGE
- 0XMR
- AIDI
- MUGI
- SUISHI
- ME
- JAI
- SAFU
- UFO
- EAR
- SKINUT
- HOSHI
- PINE
- HOODRAT
- MXGP
- WCAI
- HEHEH
- CZAR
- TOPCAT
- ONGO
- OCTO
- HEFE
- SUNNED
- VITAI
- DANA
- PIVN
- $LOGE
- WODS
- D/ACC
- SKY
- ARIX
- WBAHIA
- YNBNB
- DRONES
- LUIS
- BRK
- BABYPNUT
- IRD
- KPAD
- BLKC
- INCEPT
- LENS
- GDAO
- MUNCH
- BERAFI
- WUFC
- COG/ACC
- WTF
- BORK
- MEGA
- IOV
- SPUNK
- SASHA
- SNAP
- TYKE
- BUN
- MAPE
- VICKY
- BOB
- WLEG
- MAX
- SNOW
- XGN
- $JACKY
- WNAVI
- PEPEGA
- MINIDOGE
- ZERO
- COLANA
- ETF
- PIZZA
- GINGER
- OPPIE
- EQUAL
- MAD
- GUS
- ARIE
- $PLPC
- MIHARU
- AUDIT
- TRONDOG
- PIX
- KAPPY
- XIO
- EFX
- ZEEK
- 1ON8
- SOCKS
- ND
- DVINCI
- GENIE
- HACHI
- ZENITH
- STORM
- SCOIN
- WVERDAO
- CELT
- ABE
- KPOP
- ALPHA
- DVT
- PRICEAI
- MIS
- RIZZ
- W$C
- CMPS
- FROYO
- SKM
- ELE
- LINQ
- SHIRO
- WHASHTAG
- PARRY
- AEJO
- TSUJI
- CAT
- ORCL
- CORGIB
- OMNI
- EDEN
- CURLY
- PEENO
- $MEMES
- SOX
- CHEF
- SCAN
- YELPE
- DUSTY
- HYPU
- CRUNCH
- ANON
- LOL
- FIU
- WVASCO
- BOYSS
- $CRDN
- BHOLE
- DUDE
- FILTER
- SUIDOG
- XP
- BLUFF
- WATER
- PEPEAI
- LORE
- GECKY
- SENC
- JEWELS
- TORA
- XSEI
- BTCAT
- SHIMMY
- ETHPRINTER
- BABYMIGGLE
- WTIGERS
- MONA
- BLS
- FIGS
- BUDDHA
- REM
- QGG
- FINE
- FINN
- LET
- MPX
- WSARRIES
- TCP
- LAPUPU
- PAPU
- FUN
- WFOR
- QUBIT
- BOGUS
- UNIPCS
- VERA
- DAOS
- PEPE
- PHX
- SPQR
- DAM
- CUSD
- CNET
- POG
- RAIN
- PMD
- LCN
- WIZARD
- WSACI
- SNK
- DPY
- FLS
- SUNLION
- CULO
- WISTA
- DOKY
- WBENFICA
- MILK2
- FAPTAX
- WFLU
- MIKO
- TONIC
- CHINU
- FEDJA
- SYNTH
- SOLY
- TILLY
- FKSK
- BPX
- LONGEVITY
- AETHER
- $NODE
- KET
- TUCKER
- TCAP
- FRUG
- WSHARKS
- MOON
- STORAGENT
- UT
- CHEESEBALL
- AZUKI
- MORE
- DOE
- RS
- CWC
- DOOGLE
- LIQ
- SAI
- VOLTA
- PWAR
- PEW
- ALN
- DJCAT
- MAGASHIB
- WTRA
- TBFT
- SMILEK
- TIRED
- BLUBIA
- PLEB
- PAWSY
- SNIFFS
- THN
- WSFP
- BEING_AI
- AIKA
- NINJAPUMP
- DOGIUS
- TIME
- BAO
- TNC
- HHGTTG
- NEIRO
- AAAHHM
- BTCW
- UNDEAD
- KFUCAT
- DEARBOOK
- BRIDGE
- BHC
- PRARE
- P3NGUIN
- XENO
- FUR
- QOAT
- KAIA
- GOATX
- LOTION
- EGOLD
- HODL
- CHADCAT
- VERA
- HARAMBE
- WALL
- BABYPNUT
- صباح الفر
- GMAT
- ABI
- PETOSHI
- RIDERS
- BALLS
- LFG
- CAT
- AGV
- PTS
- XTT-B20
- SPQR
- SONIC
- WNAP
- DELAY
- CCTV
- WAGMI
- HAVA
- PCHF
- CHUANPU
- SOLPAC
- PEPE
- DRA
- HUHCAT
- NERDY
- FUD
- GIF
- ICE
- DWA
- FDREAM
- KINGNEIRO
- ATH
- LAMA
- BAILEY
- BDRM
- RONDA
- BOLI
- SPEX
- LUN
- YOBASE
- DOGER
- 8008
- SOOTCASE
- SANIN
- NDAS
- CHILLGIRL
- PEL
- MILEI
- KEK
- TMNS
- SPLASH
- ROSSCOIN
- BRACE
- KOI
- BINARY
- OGGY
- BBK
- GUBERTO
- TETHYS
- FX
- LILA
- LABZ
- 69420
- ALAN
- BWED
- CMST
- LOOPY
- $KEK
- VIOLET
- STACY
- CAT
- FVM
- COCAINE
- 0XDEV
- DOGY
- GARD
- NEIRO
- TRUMPIE
- GAMMA
- IZUMI
- LONER
- ZOA
- XMAS
- BOBY
- MAYA
- SAMI1
- ADAX
- SUPAI
- $YUMI
- COPE
- BICHO
- N1
- PST
- SPIKE
- WAM
- ERC-AI
- DEGEN
- PAL
- CHEEKS
- DND
- FMT
- OKANE
- PDOGE
- NSURE
- MEE
- BPRIVA
- MAN
- WGFK
- NIGI
- REGI
- ONE
- APRIL
- SOLANA
- ATLAS
- ASTRO
- SANTINO
- PNUT
- WMIBR
- POU
- SKULL
- GINNAN
- BABYGOAT
- MTK
- ASTRO
- BUFFI
- SAP
- YDF
- BRUH
- SBET
- $CHEUNGUS
- BALLS
- PEPITO
- $PMW
- PRCY
- 1%
- $MAMA
- WAPL
- POPO
- BTC
- COOL
- OMOCHI
- AGI
- SANTA
- FOMO
- NOTWORK
- NFI
- MATRIX
- ROAD
- SCHIZO
- $ROBIE
- WRSO
- PVP
- SOFAC
- BUB
- MOFI
- MWM
- LUMIO
- ZYB
- DOS
- BOY
- RONOUT
- CAT
- JUSTICE
- EAGLE
- SUNPUMP
- CLX
- MOLLY
- QMIND
- MOCHICAT
- SQRL
- PNET
- RUSTEE
- SGTV2
- GERTA
- SUYA
- WLEV
- RAZE
- KEN
- MAMOON
- SOLALA
- RINO
- CHANT
- CHOCCY
- LEV
- COZY
- CRAB
- CATFISH
- LAB
- WAGMI
- MONGY
- OASIS
- CUFF
- ZOLA
- NWO
- DONT
- UNO
- BITCAT
- FOMO
- STANDARD
- $BBT
- NAMI
- DEGEN
- 1EX
- GHNY
- YANN
- EXO
- WSAN
- CULTEL
- FINKEY
- GUDTEK
- BABYDENG
- VISION
- FUSION
- WLUFC
- AD
- RUNNER
- ROCKETAI
- WGOZ
- BLAKE
- DNZ
- ZAAR
- PDOGE
- WJDT
- RHINO
- TRUMP47
- FPFT
- GMMF
- CYS
- CAPY
- PTSHP
- PUNK3493
- 🤡
- WANNA
- WCHVS
- WUDI
- SHOOT
- CNTR
- AESOPERATO
- WAIN
- WVCF
- KRYPT
- WDZG
- POCHITA
- SANTAHAT
- USAID
- CHILLFAM
- LOVE
- STENCHCOIN
- DABOO
- CYBORGISM
- GENZAI
- PREDICT
- WBFC
- CEICAT
- PEPE
- SPIZ
- GBOY
- TRUTHS
- BUNNY
- PISSCOIN
- HONKLER
- WQUINS
- GRINGO
- FARTGPT
- LEPER
- 0KN
- UTYAB
- MACKE
- JIN
- DOGEX
- MONKEY
- HACHI
- WUCH
- FTX
- PUFF
- KUMA
- POLLO
- LONG
- DEGPT
- DNXC
- WITA
- MPRO
- KASBOT
- CROW
- ANSOM
- PSY
- REBD
- $KOLT
- BAVA
- DOTZ
- WVIT
- FEED
- WROUSH
- $MAN
- POD
- WBUFC
- ∅
- YUKIE
- YOUNES
- GOF
- PFROG
- VALUE
- YIELD
- SOUL
- FLEX
- BICOIN
- SWQUERY
- ENFT
- FRA
- AIDOGE
- CLEG
- SITY
- WAWA
- JADE
- DC
- SS20
- RIKU
- WOTF
- ROPE
- UCM
- WIFI
- TREEB
- BLEPE
- FUKU
- CEUSDT
- RITO
- PAN
- WMFC
- KNIGHT
- RING
- PREAI
- SUMMER
- LINGYAN
- LESTER
- SHIB
- DUCKY
- RACEX
- BURRRD
- ANCHOR
- BAMBIT
- POPPY
- YSU
- DSM
- PUNCH
- BULLY
- MIVA
- QUASAR
- SNY
- FRED
- GOOCH COIN
- CATOUR
- DERP
- IDLE
- FTI
- PHILL
- GINGER
- WSCCP
- LMAO
- FLOCKY
- AISCII
- TRUST
- HTO
- ARATA
- MSWAP
- RETARDIA
- $HUSKY
- BUG
- H2W6GM6JZ
- CAF
- MAXWELL
- EARLY
- POPFISH
- GIAC
- STACKS
- FLUXT
- WAND
- IF
- ZORA
- BUTT
- FIONA
- $EGG
- RINA
- KUSH
- DOGEI
- HYPR∞
- DORKL
- URANUS
- HIVE
- BMS
- OAKS
- JUJU
- KIRBY
- SHIGGA
- OMNI
- GOOMPY
- BUTTCOIN
- AD
- ARGON
- $FROGS
- DOP
- AILIVE
- WAIFU
- NODE
- SENTAI
- DRONE
- NEIROH
- DONTDIE
- $1
- JACKPOT
- BOBBY
- MAGAPEPE
- RODOLFO
- IHT
- TRONCHES
- MARSK
- BBC
- PE
- MEOW
- PHTEVE
- HMX
- KITTY
- DADDYCHILL
- PSOL
- GARBAGE
- AITRUMP
- POPDOG
- GIB
- APRT
- MOLLY
- CRYPTO
- AUTISTA
- $GOODLE
- SHILL
- DWB
- HANABI
- PIZZAGUY
- CHIBI
- WUKONG
- CHLOE
- PONK
- SAD
- BVM
- GOOSEPUMPS
- ISHND
- H0L0
- PICKLE
- TITAN
- DIOM
- MOM
- AII
- USC
- BWULL
- EFT
- RDOG
- BILL
- PPDEX
- OTIA
- SULLY
- RAGE
- WOLF
- CHAD
- BABYPURPE
- AITT
- SHARK
- START
- BLITZ
- LIQ
- AINTI
- MOON
- CLAMS
- LINK
- $MIHARU
- ESES
- JAPAN
- QUBE
- MARS
- KRON
- SILLYCAT
- TI
- MOBIC
- HOODRAT
- WGALO
- SKULL
- VBEA
- POI$ON
- WSEVILLA
- WMENGO
- BKN
- DARK
- CROCDOG
- APYS
- WRACING
- SOLCAT
- PLANKTON
- NEVA
- LSD
- LOLA
- POWERAI
- BULL
- PMPY
- FARM
- DOGE1
- MDEL
- CROY
- WALA
- CNC
- AGENT2025
- DOLA
- YIN
- GUM
- LOVECOIN
- GONESLER
- TAO
- WOLFINA
- WDAVIS
- WENDCEX
- SHITCOIN
- SBF
- TIM
- PINEOWL
- LEGEND
- SION
- GRIN
- SUIEET
- ALPHR
- BOB
- REEE
- DLT
- USTX
- HMMM
- BOLLY
- FRYER
- LOONG
- SWORD
- BUDDY
- FOMO
- SUICAT
- CHARLIE
- VIDAI
- $R3D
- DOGE
- HAMMER
- EGGY
- SNEK
- FRATT
- WATLAS
- BCPAY
- D.O.G.E
- TEST
- WEFC
- AVXT
- POW
- ATO
- MMO
- UP
- SOLITO
- BEE
- PONKEI
- MEFI
- ETHARDIO
- ALIENB
- CA
