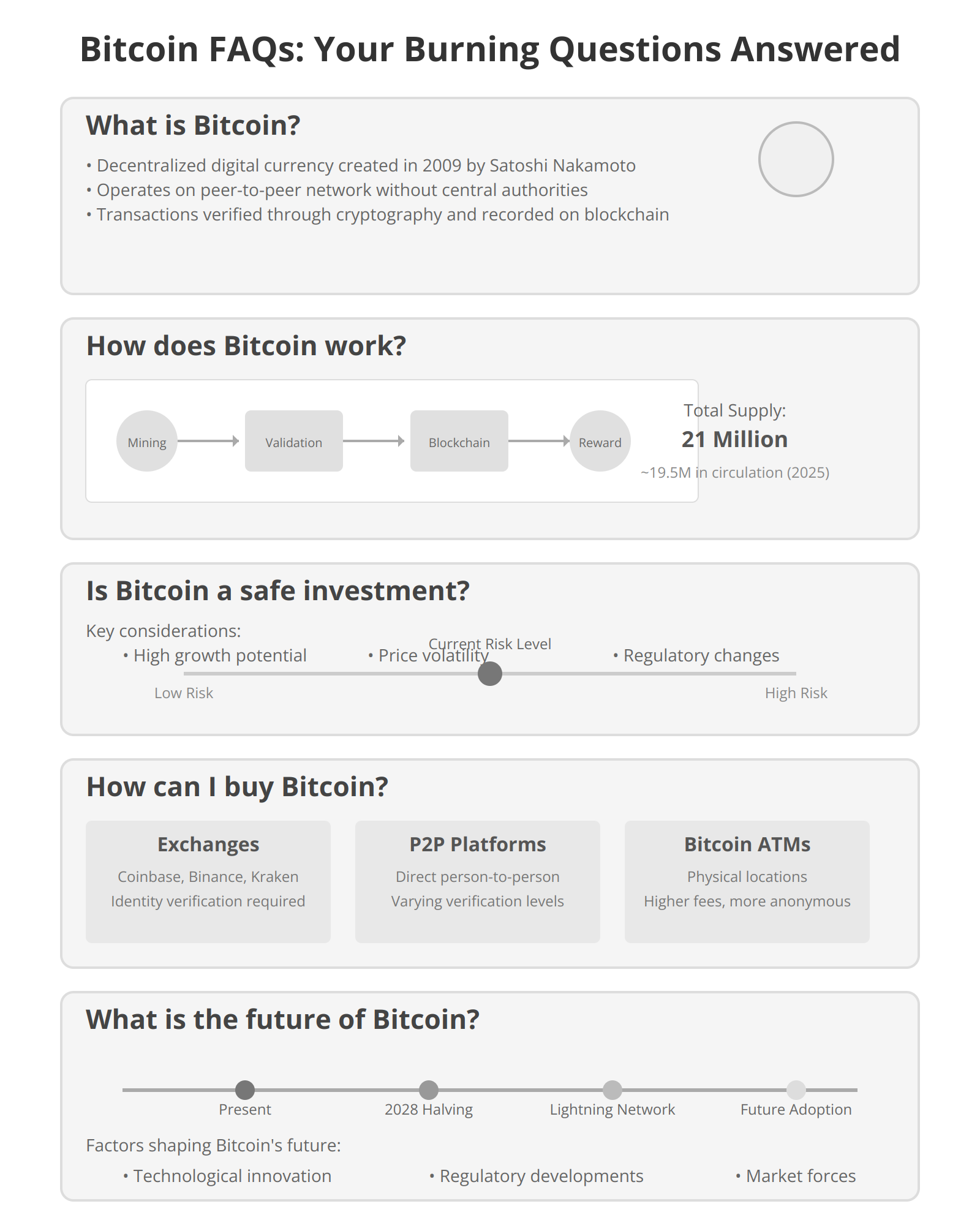
- Zoom
- Type
Table of Contents
Where to buy Bitcoin?