- HIGHER
- DOGER
- AUC
- BLES
- REMILIA
- $TRAIMP
- BEE
- TRUMP
- FALCON
- SHIB
- CTO
- CROC
- CONVICTION
- GENIE
- DOV
- GCAT
- DJT
- LONGAI
- BROWSER
- BOPPY
- BABI
- ZNZ
- RARE
- PONZI
- DESY
- MIW
- QAI
- JENNA
- DEXAI
- ENVOY
- AM
- CTOAD
- WHY
- 9TO5
- $SCOT
- XEN
- UPG
- ATHENA
- KAMABLA
- DOLAN
- TOX
- SNOB
- $VENKO
- BEZOGE
- SEALS
- ALINAINTEL
- UPI
- WSPFC
- ANIME
- PEPE
- DANNY
- MALAKAI
- AICRYNODE
- SLAV
- SHIB
- COVE
- TARDI
- $SPACE
- LOGOS
- OMN
- BADGER
- DAVIDO
- CODERGF
- POTATO
- DHANDS
- CORGI
- SARAH
- SUID
- WTIGRES
- SQID
- DUCK
- RICH
- GFR
- YOD
- BABY CZHAO
- JRRY
- BABYLOFI
- KCAT
- PUMPTRUMP
- M7F
- DAK
- FUFU
- BUDDY
- AOC
- PEBLO
- $BANE
- BIBI
- KIT
- GMEOW
- STUPIDCOIN
- MAT
- GIGA🧠
- VIVEK
- FROG
- MECHAZILLA
- PUMPCAT
- NOFAP
- SBTC
- OOF
- SUGAR
- BOMB
- MIND
- CODED
- BARON
- BOOBS
- GATO
- ROXY
- SHOE
- AVS
- KUNDALINI
- GEO
- $HONEY
- BRAIN
- POPGOAT
- BASED
- RYOSHI
- $PXAI
- MATRIX
- EPEP
- UNW
- ZKE
- BSIM
- PCT
- $LOUIE
- CSR
- GAME
- MYB
- METAIVERSE
- RUNEVM
- FARTGUY
- WAGMI
- PAT
- LKR
- MST
- CAIRO
- DMLG
- KAFKA
- ALTOID
- POOWEL
- L24AI
- INC
- ATHCAT
- BABYGOAT
- SCRL
- WCC
- WAG
- WASM
- COIN
- HUNTBODEN
- GEM
- YESBUT
- AQUA
- CRAB
- PULSE
- PAUL
- WCPFC
- SUNNEIRO
- LUS
- RAFF
- FANX
- SOLPOD
- SHARDS
- MEMEGAME
- CEDAR
- WEVE
- LORIA
- MOCK
- DOT
- GUUFY
- MORRIS
- SHUFFLE
- E
- $XAI
- HAMMY
- SNAKE2025
- MINJI
- CRW
- WOOFER
- X/ACC
- TANGO
- CAL
- ZALPHA
- TROLLICTO
- LONG
- MENG
- SDOGE
- JINX
- XLN
- GRUG
- GOP
- $SADDY
- ZOAI
- NERVE
- YOU
- BOB
- AFYON
- XETRA
- MDF
- DEGEN
- MAXX
- BTCWIZ
- CRC
- MULA
- SMZAI
- JETCAT
- DRX
- MOONTHAT
- HODL
- NUT
- IRENE
- FLOWER
- TYLER
- MOON
- KOK
- GLEBE
- BABYMAGA
- KRAMPUS
- SWIO
- BROTON
- TRUMP
- ACCORD
- DEO
- GNT
- MRCH
- SPARTA
- SPELL
- LUV
- CATJAK
- EARN
- MOOCAT
- CRISP
- CSTR
- BOOTS
- ZKGPT
- OBS
- WSOH
- TON
- DOGSHEET
- QUANT
- BTM
- MSTR
- MOON
- FFF
- POS
- AURA
- BABYDEGEN
- SSF
- DEUS
- SIKA
- WSTETH
- HGAI
- $POOKU
- IRO
- MARIE
- BLOCK
- PAWPAW
- POPWIF
- AGXBT
- FLOOF
- SCINET
- JMTAI
- PERA
- ACHI
- FTS
- PIM
- XPOW
- OMNIT
- GROOMER
- BITS
- $AIGCR
- GRIFT
- POZI
- FROGIE
- HACHI
- N64
- FOMO3D.FUN
- PEPEWIFHAT
- NXR
- DOPAMINE
- AURORA
- CICADA
- FLOYX
- HAT
- WIBWOB
- MONDO
- DMG
- TWOCAT
- LCY
- CHANGO
- SNAKES
- THL
- SHRUBIUS
- FNC
- TUKI
- HMU
- X
- BDOGE
- BKC
- TOMMY
- DOGO
- LFW
- DISCIPLINE
- XMUSK
- CORE
- CHINAU
- WOW
- GM
- SUPR
- FROX
- AURI
- GTUSDC
- BUSTER
- YUNA
- BULLISH
- KOMA
- GRUMP
- PWOG
- BABYSHIRO
- GOATSE
- KOLANA
- DP
- QUEEN
- O3D
- ASAP
- BBANK
- 4WIN
- USH
- $PACO
- WIBFK
- SOAI
- CATINO
- TAD
- FAML
- MAGA
- LATENT
- PGEN
- AZIZI
- $TRUST
- LOLA
- TDX
- HENTAI
- SOHOT
- LAPUTA
- MEH
- HAMI
- $VERTEX
- TAOTOOLS
- BUENO
- WSAUBER
- FROG
- OLIVE
- ESTEE
- KHA
- MEOW
- DECKO
- SEAT
- WOMEN
- FUG
- MWH
- NPC
- DGOLD
- ODIE
- UMI
- XENO
- CHILLCAPY
- COPE
- BEEP
- TWURTLE
- CHART
- BANKSY
- PAUL
- MORE
- APL
- WRT
- COIN
- DOUG
- CFT
- WSB
- CBK
- SEDGE
- RUBY
- CIG
- VAB
- GAISHA
- BITORB
- PEMDAS
- MAIN
- QUIL
- DUEL
- MAAI
- W
- RIB
- ESP
- MDOGAI
- YOWIE
- GIGA
- APE
- MIKU
- NEURO
- 2025
- KONG
- DINO
- HOOT
- JONAH
- BTB
- CMFI
- EUROB
- GPUINU
- YUP
- CUB
- RETARD
- SHR00M
- SWEG69
- ISA
- BOB
- PHNX
- THOL
- FELICETTE
- $DUB
- ORI
- AKACHI
- SPECU
- KNU
- BRO
- PACATO
- LATTE
- CAPY
- DOMO
- GOBLINTOWN
- PINKY
- CET
- CRYPT
- SCROLLY
- MCAIFEE
- IMGX2
- SLAP
- TOGE
- COW
- GRIDDY
- $GOLDEN
- ALMC
- POOTI
- HORUS
- WOP
- WELF
- ALIVE
- CHONK
- POP
- DRIFTY
- APEDEV
- KAILY
- GAPE
- BL00P
- ROBOCOIN
- XERAI
- TRILLY
- VIORA
- CUCK
- SLIME
- SUMI
- $TALAHON
- PTP
- RAJU
- DEERMAN
- NOOSUM
- SKG888
- MORTI
- CHARM
- $KHAMOO
- GOSPODIN
- NDX
- COC
- PC
- RIZZYEAR
- POWER
- LOVELY
- FOTUS
- BITCORN
- CHUNK
- KSG
- TUNE
- WIFMAS
- MAXI
- RINTARO
- MANYU
- PARROT
- EGL
- AICAT
- SAI
- FERG
- BONSAI
- GNOME
- Z
- PUN
- PRAIST
- BCUG
- MORPH
- DOGETHER
- TRUMPED.AI
- JIFF
- DTORO
- DATBOI
- NAS
- FLOOF
- YUKI
- VDAO
- SKULL
- SSE
- AI99X
- CAFE
- FLOW
- BETA
- FUBB
- MARS
- SOLPAKA
- GM
- TUCKER
- IF
- UPDOG
- MILO
- RAINBOW
- BULLA
- SOK
- CATGUY
- KIKI
- KAI
- MTGRD
- ONYX
- OTTI
- AVAXMINERA
- SPWN
- BOLTAI
- SHSH
- JOSE
- MANDY
- GOOFY
- MONKU
- BRC20
- BTL
- SHA
- EYARE
- VS
- CRTB
- CROW
- MOZ
- BITDOG
- MAND
- NIB
- SALTY
- $BULL
- BUBL
- BAKENEKO
- RIA
- $COUCH
- HOLI
- STARRI
- ZEUS
- YUGE
- SEALS
- $DREAM
- KONGZ
- $VENTI
- PUB
- PEPE
- MEOWKA
- DONKEE
- MONKEYAI
- PENOSE
- XNF
- ERSDL
- AIPETS
- ENT
- RBIS
- DOKI
- MARE
- SKILL
- WAPE
- CVT
- SIMAI
- OMN
- BULL
- GM
- OJA
- ETHA
- PUPPET
- SARCO
- ALPHADOGE
- BREAK
- GPUL
- DOGB
- ROMEO
- HIM
- JU
- SIBERT
- MTC
- ISLA
- CTO
- MBC
- VIRUS
- SPCTR
- CHILLA
- $MANGA
- MCRN
- SOLA
- RPG
- WIZ
- OUTER
- SIN
- DOCTOR
- CHERRY
- $SLCE
- SMCT
- SOLYMPICS
- YDR
- AIGMX
- BWOB
- CAP
- STAK
- SKYRIM
- 4TOKEN
- KAIA
- UP
- $JBM
- EARLY
- PEPEMAGA
- FUBAO
- $ERNIE
- TXN
- OGLG
- GIGACAT
- ECO
- POODL
- $BLOOD
- PUPPET
- KING
- WIZZIE
- BROOD
- PIPO
- 3D3D
- BNOM
- LILCAT
- CRAFT
- BUIO
- CORTEXZERO
- ERMINE
- DMTC
- PNG
- UARB
- ITA
- BOOF
- FAPCOIN
- PRESS
- WIZARD
- NUKEY
- EDM
- CHAD
- WNETZ
- HERMY
- WOS
- UMINT
- FATCAT
- MEMECUP
- GLAZE
- JRIT
- SOAI
- PEG
- SAI
- ACTP
- DASH
- LEMON
- CSUN
- PUMP
- LIMON
- CROCHET
- DCC
- WOME
- GSLAM
- SED
- FREAK
- JACK
- TISM
- PIPI
- KUMA
- JACK
- 4547
- BIO
- 1984
- BOL
- TOCO
- ETF
- PET
- PSYCAT
- AIDAOVC
- WHISPY
- CHADY
- 777
- CAVIAR
- ORCL
- VRTX
- MOMO V2
- NEWERA
- EDSE
- MIKI
- KING
- SUDO
- SERALPHA
- ITX
- CASH
- ECO
- POP
- SKIBIDI
- ASCIA
- ZAZA
- ORA
- BETA
- ONLYUP
- GEM
- KABAL
- DEGEN
- VERTEX
- MURTIS
- AAAI
- FIRA
- POPNUT
- SLURP
- WIFEAR
- POSHI
- FROSTY
- BALD
- CANGURO
- EGG
- FREG
- HODL
- HAPPYDOG
- SUKI
- CONOR
- AMPLY
- KACY
- $LUMI
- VTRA
- SOLYCAT
- ROCK
- UNREAL
- APED
- VIVEK
- PING
- EYZ
- SKATECAT
- HORNT
- XP
- ALOT
- $CROCO
- $ROFL
- CLICK
- MOJI
- CNB
- $SHEESH
- JET
- PEPIG
- GOLDN
- FINDME
- WINSTON
- NOSE
- DUCKEY
- ANGRYGUY
- SMORE
- KRPZA
- TESOURO
- OP
- ECT
- BURNT
- BSOV
- CUTE
- WARS
- FUKUROU
- WOLT
- LS
- COOL
- HOTDOGE
- TYPEN
- EQU
- $ILENCE
- SBABE
- CHI
- LAWN
- TYLER
- ATROFA
- WILLY
- $WIF2
- GTM
- INFC
- GFN
- BAOLONG
- PCAT
- ERB
- $MAX
- PLUTO
- PEW
- BXNF
- MGOD
- LGCY
- KAPI
- PONZIO
- MOON
- FLY
- LEONAI
- WTC
- XTE
- SASHA
- JOOPS
- IAI
- LIDYA
- KEK
- MOZART
- ROSIE
- KOZUE
- CHAT
- KURO
- METADOGE
- $WAIFU
- TRONARMY
- LOLCAT
- K
- MOFI
- HCAT
- $HOPE
- NOAI
- HABI
- TGPU
- MATRIX
- ISKY
- SQUARES
- PLN
- EGGY
- EMOTI
- $GODFATHER
- RETARD
- QRK