| # | Source | Pair | Volume | Price | Change | Updated |
|---|
Historical Bitcoin price
* Currency in USD
| Date | Open | Close | High | Low | Volume |
|---|
Bitcoin Calculator
- BTC
- ETH
- USDT
- XRP
- BNB
- SOL
- USDC
- ADA
- DOGE
- TRX
- STETH
- LBTC
- PI
- WBTC
- LEO
- LINK
- HBAR
- USDS
- XLM
- AVAX
- WSTETH
- SHIB
- SUI
- LTC
- BCH
- TON
- OM
- DOT
- USDE
- WETH
- BSC-USD
- BGB
- HYPE
- WBT
- XMR
- WEETH
- UNI
- SUSDS
- DAI
- APT
- NEAR
- PEPE
- ONDO
- ETC
- ICP
- AAVE
- CBBTC
- MNT
- GT
- OKB
- CRO
- TAO
- TKX
- TRUMP
- VET
- FDUSD
- ENA
- TIA
- KAS
- POL
- FIL
- FTN
- ATOM
- ALGO
- IP
- RENDER
- ARB
- S
- USDT
- OP
- JUP
- KCS
- SOLVBTC
- FET
- MOVE
- WETH
- RSETH
- NEXO
- XDC
- DEXE
- USD0
- STX
- IMX
- MKR
- RETH
- INJ
- WLD
- FLR
- THETA
- GRT
- SEI
- USDT
- BNSOL
- SOLVBTC.BB
- BONK
- LDO
- EOS
- METH
- XAUT
- GALA
- PYUSD
- XTZ
- USDC.E
- USDC
- WBNB
- BTT
- WBTC
- SAND
- BERA
- IOTA
- BSV
- MONKEYS
- JTO
- JASMY
- KAIA
- USDX
- BUIDL
- FLOW
- PAXG
- MSOL
- EZETH
- FLOKI
- NEO
- ENS
- TEL
- USR
- HONEY
- CRV
- PYTH
- BDX
- HNT
- JUPSOL
- EGLD
- AXS
- RON
- MANA
- TUSD
- WIF
- ZEC
- PUMPBTC
- RAY
- DYDX
- STRK
- KAVA
- USDC.E
- CAKE
- WETH
- XCN
- CMETH
- DOGE
- STBTC
- NFT
- BTC.B
- WETH
- AERO
- CLBTC
- XEC
- CHZ
- RUNE
- APE
- OUSG
- USYC
- USDB
- CORE
- CFX
- AR
- VIRTUAL
- FRAX
- MATIC
- USDY
- IBERA
- KAITO
- EETH
- COMP
- PENGU
- TWT
- OHM
- TBTC
- CGETH.HASH
- AMP
- PENDLE
- AXL
- AKT
- LUNC
- OSETH
- USDT
- BUSD
- GRASS
- VRSC
- GNO
- SPX
- BEAM
- BRETT
- MINA
- GLM
- RSR
- MORPHO
- AIOZ
- BERASTONE
- JST
- FARTCOIN
- CTC
- CBETH
- PLUME
- EIGEN
- SNX
- WETH
- SFP
- 1INCH
- DEUSD
- WBTC
- ETHX
- DASH
- MX
- SNEK
- KSM
- SATS
- TFUEL
- W
- CWBTC
- ZK
- ATH
- EBTC
- SUPEROETHB
- SWETH
- QGOLD
- FRXETH
- LAYER
- ZIL
- ASTR
- BLUR
- SAFE
- CKB
- QTUM
- NOT
- USDD
- ETHDYDX
- BAT
- MASK
- AIC
- USDC.E
- ROSE
- VTHO
- DEEP
- ABTC
- LPT
- ZRX
- CHEX
- GHO
- ZRO
- LSETH
- MEOW
- TOSHI
- SUPER
- PRIME
- USDA
- BABYDOGE
- HOT
- WEMIX
- TRAC
- FLUID
- STG
- AI16Z
- BORG
- CHEEMS
- ARKM
- OSMO
- DCR
- CELO
- GAS
- KET
- WSTUSR
- ACT
- AGENTFUN
- ORDI
- XCH
- RVN
- MWC
- DOG
- SFRXETH
- RLB
- APFC
- TRIP
- SAVAX
- MOG
- ELF
- GOMINING
- XEM
- ANKR
- SC
- MOCA
- YFI
- $RCGE
- RED
- ETH
- T
- AUCTION
- ENJ
- BTSE
- MEW
- VANA
- PNUT
- HONEY
- POPCAT
- TRIBE
- TETH
- CET
- DAG
- SDEUSD
- SUN
- IOTX
- ETHFI
- ZETA
- SKL
- WOO
- CVX
- ETHW
- ACT