- VOID
- $CATA
- GIZMO
- MNTA
- HAZEL
- MCBROKEN
- CHED
- DISKNEE
- ETHFAI
- CHARLIE
- BRUCE
- BAOBAO
- DIF
- MM
- REIKO
- OPRV
- BBYDEV
- COCO
- GOLC
- DOGGO
- NUM
- CHILLA
- BARK
- SHAKE
- $PIVOT
- ORB
- DFAI
- HUB
- LICKER
- TOKI
- MOVEZ
- KOL
- $INSORA
- WENIS
- IUX
- DWAKE
- LONG
- LENNI
- SIGHT
- GVR
- RPG
- 0XP
- WORK
- BG
- SOON
- WADU
- GACHA
- BOLGUR
- STRESSGUY
- NEXEA
- PEEP
- MOJO
- PHILLIP
- FEG
- PITTY
- GEN
- POLAR
- TARO
- $VIBE
- LAIFU
- KITTEN
- RIVUS
- KYRA
- FLAME
- PUNGU
- YUNKI
- PWOT
- CRY
- NEBULA
- RICE
- DANK
- SMH
- GUGU
- $LOLA
- SGLY
- FAT
- $ωMσGA
- TMFT
- DEKOPON
- DONK
- MIGRAINE
- MINTYGIRL
- TRIANGLE
- DIGGAI
- MARSHALL
- BONG
- STARS
- MOSHI
- $BUN
- NOO
- $OCCER
- AG
- URMOM
- ODIN
- CERBER
- NRC
- GENESIS
- CYCE
- KGC
- UFIL
- ACTII
- ALMAN
- APED
- AIRENA
- WIMPO
- FROP
- DCT
- SNARC
- LTT
- IRS
- KIMCHI
- L
- TOLYCAT
- NFTS
- WAGIE
- SPIX
- ONIGCHI
- BOB
- JILLBODEN
- EPOCH
- TODD
- WEN
- BITARD
- SWAN
- BONKEY
- PJ
- CUMS
- BCI
- BURGIIR
- $BLK
- BILLI
- NOTDOG
- APOW
- PAMP
- $BIRDIE
- SHNJ
- GLUB
- SHADOAI
- CZOL
- ZECK
- MIMAS
- ZERESCAN
- SENDR
- MOOTUN
- NORM
- GLOOM
- $SQUISH
- CHRYSTAL
- GDOG
- TWINNY
- CHADAI
- CHILLWHALE
- PELICAN
- VAI
- BSPT
- AMAI
- GOOSE
- PEWPEW
- MAGIC
- GIC
- VOTEDOGE
- ROK
- NOM
- FUG
- IF
- FCAT
- PEPCAT
- CROAK
- ALDIN
- SHARP
- SQRB
- AST
- MOLLY
- CANCER
- SWAGGY
- SFAI
- ISEC
- TENDIE
- FITT
- IUSDC
- HACK
- ORION
- POLY
- MOON
- KRATOM
- MOON
- RAINBOW
- XTCASH
- BLOOP
- BIC
- MEEB
- PKIN
- FUM
- CROISSANT
- ASTA
- BIAO
- FREEDOM
- CRINGE
- TOOT
- UWU
- LOAF
- BLUE
- LBW
- BABYP
- PEPEK
- CHOLO
- CRAZY
- DWOG
- BOT
- CHECKR
- CGF
- CTAX
- LOAF
- GIRLS
- GM
- MOB
- MAGIC
- NOD
- OIACAT
- SPURDO
- BLUE
- JUMP4EVER
- RYNO
- HCAT
- KLEIN
- DAIO
- PIGGA
- KINI
- DGEN
- BOP
- ASAFE
- AGSYS
- DECATS
- FROGGY
- GGAINS
- 2025
- HAKU
- WHC
- GARGOYLE
- OGAI
- PEPEWFPORK
- DWOLF
- TRM
- CLAUDE 2
- MOO
- UHOSU
- PRTCLE
- NODEV
- POU
- GBTC
- TITAN
- BULLCAT
- GONG
- MEN
- FINE
- SPOON
- BOBA
- NML
- MOON
- DOCTOR
- POPFROG
- MGGA
- YURO
- PEPINU
- LPP
- TDT
- TWOOD
- $NUKUMUTU
- EVIN
- PUSH
- SASHA
- PEPEZ
- FSC
- FIRA
- DRAKO
- PUMP
- SAF
- YEET
- DCA
- FINDER
- $BITB
- YOOMI
- KAKA
- ALPACA
- FRKT
- $COST
- RUNNER
- BBAXOL
- TETHER
- IWBTC
- RIZZMASEVE
- BUBBLU
- VRN
- CRX
- ADEL
- CORX
- BOOK
- FORKY
- MICU
- MX
- KAPSEL
- RAT
- CHENG
- NEB
- LIFE
- SLOW
- RGP
- MONKIE
- WEEBS
- BELUGA
- DUKIE
- DERMO
- ONAI
- DOX
- RUGRAT
- REGRET
- GRACIE
- BAND
- LFDOG
- GINGER
- AINAL
- ACM
- ABCDE
- SMOL
- TSU
- DWOG
- $SCANNING
- MLNR
- ROLLIE
- LARPAI
- SCALEX
- KOOKY
- $SPOT
- CTT
- AXIAL
- NAME
- SANTAPEPE
- STANK
- CT100
- HOMELESS
- UPX
- PIZA
- RE7USDC
- TOBY
- SOR
- $LILY
- TUB
- APET
- HYRAX
- APE
- MD
- GG
- AFEN
- BRRRIAN
- SPACE
- FLYCAT
- CHUMP
- NYANDOGE
- DEPIN
- SFX
- ELE
- AVI
- WRINKLE
- DOGM
- NIPZ
- AVA
- $HACK
- BSL
- ICE
- SAGEL
- FFROG
- ARGY
- MONET
- LOST
- GOLEM
- N.E.R.D
- RBT
- MIRAI
- MSI
- KICHI
- TUNP
- DOGGY
- MAGNUS
- MONKE
- CAESAR
- WOOF
- HYP
- TRIP
- SOLP
- SVN
- FIBER
- EGS
- LUI
- HELLO
- YNBTCK
- STI
- SKYH
- USDT.B
- 1FLR
- WQT
- TURBO
- JES
- OLUMPC
- MCAI
- MUSK
- ZOID
- PUGGY
- SUZAN
- REBEL
- TROOP
- BLACKY
- PSI
- MC
- UCRO
- YARD
- LOADING
- AOK
- TPCAT
- SSOL
- TECH
- FRANK
- DDIM
- PEPECAT
- JAW
- GRWV
- BUDDY
- MAWA
- NOLE
- WORMS
- DOGNUS
- SAO
- UBE
- SMAS
- GARY
- SNV
- TRX
- WIWI
- CHOWIE
- RIZZO
- $WANTED
- CRIP
- WERK
- SAIKO
- ARAI
- SWC
- NUBDOG
- BIR
- CLOWN
- BUNDL
- BRINT
- PEKO
- CRIPPL
- LOS
- TRUFF
- VIPER
- MOLECULAR
- INVIFY
- WAG
- SEAI
- ORO
- EYE
- CDR
- TRN
- $STICKY
- WRAP
- $SODA
- $CLUB
- S
- $🧲6900
- BATYA
- MEVR
- RPD
- APE
- AIS
- ULTRAETHS
- DEG
- CHILLMAS
- FOOKER
- MPAD
- MTK
- SEX
- GORILLA
- MSHARE
- SOLOTH
- TXA
- EZETH
- TME
- MSHIBA
- INME
- MOOND
- META
- APEDOG
- ARIA
- RUBY
- M
- UFET
- LEMON
- DOE
- NRFB
- NANA
- NON
- EGGP
- SXS
- COSMIC
- CRYSTL
- NEXIS
- SING
- RUN
- WIRTUAL
- KINQ
- ROULETTE
- DEXSHARE
- HAPPY
- AGS
- KUNCI
- ALEXIS
- STON
- TRANQ
- MN2
- TSAI
- FIRE
- COW
- NUTZ
- JOSH
- NYANTE
- ROOM
- R1
- ALAI
- WOOLY
- CPOO
- GRASS
- BB
- NET
- OPX
- $DUCKY
- KLAP
- IME
- LANA
- XHV
- LORDZ
- ONI
- VST
- BABY
- CPO
- TRY
- PRMX
- PNUTS
- W3KT
- SWINE
- KURO
- DIAMOND
- BRTR
- BITS
- TOON
- V
- HERB
- DRACE
- PALG
- DDD
- DEGENUSDC
- IDAI
- MC.USD0
- MILK
- PANIC
- VIBE
- DCNT
- FOTA
- FAB
- SHEZUSD
- GMICHI
- UADA
- SLX
- CATT
- USDT
- CRX
- BANANA
- HUSL
- ZM
- ARTR
- RNBW
- SHILL
- 1EARTH
- KFN
- HASBULL
- BABY NEIRO
- FROGEX
- MFTU
- AFN
- AED
- ALL
- AMD
- ANG
- AOA
- ARS
- AUD
- AWG
- AZN
- BAM
- BBD
- BDT
- BGN
- BHD
- BIF
- BMD
- BND
- BOB
- BRL
- BSD
- BYN
- BYR
- BTC
- CLF
- BTN
- BZD
- CHF
- CUC
- CAD
- CRC
- CLP
- DKK
- CUP
- CNY
- DJF
- ETB
- DOP
- CVE
- ERN
- GEL
- EUR
- GBP
- GBX
- DZD
- GNF
- GMD
- GGP
- FJD
- HRK
- HNL
- GTQ
- IMP
- GHS
- ILS
- ILA
- HTG
- JEP
- ISK
- INR
- KGS
- GYD
- KES
- BWP
- JMD
- HUF
- KRW
- KWD
- KHR
- LKR
- LBP
- IQD
- CDF
- KYD
- LYD
- LVL
- COP
- MMK
- JOD
- LRD
- MKD
- KMF
- MVR
- CZK
- MAD
- MUR
- KZT
- MNT
- EGP
- MZN
- NAD
- LSL
- FKP
- MWK
- NPR
- NZD
- GIP
- MDL
- NGN
- PHP
- HKD
- MOP
- OMR
- PGK
- RON
- IDR
- PKR
- MXN
- SBD
- QAR
- NIO
- RSD
- IRR
- SAR
- SHP
- SCR
- JPY
- PAB
- SLL
- SGD
- SVC
- PLN
- KPW
- SYP
- STD
- TMT
- RUB
- LAK
- TND
- TJS
- TWD
- SDG
- LTL
- TZS
- TTD
- UYU
- SOS
- USD
- USX
- UZS
- MGA
- WST
- VUV
- XAF
- MRO
- XDR
- SZL
- XCD
- TOP
- MYR
- ZMK
- UAH
- ZAR
- ZAc
- XOF
- NOK
- VEF
- ZMW
- XAG
- PEN
- XPF
- PYG
- ZWL
- RWF
- SEK
- SRD
- THB
- TRY
- UGX
- VND
- XAU
- YER
- SLE
- VES
- SSP
- MRU
- CNH
What is Cardano (ADA)? The Revolutionary Blockchain Platform Explained
Cardano (ADA) is a third-generation blockchain platform that emerged in 2017 as a groundbreaking solution to the scalability, interoperability, and sustainability challenges faced by earlier cryptocurrencies. Founded by Charles Hoskinson, a co-founder of Ethereum, Cardano distinguishes itself through its research-driven approach and rigorous academic peer review process. The platform’s core mission is to redistribute power from unaccountable structures to individuals, fostering positive change and progress in the global financial landscape. Unlike many of its predecessors, Cardano utilizes a unique proof-of-stake consensus mechanism called Ouroboros, which significantly reduces energy consumption compared to proof-of-work systems. This innovative protocol enables Cardano to process transactions more efficiently while maintaining a high level of security.