- TURBO
- KUB
- DRIFT
- DGB
- XNO
- UXLINK
- FAI
- XYO
- POLYX
- VENOM
- WAVES
- LCX
- ZEN
- WETH
- GMX
- WBETH
- HMSTR
- KOGE
- CSPR
- MPLX
- SOL
- EURC
- ONE
- ME
- BIO
- KAU
- EURS
- WAVAX
- RLUSD
- KDA
- BBSOL
- B3
- MYTH
- LUNA
- GMT
- MAG7.SSI
- WMTX
- USDG
- LRC
- USDC
- FXS
- ONT
- AMAPT
- GAL
- KAG
- GIGA
- GPRO
- GCB
- ZKJ
- DAI
- MMX
- SXP
- NXM
- EUTBL
- IO
- ETH+
- COW
- SUSHI
- BAND
- STPT
- ACH
- NKYC
- PTGC
- COTI
- SWFTC
- USUAL
- HIVE
- SYRUP
- USDC.E
- USDZ
- RPL
- ZIG
- FIDA
- QUBIC
- PROM
- XPR
- BICO
- UXP
- AUDIO
- SOLO
- G
- NEIRO
- REG
- MELANIA
- ICX
- STEAKUSDC
- VVV
- ILV
- AEVO
- METIS
- EUL
- USDF
- RLP
- UMA
- MEME
- VVS
- QUSDT
- ID
- FLUX
- IOST
- AVAIL
- VEE
- IGT
- IAG
- ANIME
- ALEO
- ALT
- CETH
- ECOIN
- MANTA
- SUPRA
- LSK
- FRXUSD
- BOME
- ACX
- SNT
- SPELL
- SAROS
- BORA
- DESO
- AIXBT
- DSOL
- AGLD
- PHA
- ZANO
- CPOOL
- TNSR
- VELO
- BAL
- IQ
- XVS
- GAMA
- ZEUS
- ASBNB
- SSOL
- ORBS
- POWR
- USDT
- OKT
- DF
- RLC
- CTF
- ZRC
- POND
- FRXUSD
- TEMPLE
- SBTC
- REQ
- LON
- SONIC
- CHR
- GLMR
- PAAL
- ONG
- DKA
- FBTC
- GEOD
- METFI
- YGG
- BLAST
- USDT0
- BIGTIME
- WAXP
- ELX
- ZENT
- MVL
- ORCA
- USDP
- BDCA
- SYRUPUSDC
- WETH
- XVG
- PEOPLE
- BMX
- AVL
- WATC
- CVC
- CGPT
- COREUM
- ABT
- WBTC
- STRAX
- HT
- AGI
- DYM
- SGB
- PXT
- USDX
- DOLA
- PUNDIX
- OAS
- LVLUSD
- PEAQ
- ELON
- PUFF
- TRB
- HSK
- MLK
- GFI
- 0X0
- XRD
- KEEP
- SLP
- CRVUSD
- ZBCN
- TAIKO
- JOE
- ARC
- SHELL
- WETH
- SFRAX
- RARE
- XAI
- NOS
- DENT
- SLND
- AGIX
- OMI
- LQTY
- USTBL
- DODO
- NMT
- API3
- KMNO
- BWB
- CLANKER
- ISLM
- PIN
- USTC
- DOGS
- AGETH
- PUNDIAI
- SAAS
- NMR
- SCR
- ANON
- MED
- C98
- STEEM
- ERG
- DAKU
- OETH
- CETUS
- PCI
- CFG
- SOLV
- AMPL
- EZSOL
- GPS
- HEART
- USDF
- CTSI
- MTL
- OBT
- WELL
- ARK
- ACS
- NPC
- BUSD
- MPL
- USDL
- OLAS
- B2M
- CARV
- USUALX
- CORGIAI
- GAME
- QUAI
- OMNI
- ARDR
- TST
- GL-BTC
- WSTETH
- WIN
- SCRT
- MWETH
- ANT
- AAI
- BAN
- COOKIE
- WEETH
- USDC.E
- KNC
- PZETH
- AURORA
- TON
- DEGEN
- M87
- AXGT
- GOAT
- CELR
- MIM
- UFD
- VANRY
- $FARTBOY
- H2O
- AIAT
- BONE
- JET
- DEVVE
- MOVR
- ALCH
- USDT
- BITCOIN
- CTK
- GUSD
- BTG
- FMC
- EWT
- VCNT
- FIUSD
- ERN
- TRUAPT
- SSV
- EKUBO
- PONKE
- WILD
- BANANA
- WETH
- SHX
- TARA
- BOBA
- CAT
- UDS
- LUSD
- QANX
- QKC
- JNFTC
- LOOM
- QI
- SHFL
- ALICE
- HUNT
- USD+
- USDM
- BB
- CBK
- USDC
- DIA
- FORT
- REZ
- OI
- APEX
- WETH