Key Features of Cardano
Cardano’s architecture is built on a layered protocol that separates accounting and computation, allowing for greater flexibility and easier upgrades. The platform supports smart contracts through its Plutus scripting language and facilitates the creation of decentralized applications (dApps) via its Marlowe domain-specific language. Cardano’s native cryptocurrency, ADA, named after the 19th-century mathematician Ada Lovelace, serves as both a digital currency and a means to interact with the platform’s various features.
Cardano’s Developmental Stages
The development of Cardano follows a meticulously planned roadmap divided into five eras:
- Byron: Foundation of the network
- Shelley: Decentralization and staking
- Goguen: Smart contract functionality
- Basho: Scaling and optimization
- Voltaire: Governance and treasury system
As of 2025, Cardano has successfully implemented smart contracts and is actively working on scaling solutions and governance mechanisms. With its commitment to scientific rigor, sustainability, and scalability, Cardano aims to become a leading platform for financial and social applications on a global scale, potentially revolutionizing industries ranging from finance and healthcare to supply chain management and digital identity verification.

The Technology Behind Cardano: Ouroboros and Proof-of-Stake Demystified
At the core of Cardano’s innovative blockchain architecture lies Ouroboros, the first provably secure proof-of-stake (PoS) protocol. Developed through rigorous academic research, Ouroboros represents a significant leap forward in blockchain technology, offering enhanced security, scalability, and energy efficiency compared to traditional proof-of-work systems. This protocol divides time into epochs, which are further subdivided into slots. Each slot has a designated slot leader, chosen through a lottery-like system based on stake distribution, responsible for creating and validating new blocks.
Key Features of Ouroboros
1. Mathematically Verifiable Security: Ouroboros provides cryptographic proof of its security, ensuring resistance against various types of attacks, including nothing-at-stake and long-range attacks.
2. Energy Efficiency: By eliminating the need for energy-intensive mining operations, Ouroboros consumes only a fraction of the energy required by proof-of-work systems, making Cardano significantly more environmentally friendly.
3. Scalability: The protocol’s design allows for horizontal scaling, enabling the network to process a high volume of transactions without compromising security or decentralization.
4. Fair Reward Distribution: Ouroboros implements a reward-sharing scheme that incentivizes participation and ensures a fair distribution of rewards among stakeholders.
The Proof-of-Stake Mechanism Explained
In Cardano’s PoS system, participants, known as stake pool operators, create pools to which ADA holders can delegate their stake. The probability of a pool being selected to produce a block is proportional to the amount of ADA staked in it. This mechanism not only secures the network but also promotes decentralization by allowing a wide range of participants to contribute to the consensus process.
Stake Delegation and Rewards
ADA holders can participate in the network’s operation and earn rewards by delegating their stake to pools. This process does not require transferring ownership of tokens, ensuring that users maintain control over their assets while contributing to network security. The reward system is designed to incentivize long-term participation and discourage the concentration of power.
| Feature | Ouroboros (PoS) | Traditional PoW |
|---|---|---|
| Energy Consumption | Low | High |
| Scalability | High | Limited |
| Security Model | Mathematically Proven | Empirically Tested |
| Decentralization | Stake-based | Hash Power-based |
Through its implementation of Ouroboros, Cardano has established a foundation for a highly secure, scalable, and sustainable blockchain ecosystem. This technology not only addresses the limitations of earlier blockchain generations but also paves the way for innovative applications in decentralized finance, governance, and beyond.
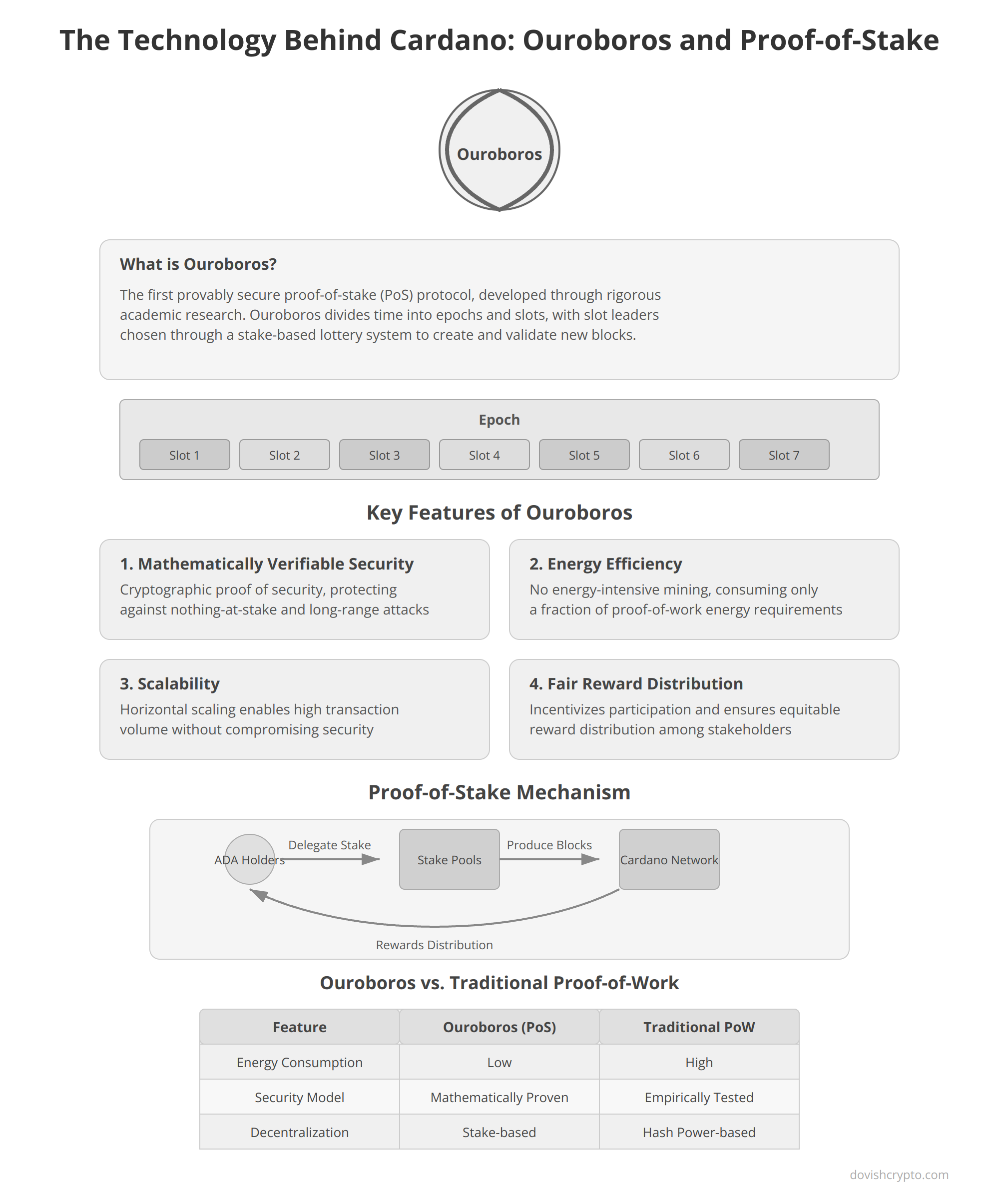
Cardano’s Roadmap: From Byron to Voltaire – Charting the Path to Full Decentralization
Cardano’s development roadmap is meticulously structured into five distinct eras, each named after influential historical figures and designed to address specific aspects of blockchain technology. The journey begins with the Byron era, which established the network’s foundation and introduced the ADA cryptocurrency. Following Byron, the Shelley era marked a significant shift towards decentralization by implementing a proof-of-stake consensus mechanism and enabling community-run stake pools. The Goguen era brought smart contract functionality to Cardano through the Alonzo hard fork, enabling the creation of decentralized applications (DApps) and native tokens. Currently, Cardano is progressing through the Basho era, which focuses on optimizing scalability and interoperability. Key developments in this phase include the implementation of Hydra, a layer-2 scaling solution, and sidechains to enhance network capacity. The final stage, the Voltaire era, aims to establish a fully decentralized governance model, allowing ADA holders to participate in decision-making processes for the network’s future. As of 2024, Cardano has implemented on-chain governance through the Plomin hard fork, introducing Delegate Representatives (dReps) to vote on behalf of ADA holders. The roadmap’s completion will culminate in a self-sustaining, community-driven blockchain ecosystem capable of serving billions of users by 2030.
Cardano Eras and Their Key Features
| Era | Key Features | Status |
|---|---|---|
| Byron | Network foundation, ADA launch | Completed |
| Shelley | Proof-of-stake, stake pools | Completed |
| Goguen | Smart contracts, native tokens | Completed |
| Basho | Scalability, Hydra, sidechains | In progress |
| Voltaire | Decentralized governance, treasury system | Partially implemented |
Future Developments
Looking ahead, Cardano’s roadmap for 2025 and beyond includes ambitious plans to further enhance the network’s capabilities. These include the integration of zero-knowledge rollups, the implementation of Ouroboros Leios and Peras consensus protocols for parallel block creation, and the development of Mithril certificates for efficient transaction verification. Additionally, Cardano aims to improve interoperability through an Inter-Blockchain Communication (IBC) protocol and the introduction of Minotaur, a new consensus mechanism designed for trustless interoperability with other blockchains. The ultimate goal is to position Cardano as a leading blockchain platform capable of supporting a wide range of decentralized applications and services while maintaining its commitment to security, sustainability, and decentralization.