- VELO
- BEL
- USDC
- ORAI
- NYM
- DUSK
- GRIFFAIN
- USDC.E
- PRO
- APU
- ACA
- SUSDA
- MERL
- HIFI
- SUNDOG
- SURE
- EURCV
- FUEL
- TRU
- GNS
- BNT
- CYBER
- SQD
- OCEAN
- COQ
- SWARMS
- PURR
- METAL
- VIC
- HPO
- AITECH
- OXT
- ASM
- EGGS
- AVA
- DBR
- ALU
- RAD
- FWOG
- BFC
- EDU
- WBTC
- OGN
- PEPECOIN
- SKI
- STRIKE
- HIPPO
- DEGO
- EDGE
- UQC
- ANDY
- MAGIC
- AVA
- ZUSDC
- NCT
- TAI
- WBTC
- STORJ
- RIF
- CCD
- ZEDXION
- SFUND
- WXRP
- SN
- ALI
- TMG
- SDEX
- CX
- SB
- BERAETH
- PWEASE
- MBL
- XTER
- SAGA
- SYN
- AZERO
- MBX
- FINVESTA
- RUSD
- STMX
- IOT
- SWEAT
- MOODENG
- ANVL
- D
- AVAX
- SD
- LISUSD
- JETT
- HFT
- SILO
- BRBTC
- BAKE
- KUJI
- ROAM
- SYS
- PLT
- CUSDC
- BADGER
- OSAK
- NTRN
- REACT
- ELA
- XT
- HDX
- RACA
- DAI
- TLOS
- THAPT
- MIN
- MBOX
- BROCCOLI
- SOSO
- GODS
- TRUMATIC
- STONKS
- CUSD
- USD3
- MAV
- MCDULL
- INF
- NKN
- XMW
- SOLVBTC.CO
- MNDE
- BINK
- BIM
- ACE
- A1C
- META
- ALPHA
- FLIP
- BC
- GRND
- VR
- ETN
- REUSDC
- LUMIA
- DEP
- WNXM
- ALPH
- RAIL
- SOC
- CXT
- NFP
- F
- HMT
- PEPU
- HBD
- XION
- PEAS
- PYR
- SLVLUSD
- DAO
- XTUSD
- LOOMOLD
- PNG
- TKP
- CATI
- NEIRO
- WPOL
- GPU
- TT
- MIM
- DEFI
- CRE
- CXO
- HOOK
- HEI
- CLV
- RSC
- USN
- AERGO
- LEVER
- ZEREBRO
- ORDER
- CTXC
- VINE
- WOLF
- PRQ
- SRX
- TJRM
- ATA
- DXI
- CULT
- BTU
- DG
- TLM
- SAUCE
- MARSO
- BNKR
- LISTA
- UNIETH
- LCAT
- UFO
- CUDOS
- USDT.E
- KEYCAT
- RBNT
- FTW
- MFT
- VSC
- MRB
- PIXEL
- SPA
- MOR
- BURN
- KYSOL
- FORTH
- NEON
- NAVX
- XPLA
- GFAL
- PHB
- META
- SLERF
- MIGGLES
- MAPO
- ASUSDF
- MOC
- J
- BOLD
- RDNT
- AQT
- OMIKAMI
- WHITE
- ZCX
- HASHAI
- OMG
- CHILLGUY
- VITA
- VRO
- LAT
- TOKEN
- FCT
- SERAPH
- PSP
- CAM
- GEAR
- BRISE
- BMEX
- LBT
- L3
- MIMATIC
- T99
- WFRAGSOL
- RSS3
- EURT
- MATICX
- LYX
- DOGINME
- NEURAL
- PRCL
- MLN
- GRS
- LMWR
- AQUA
- IXS
- IDEX
- LTO
- WHY
- DRV
- SAI
- ARPA
- SVM
- SUSD
- VON
- FIS
- GGP
- OS
- POKT
- USDC
- POLY
- ANYONE
- EUSD
- MATH
- MYRIA
- LADYS
- ICE
- EL
- TORN
- ALEX
- SFM
- QUIL
- X33
- PERP
- WZRD
- SPEC
- CAW
- A8
- ARRR
- CDAI
- SDL
- GME
- RARI
- A47
- PLXY
- TPT
- PROS
- CROWN
- SIREN
- DAI
- REI
- QRL
- ALCX
- SUSD
- GYD
- HOPR
- ANKRETH
- NPXS
- BOUNTY
- COL
- XSGD
- SHDW
- PALM
- ATLAS
- STEP
- $DOGEAI
- NAKA
- AI
- HEGIC
- STRD
- DADDY
- NNN
- VRTX
- HFUN
- OGY
- UM
- BLUE
- MCADE
- AHT
- STTON
- PIKA
- MLC
- XAI
- ELON4AFD
- LIT
- POLS
- PINKSALE
- KMD
- SX
- SEND