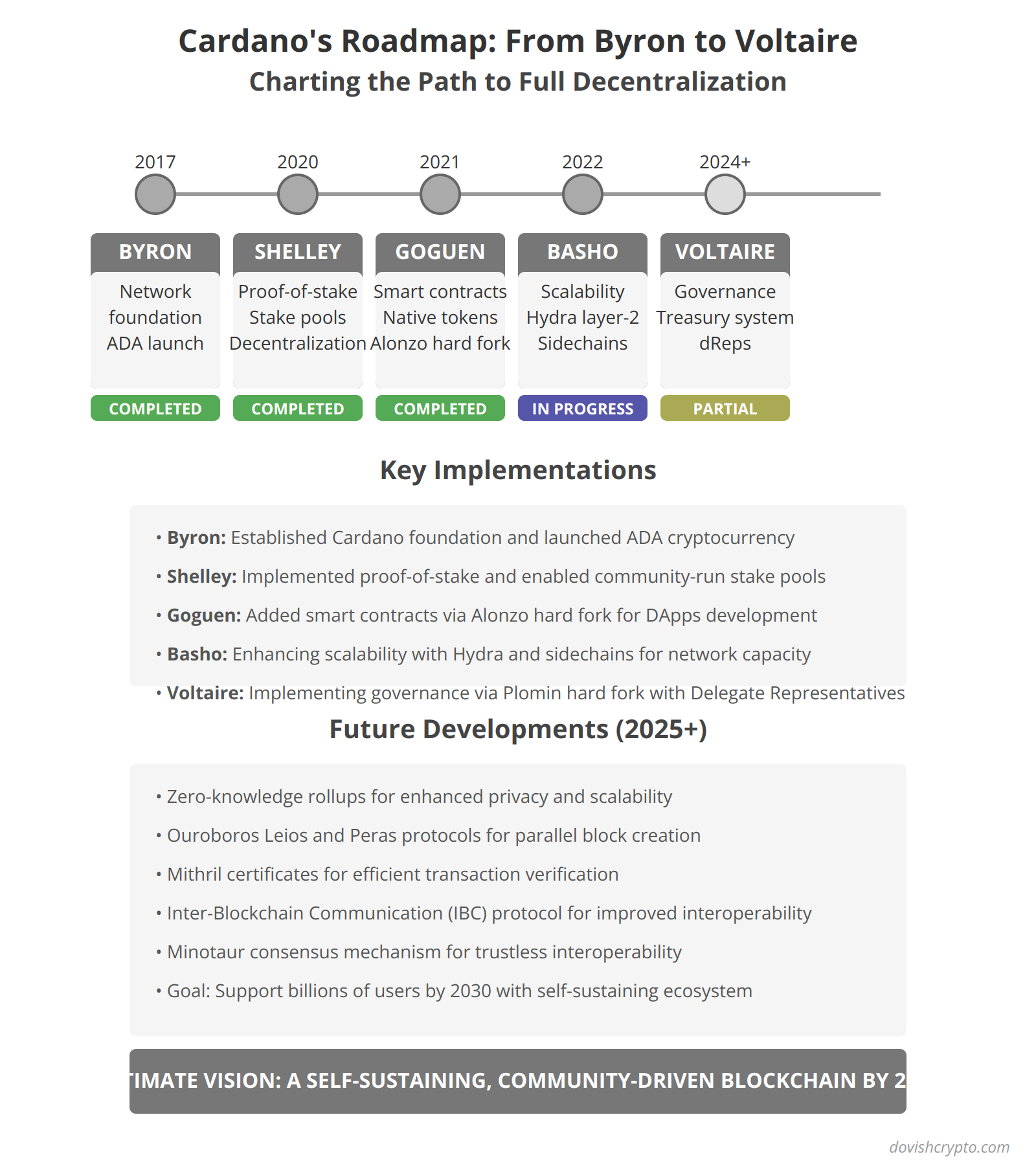
ADA Token: Understanding Cardano’s Native Cryptocurrency and Its Utility
The ADA token, named after mathematician Ada Lovelace, serves as the native cryptocurrency of the Cardano blockchain. As a multi-faceted digital asset, ADA plays a pivotal role within the Cardano ecosystem, offering a range of utilities beyond mere value transfer. Primarily, ADA functions as the medium for transaction fees, ensuring the network’s operational efficiency and security. Cardano’s unique proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, Ouroboros, relies on ADA for staking, allowing token holders to participate in network validation and earn rewards. This process not only secures the blockchain but also promotes decentralization.
ADA’s Diverse Use Cases
ADA’s utility extends to several key areas:
- Governance: ADA holders can participate in on-chain voting, influencing the future development and direction of the Cardano protocol.
- Smart Contracts: With the implementation of smart contract functionality, ADA serves as fuel for executing decentralized applications (dApps) on the Cardano platform.
- Tokenization: The Cardano blockchain supports the creation of native tokens, with ADA playing a crucial role in minting and managing these assets.
- DeFi Operations: As the Cardano ecosystem expands, ADA is increasingly utilized in decentralized finance (DeFi) applications for lending, borrowing, and liquidity provision.
Tokenomics and Supply Dynamics
Understanding ADA’s tokenomics is essential for grasping its long-term value proposition:
- Maximum Supply: ADA has a capped supply of 45 billion tokens, ensuring scarcity and potential value appreciation over time.
- Circulating Supply: As of 2024, approximately 35 billion ADA are in circulation, with the remaining tokens released through a controlled emission schedule.
- Distribution: Initial token distribution occurred through several public sales and strategic partnerships, aiming for a fair and wide distribution.
ADA’s Role in Cardano’s Layered Architecture
Cardano’s unique two-layer architecture comprises the Cardano Settlement Layer (CSL) and the Cardano Computation Layer (CCL). ADA operates primarily on the CSL, facilitating fast and secure transactions, while also interacting with the CCL to enable complex smart contract functionalities. This separation enhances scalability and allows for future upgrades without disrupting the core network operations.
As Cardano continues to evolve through its development roadmap, including the Basho and Voltaire eras, ADA’s utility is expected to expand further. The token’s role in facilitating cross-chain interoperability, powering sidechains, and enabling more sophisticated governance mechanisms underscores its importance in Cardano’s vision of a global, scalable blockchain ecosystem.
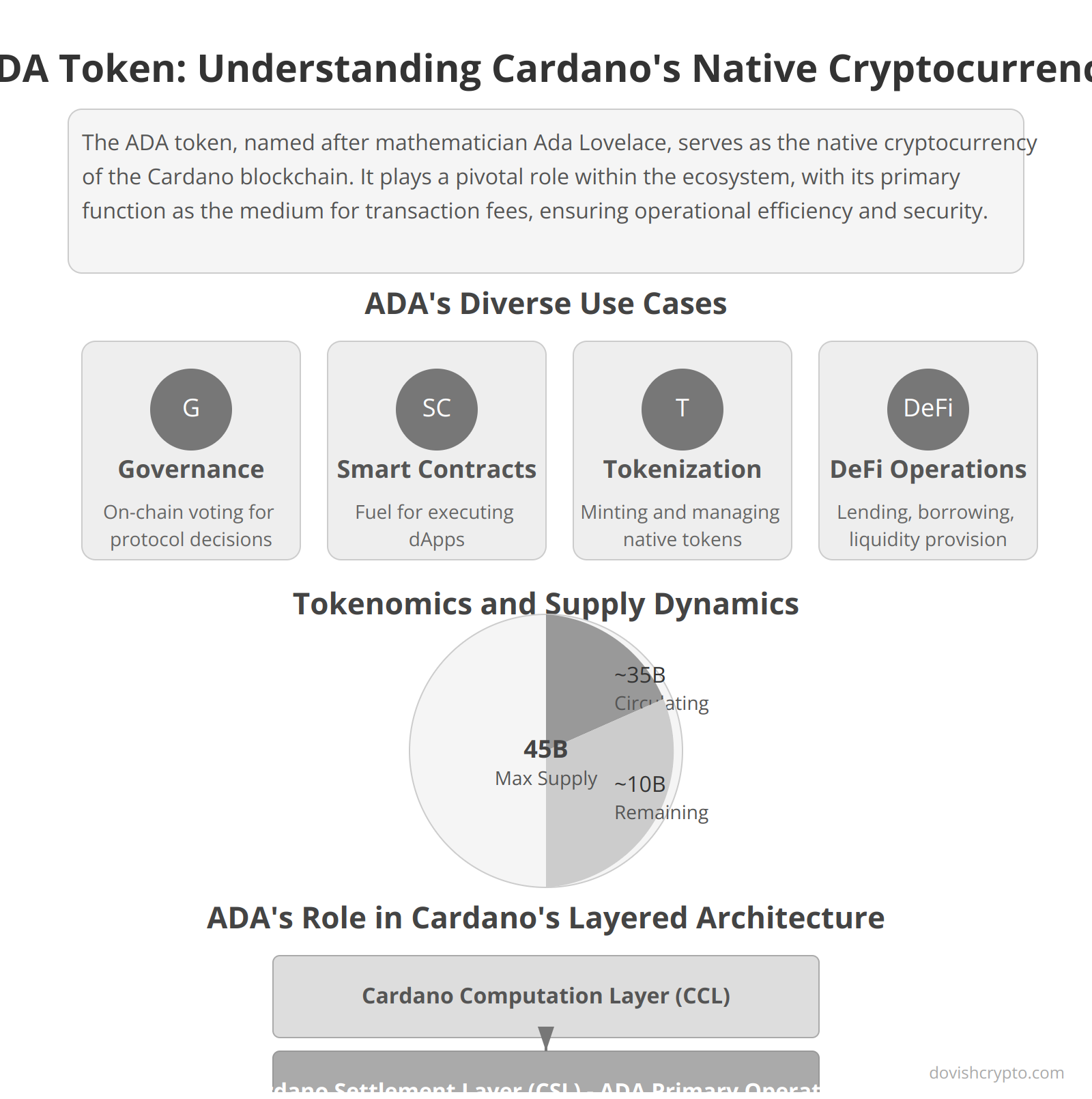
Staking Cardano: Maximizing Your ADA Returns Through Delegation
Staking Cardano (ADA) offers an opportunity to earn passive income while contributing to network security. The process involves delegating ADA tokens to stake pools, which participate in block production and validation. To maximize returns, investors should carefully select stake pools based on performance metrics, fees, and saturation levels. The current average annual percentage yield (APY) for Cardano staking ranges from 3% to 5%, with rewards distributed every epoch (5 days).
Choosing the Right Stake Pool
When selecting a stake pool, consider the following factors:
- Pool Performance: Evaluate the pool’s track record in producing blocks and distributing rewards.
- Fees: Compare fixed costs and variable fees across pools to maximize net returns.
- Saturation: Avoid oversaturated pools (>64 million ADA) as they offer diminishing rewards.
- Pledge: Higher operator pledges often indicate greater commitment and stability.
Staking Process
To stake ADA, follow these steps:
- Set up a Cardano wallet (e.g., Daedalus, Yoroi, or AdaLite).
- Transfer ADA to your wallet.
- Navigate to the staking or delegation section.
- Choose a stake pool and specify the amount to delegate.
- Confirm the transaction and pay the small delegation fee.
Reward Distribution
Staking rewards are automatically added to your delegated balance, compounding your returns. The first rewards appear after 15-20 days, with subsequent rewards distributed every epoch. Importantly, delegated ADA remains liquid and can be withdrawn or spent at any time without a lock-up period.
| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Average APY | 3-5% |
| Reward Frequency | Every 5 days |
| Minimum Stake | 10 ADA |
| Lock-up Period | None |
By carefully selecting stake pools and regularly monitoring performance, ADA holders can optimize their staking strategy and maximize long-term returns while supporting the Cardano network’s decentralization and security.