- WGBERA
- OHO
- SNAI
- TREE
- PUFFER
- DORA
- APX
- WAN
- OSOL
- SLF
- SHADOW
- SETH
- SBETH
- CKBTC
- NATI
- ULT
- FT
- DMTR
- HTM
- WAGMI
- VARA
- KOMA
- ELG
- ANON
- FUN
- QUICK
- NS
- DEXT
- XUSD
- MNGO
- LAINESOL
- XPRT
- FRONT
- $ADS
- ECOX
- AUKI
- BMT
- GTC
- UOS
- ALOT
- SWELL
- CBAT
- FLM
- TRUNEAR
- GHST
- UNX
- CONX
- BTCPX
- BANANAS31
- QUICK
- ADS
- FLIX
- COS
- MMUI
- BTY
- MNEE
- COCA
- KLV
- BLD
- EURA
- STHYPE
- BOOE
- HARD
- GXC
- REEF
- STRIKE
- STRX
- DNT
- LOFI
- INDY
- GLC
- INV
- PURPE
- ZUSD
- MPT
- TDROP
- BLZ
- LMT
- OPUL
- WCFG
- DIMO
- NFTX
- BEAR
- USDC
- MOOX
- ZND
- CWEB
- SSUI
- BASEDAI
- THE
- USDTE
- COLLAT
- OL
- ADCO
- USDC
- FARTCOIN
- EURE
- PIPPIN
- BFG
- DIONE
- CAW
- ASD
- WUF
- KARRAT
- NST
- RETARDIO
- SPECTRE
- PAIN
- IBGT
- MCOIN
- BXN
- YULI
- PEP
- AVT
- FB
- USDC
- ATR
- BETA
- POLIS
- KISHU
- PUPS
- WOJAK
- FARM
- IDRT
- CHESS
- DAI
- ORN
- LAVA
- MGP
- IDIA
- HAI
- FIRO
- NUM
- NRN
- WXM
- IXT
- SERV
- USDC.E
- FIDU
- CSWAP
- DUCK
- BZZ
- CHEQ
- GEL
- METH
- MSM
- FOX
- BSW
- XBG
- ARMY
- DRGN
- IMO
- WOS
- USDC
- NOW
- $MYRO
- OFT
- VRA
- DRB
- TSWAP
- HANU
- MOZ
- COPI
- VOXEL
- OG
- OX
- SDT
- SCRVUSD
- STRDY
- SANTOS
- SKEY
- $NUMBER
- TOKE
- BENJI
- ALPHA
- LIBRA
- USDC
- CEEK
- USDBC
- CUSDO
- FLEX
- HAIR
- WETH
- WOD
- PSG
- STSOL
- GGAVAX
- $GROK
- AURABAL
- GAME
- KIN
- PHB
- ADX
- BAR
- CTX
- TRIAS
- GHX
- RBTC
- CLOUD
- MDT
- PORK
- OORT
- PORTAL
- USX
- USDX
- ROOT
- LOOKS
- PEPE
- RAMP
- BOSON
- STUFF
- ALUSD
- DINERO
- STATOM
- CRT
- B3TR
- BOBO
- RBN
- MERC
- SPC
- USC
- TERA
- QASH
- AKI
- GEMS
- LEASH
- VOLT
- SUKU
- KEKIUS
- UCASH
- XCP
- SEAM
- YNE
- MEMDEX
- TROY
- OXA
- QUACK
- LRDS
- USA
- ENQ
- USDC.E
- NULS
- TKO
- DATA
- JKL
- DEXNET
- SYNT
- AIDOGE
- JOE
- DAI
- BIFI
- BOB
- MOCHI
- PIVX
- PHAR
- XCM
- BTR
- EVER
- TOPIA
- BROCCOLI
- ZKCRO
- GAFI
- WING
- HENLO
- DOGE
- XRETH
- LINA
- FROK
- XEN
- OZO
- SHIRO
- RAI
- MOODENG
- DLC
- CACAO
- AVUSD
- GS
- REKT
- BKN
- CREAM
- FIO
- XDATA
- LYXE
- FXUSD
- OX OLD
- ORA
- ZCHF
- MAX
- ODINDOG
- MONKY
- TRUMP
- $MICHI
- ECET
- OCTA
- VINU
- MASA
- DOG
- USDT
- KRL
- NIM
- JMPT
- ALEPH
- COMBO
- AUSD
- LOCK
- NATIX
- LOKA
- SFLR
- SAMO
- PIRATE
- SWBTC
- ARENA
- DEFI.SSI
- FOXSY
- CLY
- TRYB
- FLAY
- VLX
- KARATE
- PYTHIA
- BTC
- PHNIX
- SVL
- CAST
- 10SET
- RIO
- FARM
- PROPC
- UNION
- EPS
- LOOPIN
- GOLDAO
- WMNT
- HYPERSKIDS
- VERTAI
- FLEXUSD
- ALPACA
- AMO
- MON
- MAG
- FOOM
- WUSD
- PIXL
- IRON
- BGSC
- NTX
- WSTEAMX
- MEOW
- BOTTO
- USSI
- YUSD
- OWN
- WEPE
- AURA
- LCT
- QTCON
- BOMB
- ZEX
- CA
- REE
- STAPT
- BGSOL
- SOV
- BLUB
- FUL
- USDC.E
- EMP
- CLUSTR
- BERT
- USDC.E
- DPI
- UPC
- CLORE
- ODOS
- XPM
- PTU
- ASF
- KASTA
- TRUMP
- MODE
- HTR
- PPC
- ZYPTO
- FPIS
- GUD
- BELLS
- NXRA
- CRTS
- ZKL
- STRONGSOL
- PAID
- SLT
- NOOT
- LAZIO
- PDA
- TREAT
- SETH2
- AGRS
- MOBY
- MERY
- BNBX
- KONET
- INDEX
- XX
- BUTTHOLE
- LWA
- SOVRN
- NVL
- GOG
- SFTMX
- REN
- CGO
- MPC
- OBSR
- STREAM
- GALEON
- FASTUSD
- USDC
- MOBILE
- SEND
- DMAIL
- GST-SOL
- MANEKI
- MONEY
- GAL
- PSTAKE
- LUNA
- GME
- NC
- SPECTRA
- PAI
- TAOBOT
- SIDUS
- VNO
- VCHF
- MIX
- WINK
- THOR
- AVC
- EPENDLE
- SCS
- ARMA
- TIME
- GYEN
- NIBI
- HERO
- KWEEN
- YFII
- CELL
- THL
- ALPINE
- ALB
- BCUT
- JAM
- HIGHKEY
- UFT
- KRD
- PNK
- PIB
- SIGMA
- 42
- EQB
- TET
- VAI
- GRAIL
- JAILSTOOL
- ASTO
- KTA
- SWAP
- RIFT
- LINGO
- FEG
- OPN
- OCT
- WCGUSD
- BUNNI
- MVC
- KAI
- PINTO
- XBT
- PUSS
- EOS
- ZKML
- WETH
- CONAN
- ETHIX
- STTAO
- YNETH
- SSE
- JUV
- DMT
- ZTX
- MEMEFI
- AST
- WINK
- BBB
- PEIPEI
- BROCCOLI
- CERE
- $SIR
- NACHO
- KYVE
- BTCP
- SEDA
- STOS
- PNP
- USDT
- STNK
- WRX
- CAR
- VIDT
- PROPS
- KNDX
- CKP
- CITY
- GOUT
- PKOIN
- BSDETH
- ZUSDT
- EVA
- PLU
- AUTOS
- XAVA
- XSWAP
- FOXY
- ASR
- HAWK
- BTCUSD
- $1
- HGPT
- AE
- OUSDT
- BAD
- STON
- YLAY
- EFI
- PLMC
- WEMIX$
- SQGROW
- UTON
- MFER
- LAI
- EMC
- DEL
- COOK
- $BORGY
- DOGI
- PACK
- USDT
- MIU
- SFRXUSD
- FLX
- $MICRO
- ARCH
- LM
- USDT
- SBD
- PARTY
- AURY
- BBT
- MTLX
- STARDOGE
- PAW
- TONIC
- ATM
- QLC
- TRADE
- BLOK
- PRIMATE
- REI
- STC
- WAGMIGAMES
- KP3R
- VISTA
- REX
- WTN
- VIB
- NPCS
- WALLET
- RYU
- JUNO
- INCO
- EXTRA
- SOUL
- GATSBY
- MEED
- GXA
- $BEAR
- CHAMP
- AXEL
- ZERC
- FNCT
- TXAU
- WBTC
- PKIN
- ROUTE
- TOBY
- COMBO
- MCB
- OUSD
- NEXA
- MUSE
- HOLD
- LAOS
- TORUS
- USDC
- OFN
- DATOM
- LIT
- TALOS
- DEAI
- LNQ
- BDC
- VEIL
- SIPHER
- NAI
- WAMPL
- USDQ
- BEETS
- FACT
- USDT
- NBLU
- GTAI
- XSUSHI
- WFI
- HOPPY
- EEIGEN
- MOXIE
- MOON
- BUZZ
- VALOR
- FPIBANK
- DINGO
- FLOCK
- DBC
- GRIFT
- KENDU
- TGT
- GLQ
- HSUITE
- HBTC
- ORE
- OBT
- SUEDE
- ZYN
- EBET
- ZNN
- LQR
- SHRAP
- CDX
- KIKI
- USDT
- BERRY
- PEPECAT
- HEGE
- KING
- BID
- TMAI
- DVPN
- DOVU
- CLEAR
- KILT
- MYST
- STARS
- CAH
- MAS
- PUNK
- DCK