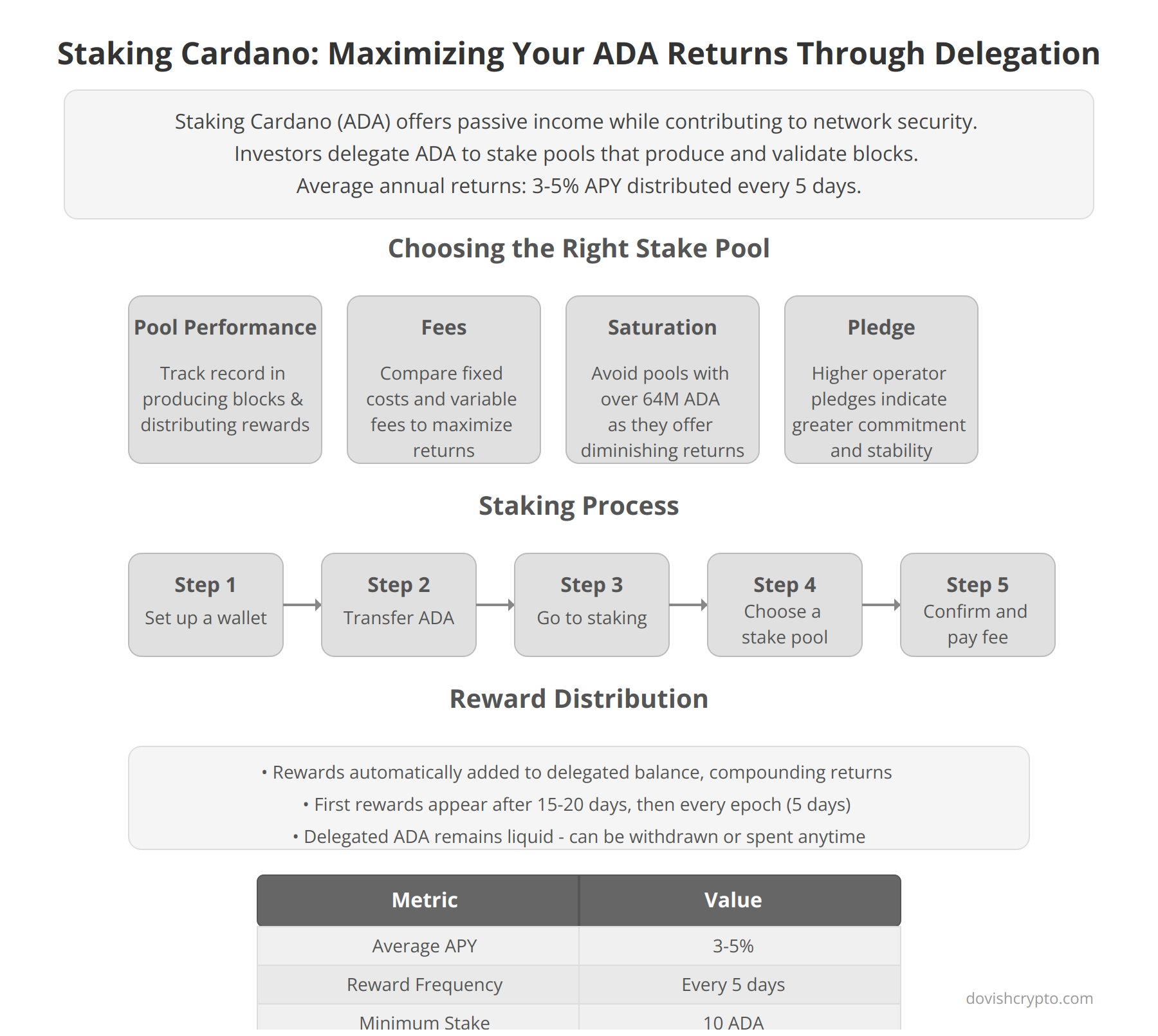
Smart Contracts on Cardano: Unleashing the Power of Plutus
Cardano’s smart contract capabilities have revolutionized the blockchain landscape, with the Plutus platform at the forefront of this innovation. Plutus, a purpose-built smart contract development and execution platform, leverages the robust foundation of Haskell to create secure, efficient, and scalable decentralized applications (dApps). The platform utilizes the Extended Unspent Transaction Output (EUTXO) model, which enhances the traditional UTXO model by allowing more complex script validations and custom data attachments to outputs. This architecture enables deterministic transaction validation, significantly reducing the risk of unexpected fees and failed transactions commonly associated with account-based models.
Key Advantages of Plutus
Plutus offers several distinct advantages over other smart contract platforms:
- Formal Verification: Built on Haskell, Plutus enables rigorous mathematical proofs of contract correctness, enhancing security and reliability.
- Separation of Concerns: Plutus distinguishes between on-chain and off-chain code, allowing for more efficient resource utilization and improved scalability.
- Native Multi-Asset Support: Seamless creation and management of custom tokens without the need for complex smart contracts.
- Cost-Efficiency: The EUTXO model facilitates more predictable transaction costs, benefiting both developers and users.
Plutus Development Ecosystem
The Plutus ecosystem encompasses a comprehensive suite of tools and frameworks:
- Plutus Playground: An interactive, web-based IDE for writing and testing Plutus smart contracts.
- Marlowe: A domain-specific language for financial contracts, simplifying the creation of complex financial instruments.
- Plutus Application Backend (PAB): A framework for building the off-chain components of Plutus applications.
Smart Contract Capabilities
Plutus enables a wide range of smart contract functionalities, including:
- Decentralized Finance (DeFi) protocols
- Non-Fungible Token (NFT) minting and management
- Decentralized Autonomous Organizations (DAOs)
- Supply chain tracking and verification
- Governance and voting systems
As of 2025, the Cardano ecosystem has witnessed exponential growth, with over 5,000 smart contracts deployed and a Total Value Locked (TVL) exceeding $10 billion. This rapid adoption underscores the robustness and versatility of the Plutus platform, positioning Cardano as a formidable contender in the blockchain space.
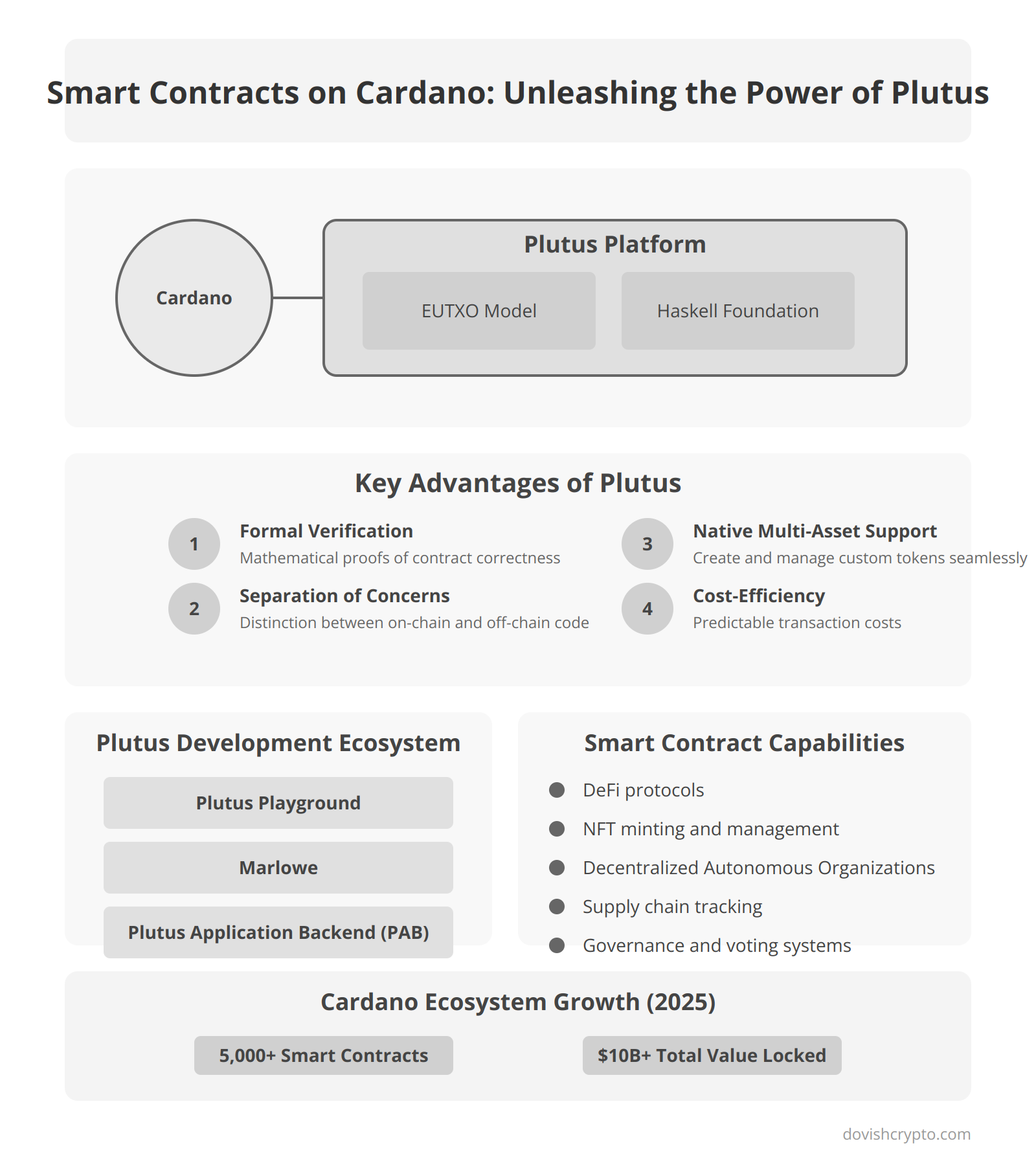
Cardano vs. Ethereum: A Comprehensive Comparison of Blockchain Titans
Cardano and Ethereum stand as two of the most prominent blockchain platforms in the cryptocurrency ecosystem, each offering unique approaches to decentralized technology. While Ethereum has long been the leader in smart contract functionality and decentralized application (dApp) development, Cardano has emerged as a formidable competitor with its research-driven approach and focus on sustainability.
Consensus Mechanisms
Ethereum’s transition from Proof-of-Work (PoW) to Proof-of-Stake (PoS) through the Ethereum 2.0 upgrade aims to address scalability and energy efficiency concerns. Cardano, on the other hand, implemented its Ouroboros PoS protocol from inception, offering enhanced energy efficiency and theoretically higher transaction throughput.
Smart Contract Capabilities
Ethereum’s smart contracts, powered by the Solidity programming language, have been the industry standard for years. Cardano’s introduction of smart contracts through the Alonzo hard fork in 2021 brought Plutus, a Haskell-based language, offering formal verification for enhanced security and reliability.
Scalability and Transaction Speed
Ethereum currently processes approximately 15-30 transactions per second (TPS), with plans to significantly increase this through sharding and Layer 2 solutions. Cardano’s layered architecture allows for theoretical speeds of up to 250 TPS, with further improvements planned through the Hydra scaling solution.
Development Philosophy
Ethereum follows an agile development approach, rapidly iterating and adapting to market demands. Cardano adheres to a rigorous, peer-reviewed academic process, prioritizing thorough testing and formal methods before implementation.
Ecosystem and Adoption
Ethereum boasts a vast ecosystem of dApps, DeFi protocols, and NFT platforms, with over 3,000 dApps and a Total Value Locked (TVL) exceeding $50 billion. Cardano’s ecosystem is growing, with over 1,000 projects in development and a TVL of approximately $200 million as of early 2025.
| Metric | Ethereum | Cardano |
|---|---|---|
| Consensus Mechanism | PoS (post-merge) | PoS (Ouroboros) |
| Smart Contract Language | Solidity | Plutus |
| Transaction Speed | 15-30 TPS | 250 TPS (theoretical) |
| Ecosystem Size | 3,000+ dApps | 1,000+ projects |
| TVL (2025) | $50+ billion | $200 million |
While Ethereum maintains its position as the leading smart contract platform, Cardano’s methodical approach to development and focus on academic rigor position it as a strong contender in the blockchain space. The choice between these two titans ultimately depends on specific use cases, development preferences, and long-term scalability requirements.
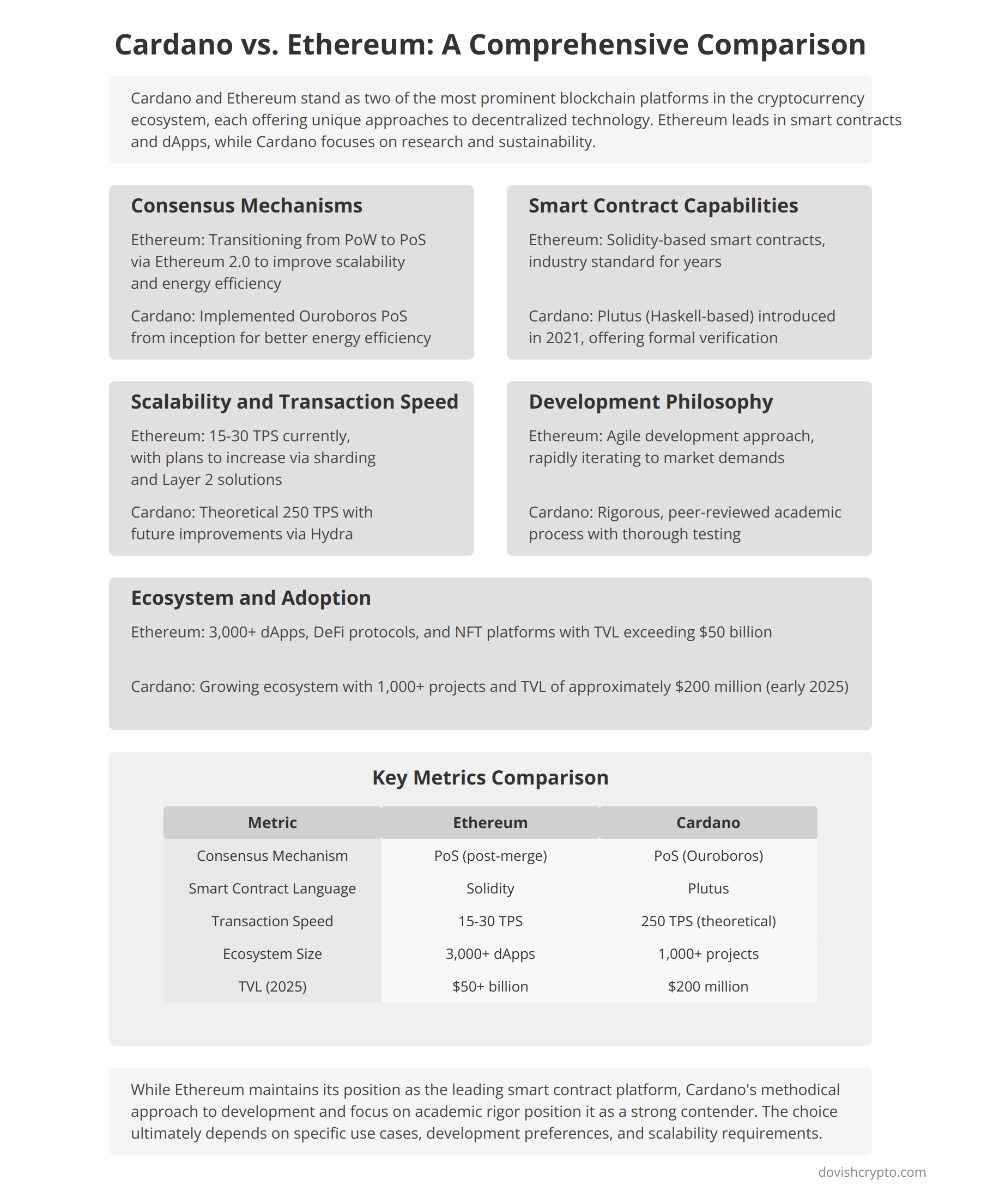
The Cardano Ecosystem: DApps, NFTs, and DeFi Projects Building on ADA
The Cardano ecosystem has experienced significant growth since the introduction of smart contract functionality in September 2021, with a diverse array of decentralized applications (DApps), non-fungible tokens (NFTs), and decentralized finance (DeFi) projects leveraging the blockchain’s capabilities. As of March 2025, over 1,000 projects are actively building on Cardano, spanning various sectors and use cases.
DeFi Landscape
Cardano’s DeFi sector has witnessed substantial expansion, with total value locked (TVL) surpassing $2 billion. Notable projects include:
- MinSwap: A leading decentralized exchange (DEX) with over $500 million in TVL
- Liqwid Finance: A lending and borrowing protocol boasting $300 million in TVL
- Indigo Protocol: A synthetic assets platform with $150 million locked
NFT Ecosystem
The Cardano NFT market has flourished, with unique collections and marketplaces emerging:
- JPG Store: The largest NFT marketplace on Cardano, facilitating over $100 million in trading volume
- Pavia: A metaverse project with virtual land parcels as NFTs
- Clay Nation: A popular generative art collection with celebrity collaborations
Innovative DApps
Cardano hosts a variety of innovative applications across different sectors:
- World Mobile: A telecommunications project aiming to connect the unconnected in Africa
- Atala PRISM: A decentralized identity solution for governments and enterprises
- Empowa: A real estate tokenization platform focused on affordable housing in emerging markets
Ecosystem Growth Metrics
| Metric | Value (as of March 2025) |
|---|---|
| Total DApps | 1,000+ |
| Daily Active Users | 500,000+ |
| Monthly Transaction Volume | $5 billion+ |
The Cardano ecosystem continues to expand rapidly, with new projects leveraging the blockchain’s scalability, interoperability, and sustainability features. As the platform matures, it is attracting increased attention from developers, investors, and enterprises seeking to build innovative solutions on a robust and research-driven blockchain infrastructure.
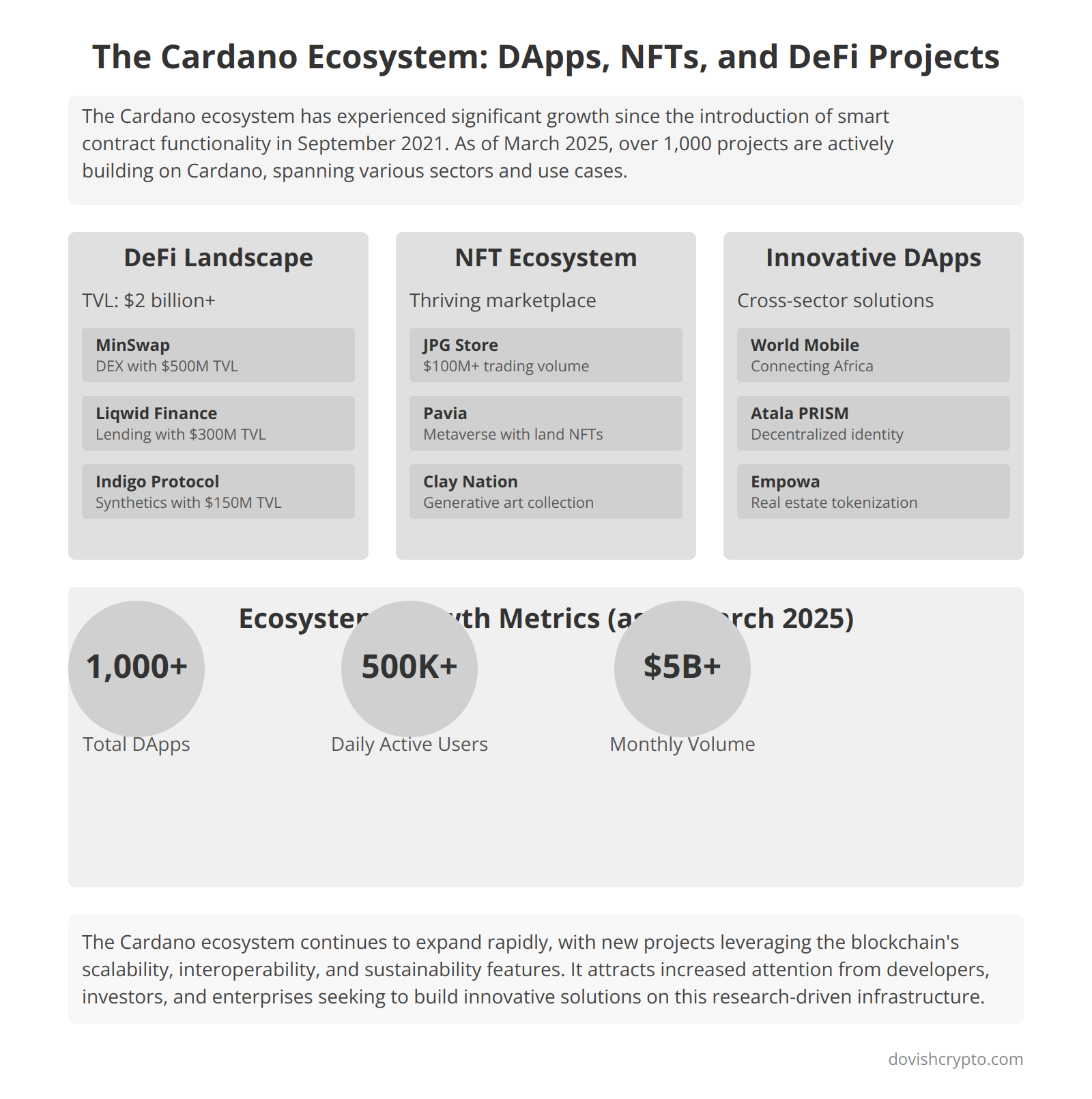
Investing in Cardano: Strategies, Risks, and Long-Term Potential
Investing in Cardano (ADA) requires a comprehensive understanding of its market dynamics, technological foundations, and potential for growth. As of March 2025, Cardano has demonstrated significant resilience, with its price hovering around $0.90, reflecting a 14.88% increase over the past year. The cryptocurrency’s market capitalization stands at approximately $27.37 billion, positioning it as the 8th largest digital asset globally. Investors considering ADA should be aware of its unique proof-of-stake consensus mechanism, Ouroboros, which offers enhanced energy efficiency and scalability compared to traditional proof-of-work systems.
Investment Strategies
When approaching Cardano investments, consider the following strategies:
- Dollar-Cost Averaging (DCA): Regularly purchasing small amounts of ADA to mitigate market volatility risks.
- Staking: Participating in Cardano’s proof-of-stake system to earn passive income, with current annual yields averaging 4-5%.
- Long-term Holding: Capitalizing on Cardano’s potential for appreciation as its ecosystem expands and adoption increases.
Risk Assessment
Investors must be cognizant of the following risks:
- Market Volatility: Cryptocurrency markets are known for rapid price fluctuations, with ADA experiencing a 52-week range of $0.31 to $1.23.
- Regulatory Uncertainty: Evolving global cryptocurrency regulations may impact Cardano’s adoption and value.
- Competition: Rival blockchain platforms like Ethereum and Solana pose ongoing competitive challenges.
- Technical Risks: Potential vulnerabilities in smart contract implementations or network upgrades could affect ADA’s stability.
Long-Term Potential
Cardano’s long-term potential is underpinned by several factors:
- Technological Advancements: Ongoing development of scalability solutions like Hydra, aiming to process millions of transactions per second.
- Institutional Adoption: Increasing interest from institutional investors, potentially driving demand and price appreciation.
- Real-World Applications: Expanding use cases in sectors such as supply chain management, education, and decentralized finance (DeFi).
- Sustainability Focus: Cardano’s energy-efficient design aligns with growing environmental concerns in the crypto space.
Price Projections
| Year | Conservative Estimate | Optimistic Estimate |
|---|---|---|
| 2025 | $1.40 | $3.11 |
| 2027 | $3.40 | $5.50 |
| 2030 | $5.50 | $10.32 |
While these projections offer insight, investors should approach them cautiously and conduct thorough due diligence. Cardano’s future success hinges on its ability to deliver on technological promises, foster widespread adoption, and navigate the complex regulatory landscape of the cryptocurrency market.

Cardano Wallets: Securing Your ADA with Top Storage Solutions
Securing Cardano (ADA) tokens requires careful consideration of wallet options, as the choice of storage solution significantly impacts the safety and accessibility of digital assets. Cardano offers a diverse ecosystem of wallets, catering to various user needs and security preferences. Hardware wallets like Ledger Nano X and Trezor Model T provide the highest level of security by storing private keys offline, making them ideal for long-term ADA storage. For daily transactions and staking, software wallets such as Daedalus, Yoroi, and Eternl offer user-friendly interfaces with robust security features. Daedalus, the full-node wallet developed by IOHK, ensures complete blockchain validation but requires significant system resources. Yoroi, a light wallet, offers faster access and mobile support. Eternl (formerly CCVault) has gained popularity for its advanced features and dApp integration capabilities.
Key Security Measures for ADA Storage
To maximize the security of ADA holdings, users should adhere to the following best practices:
- Generate and securely store wallet recovery phrases offline
- Enable two-factor authentication when available
- Regularly update wallet software to patch security vulnerabilities
- Use hardware wallets for large ADA holdings
- Verify recipient addresses before initiating transactions
- Avoid sharing private keys or recovery phrases with anyone
Comparison of Popular Cardano Wallets
| Wallet | Type | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Ledger Nano X | Hardware | Offline storage, Bluetooth connectivity |
| Daedalus | Software (Full Node) | Complete blockchain validation, staking support |
| Yoroi | Software (Light) | Fast, mobile-friendly, browser extension |
| Eternl | Software (Web/Extension) | Advanced features, dApp integration |
By carefully selecting a wallet that aligns with individual security needs and usage patterns, Cardano users can significantly enhance the protection of their ADA tokens while maintaining the flexibility to participate in the expanding Cardano ecosystem. Regular security audits and staying informed about the latest developments in wallet technology are crucial for maintaining the integrity of ADA holdings in an ever-evolving crypto landscape.