- FTD
- TYBG
- WEXO
- CEUR
- MEX
- BNC
- MYST
- VADER
- SRM
- AEROBUD
- UFO
- OSMI
- 3ULL
- HERB
- TAROT
- ACM
- BRUSH
- STFLOW
- GGMT
- USDR
- MAX
- ML
- LUCE
- MAVIA
- PAI
- RLY
- EPIC
- METRO
- TIG
- VIVI
- BCD
- MUMU
- SIXP
- DFI
- ACOLYT
- KAI
- AVIA
- EVR
- JEWEL
- THALES
- POZO
- KWENTA
- EAI
- AUDIT
- SMT
- VSTR
- ZAI
- DIVI
- SCA
- DCD
- MBC
- XRT
- PATRIOT
- PIKA
- G7
- WINR
- SAVUSD
- OVR
- ADP
- ARC
- PANDORA
- HPO
- ELYS
- SYMM
- SSLX
- BMX
- GENOME
- SDAO
- PINGO
- EDWIN
- MLG
- DEXTF
- ARTY
- PORT3
- AGRI
- VGX
- BOBAOPPA
- INTER
- MNTA
- KOKO
- LIF3
- LIKE
- WXT
- CANTO
- KATA
- LOCKIN
- VTRADING
- DHT
- PEPE2.0
- ⌘
- PLI
- POLA
- APW
- 1GUY
- ALVA
- KPN
- ARIA20
- FUSE
- HAT
- B4FWX
- XEL
- ASTRA
- SAITO
- MUBI
- XFI
- EXRD
- GSWIFT
- ICETH
- BAC
- TITS
- DNX
- MARS
- YOM
- HUBSOL
- FX
- STOP
- XCAD
- HDRO
- KOIN
- MARS
- SWISE
- LMEOW
- HIGHER
- CAPTAINBNB
- XETA
- MEY
- SWORLD
- WBTC
- CHAIN
- TSOTCHKE
- WRLD
- KAR
- FLOCK
- SLIM
- FRIC
- DMD
- BRAT
- RENBTC
- ZGD
- CROID
- KLIMA
- BAMBOO
- DOLZ
- FLT
- SNSY
- SIX
- XDB
- USDF
- SLOTH
- LZUSDC
- GDP
- CATE
- BIZA
- GENE
- ROA
- USDC
- USDT
- BEAM
- ABSTER
- TRAC
- GBYTE
- RCH
- AKUMA
- WCO
- OXY
- UCJL
- USDH
- TADA
- BST
- CLAY
- OWC
- BNUSD
- VVAIFU
- UNCX
- HNS
- VIRAL
- JESUS
- SCF
- MOTHER
- DCB
- ANT
- ASIA
- INFRA
- STOSMO
- HELLO
- SWELL
- EVERY
- BLOCK
- XZK
- ROCK
- SNK
- JOULE
- STTIA
- BEETS
- WHALE
- MAGA
- USDC.E
- OIIAOIIA
- RVF
- WIFI
- BUBBLES
- STARL
- 00
- MXC
- SFG
- BLUB
- USDC
- LEA
- ASK
- HUSD
- DIGITS
- NECT
- CULT
- METAV
- COT
- LAIKA
- RGOAT
- RE7WETH
- MNW
- XCHNG
- AFR
- $NAP
- STAT
- MOD
- EGP
- WISE
- BBONK
- SDN
- ASM
- XEP
- FORWARD
- SEN
- SWASH
- CUNI
- LOAN
- PDT
- WIKEN
- NAVI
- FP
- TRT
- VAI
- APL
- MINIMA
- BCN
- HANDY
- JELLYJELLY
- SINGULARRY
- SNPAD
- TROLL
- XOT
- MAN
- CREO
- ASTRO
- BOTIFY
- PASG
- 888
- CHAD
- SWPX
- HARAMBEAI
- LL
- USDT
- EMAID
- DKP
- MAD
- CAGA
- DC
- BXX
- SHD
- OPCAT
- GHUB
- WETH
- XAND
- ISLAND
- ETUS
- REP
- PPT
- KIMA
- APP
- CELL
- PAL
- GRAB
- MEMES
- QMV
- MEUSD
- MG8
- ABEL
- MINT
- SCFX
- TEVA
- FARM
- L1
- GOGLZ
- RONKE
- BMC
- SLN
- OXEN
- DNA
- GIKO
- RAIN
- PLAY
- AINTI
- ICHI
- SKEB
- AVINOC
- SOIL
- $KEKEC
- SHIDO
- RADAR
- NEX
- KOLIN
- DIVER
- BOA
- HI
- WELSH
- 7007
- XDAG
- SAN
- $PURGE
- AIUS
- LIMBO
- MOE
- PAI
- CVR
- TRIO
- SHOGGOTH
- CUBE
- $BILLY
- O
- FITFI
- POOLX
- KNCL
- GOAL
- ORBT