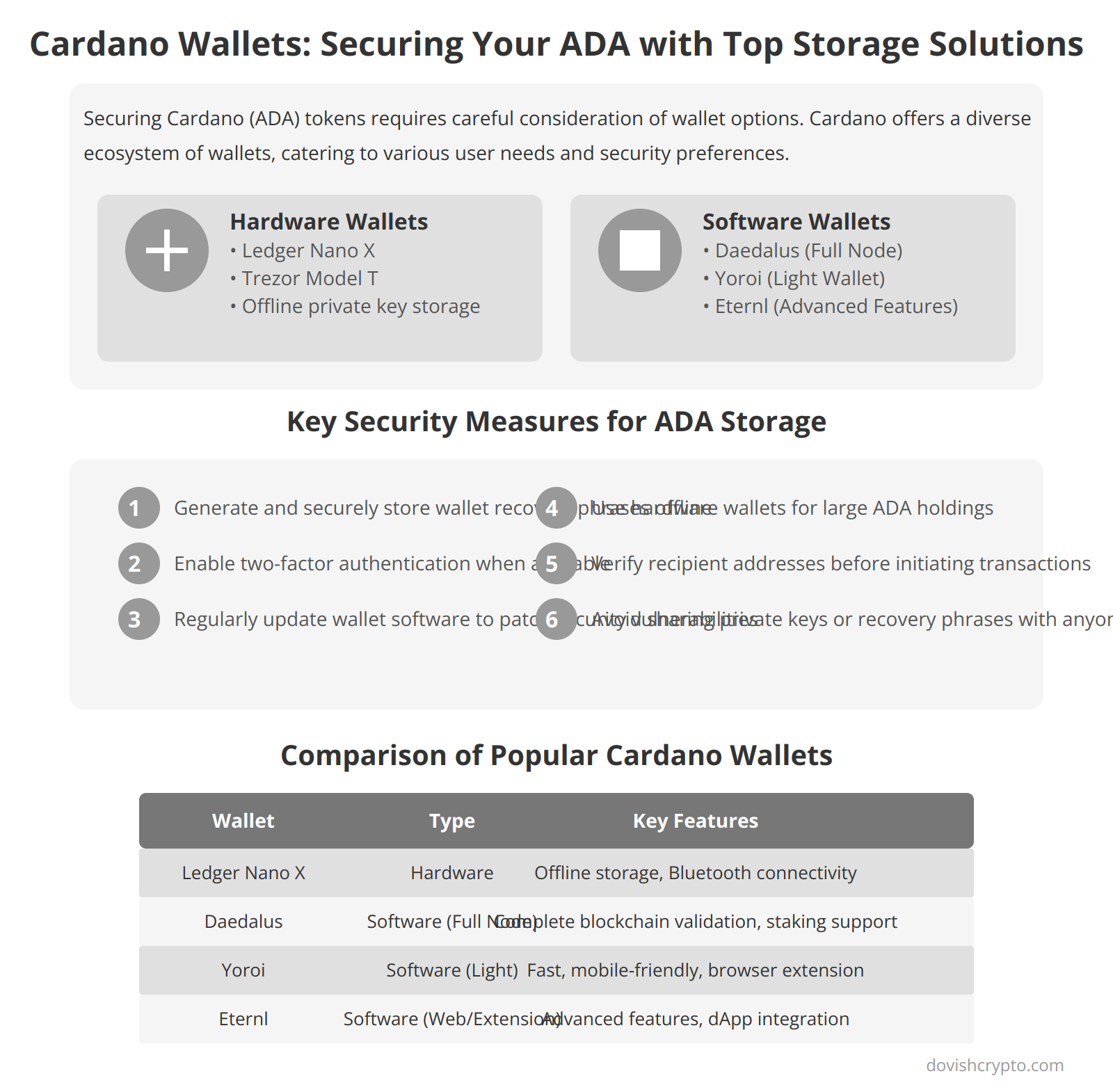
Cardano’s Environmental Impact: The Green Blockchain Revolution
Cardano stands at the forefront of the green blockchain revolution, showcasing remarkable energy efficiency and environmental sustainability compared to other blockchain networks. The platform’s innovative Ouroboros proof-of-stake (PoS) consensus mechanism significantly reduces energy consumption, consuming only 0.5479 kWh per transaction. This stark contrast to Bitcoin’s 707 kWh and Ethereum’s pre-merge 62.5 kWh per transaction highlights Cardano’s commitment to eco-friendly blockchain technology. The network’s annual energy consumption is estimated at a mere 6 GWh, equivalent to the power usage of only 600 average homes. Cardano’s sustainability efforts extend beyond its core protocol, with initiatives like the Cardano Forest project aiming to plant over 1 million trees globally. Furthermore, the platform’s layered architecture and scalability solutions contribute to maintaining low energy requirements even as transaction volumes increase.
Comparative Energy Efficiency
| Blockchain | Energy per Transaction (kWh) | Annual Energy Consumption (TWh) |
|---|---|---|
| Cardano | 0.5479 | 0.006 |
| Bitcoin | 707 | 127 |
| Ethereum (pre-merge) | 62.5 | 74.6 |
Cardano’s environmental credentials are further bolstered by its research-driven approach, which prioritizes sustainable development and long-term viability. The platform’s commitment to peer-reviewed scientific research ensures that all protocol upgrades and enhancements are thoroughly vetted for their environmental impact. This methodical approach has resulted in Cardano being recognized as one of the most sustainable blockchain networks in the industry. Additionally, Cardano’s native token, ADA, has been praised for its energy-efficient staking mechanism, which allows holders to participate in network security without the need for energy-intensive mining equipment.
Sustainability Initiatives
Beyond its core technology, Cardano actively promotes sustainability through various initiatives:
- The Cardano Forest project, aiming to offset carbon emissions through global reforestation efforts
- Partnerships with renewable energy providers to power blockchain operations
- Development of eco-friendly dApps and NFT platforms within the Cardano ecosystem
- Collaboration with environmental organizations to leverage blockchain for conservation efforts
As the blockchain industry faces increasing scrutiny over its environmental impact, Cardano’s green credentials position it as a leader in sustainable distributed ledger technology. The platform’s ability to maintain high security and decentralization while minimizing energy consumption sets a new standard for environmentally responsible blockchain networks, paving the way for widespread adoption of green crypto solutions.
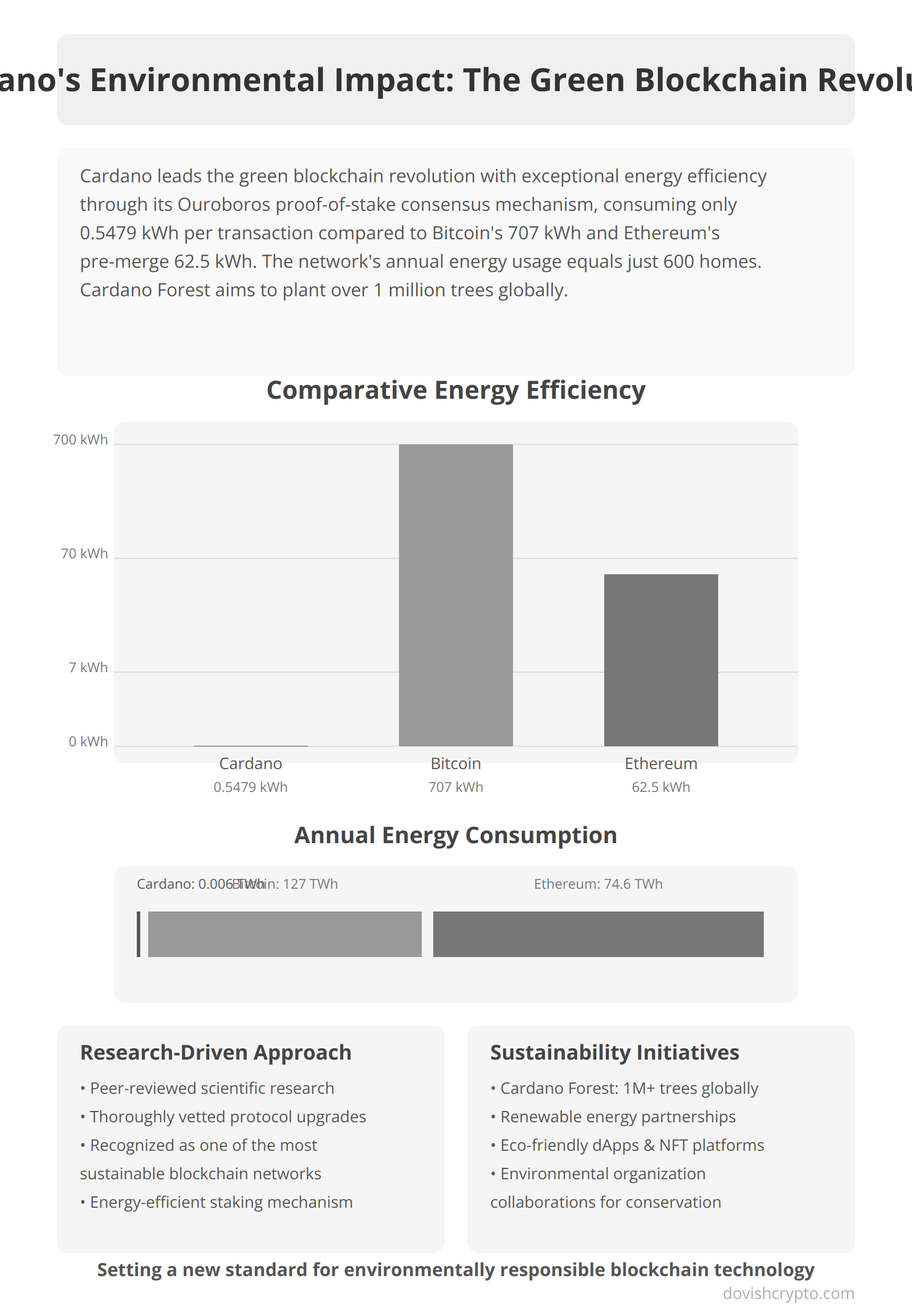
Cardano FAQ: Your Burning Questions About ADA Answered
Frequently Asked Questions About Cardano (ADA)
To address common inquiries about Cardano, we’ve compiled a comprehensive FAQ section using schema.org microdata for enhanced search engine visibility:
What is Cardano (ADA)?
Cardano is a third-generation, proof-of-stake blockchain platform designed to be more scalable, sustainable, and interoperable than its predecessors. ADA is Cardano’s native cryptocurrency, named after Ada Lovelace, a 19th-century mathematician.
How does Cardano differ from other cryptocurrencies?
Cardano distinguishes itself through its research-driven approach, utilizing peer-reviewed academic research to inform its development. It employs a unique proof-of-stake consensus mechanism called Ouroboros, which is more energy-efficient than proof-of-work systems.
What is the maximum supply of ADA tokens?
The maximum supply of ADA is capped at 45 billion tokens. As of 2025, approximately 35 billion ADA are in circulation, with the remaining tokens to be released gradually through staking rewards and ecosystem development initiatives.
What are Cardano’s key features for 2025?
Cardano’s 2025 roadmap focuses on three pillars: scalability, usability, and interoperability. Key features include Layer 2 Hydra state channels, zero-knowledge rollups, Ouroboros Leios and Peras consensus protocols, and enhanced governance mechanisms through the Voltaire era.
How can I stake ADA?
ADA can be staked directly from compatible wallets like Daedalus or Yoroi. Users delegate their ADA to stake pools, earning rewards for supporting network security. The current estimated annual reward rate for staking ADA ranges between 5% and 6%, with no lockup period required.
This FAQ section provides essential information about Cardano’s unique features, tokenomics, and future developments, addressing key points of interest for both newcomers and experienced cryptocurrency enthusiasts. The use of schema.org microdata enhances the visibility of this content in search engine results, potentially improving the article’s SEO performance.