- VITA-FAST
- BRETT
- BOB
- POLYDOGE
- NUB
- DJED
- ETH2X-FLI
- WETH
- UW3S
- AMETA
- ATS
- BTCMT
- CSIX
- LORDS
- AVB
- BIG
- PTS
- HDN
- M3M3
- SQT
- ESE
- HMND
- ISK
- HOGE
- WOOF
- CUMMIES
- SEED
- DMC
- AIPAD
- NWC
- DOME
- THRUST
- USDT
- FURM
- SOFI
- JEFF
- CAPS
- ASTRAFER
- TOMI
- WELF
- QBX
- LOGX
- SHI
- LISTEN
- MBS
- SNFTS
- LAUNCH
- VUSD
- AIR
- MNTC
- FLUXB
- KANGO
- VEUR
- TYPUS
- EDGESOL
- TRISIG
- SIS
- MIAO
- NATIVE
- ARCA
- DEGENAI
- BLENDR
- SUAI
- LLD
- DAY
- AGIXT
- HYUSD
- TVK
- ABX
- OMZ
- TRVL
- FRED
- N3
- EBTC
- AIT
- BIDZ
- GPCX
- HYPER
- TOP
- WOW
- THT
- KIP
- WETH
- VC
- LVN
- HARAMBE
- NHT
- PLN
- LTX
- OPUS
- XNA
- $EVA
- AVI
- PRISMA
- CRAI
- HXD
- NAVI
- SPURS
- KAN
- VAL
- MCRT
- PUSH
- ALD
- MOVE
- TRUF
- GPT
- MYSTERY
- SAI
- NAP
- MINI
- PREMIA
- IRIS
- DIP
- MAK
- LEDGER
- BAX
- NSASTR
- USDT
- YEET
- GMEE
- IMGNAI
- BLK
- CEL
- HAROLD
- AURA
- LANA
- CRU
- LYA
- BEER
- NYA
- KOMPETE
- ARG
- " "
- SEKOIA
- USDC
- CFGI
- CHOMP
- WITCH
- AZIT
- USDGLO
- LAND
- NOCHILL
- DERO
- CPH
- EEFI
- FIRE
- XPACK
- ATH
- TRA
- WUSDM
- UBU
- REGEN
- ZKP
- TN100X
- FIVE
- NRS
- GOVAI
- HAPPY
- EUSD
- KIBSHI
- CARROT
- LEOX
- ETF500
- BULL
- KNS
- HENLO
- HOLD
- ASIX
- SCOT
- MOEW
- DUKO
- WHINE
- PNDC
- RJV
- PZM
- PINO
- WINNIE
- AKIDS
- REF
- HERA
- BIGJIM
- BAN
- LQDR
- QORPO
- DUEL
- KLEVA
- ISP
- SNC
- EFL
- WBTC
- USDC.E
- BRYAN
- BCT
- ICBX
- IVT
- 🦝
- NRG
- LUMO
- NETVR
- LUSH
- DKING
- SWITCH
- YAYSTONE
- BTM
- EQUAL
- IBEX
- LCS
- FEI
- TITAN
- BTCB
- RE7WBTC
- STIMA
- BTC2X-FLI
- MINT
- ITHACA
- ANLOG
- DOP
- WOM
- HMX
- SOLNIC
- CAMEL
- ADX
- MAHA
- $SIGMA
- VY
- FUD
- BUT
- KEY
- BAAS
- OMAX
- EVMOS
- MZR
- PPKAS
- TAKI
- YAYAGETH
- RISE
- STFX
- MUSKIT
- USDN
- AGVE
- QUEEN2
- IMG
- DOLAN
- LTAI
- NEURON
- NSTR
- SOCKS
- SBR
- DEMI
- LMCSWAP
- USDC
- DROP
- USDT
- TOKEN
- NLS
- IMPT
- PIKA
- MSTR
- BUY
- AFC
- $CATBAL
- REWARD
- BARSIK
- SOLID
- AZUR
- GLEEC
- $POM
- JUICY
- EZEIGEN
- SPARKLET
- ZEPH
- TREMP
- APRS
- SPS
- REDO
- GUI
- VITARNA
- WEL
- FROG
- GMM
- LMR
- SPE
- SBR
- PUNDU
- SNS
- EMT
- TAOCAT
- PRE
- $SYMP
- YAK
- RWA
- Y2K
- PSPS
- MUSD
- ZARP
- FUTURE
- WANBTC
- BONGO
- RBX
- STRP
- CYG
- SCHIZO
- $CWIF
- W3S
- FARTGIRL
- MV
- NYAN
- VTC
- ELIZA
- GRIN
- 1000X
- OPSEC
- BUDDY
- USDC
- CREDI
- STORM
- RBC
- KCT
- SYLO
- SOON
- EPIK
- ANGLE
- WAFFLES
- BTS
- MASQ
- CGX
- LKY
- DIKO
- POR
- FURI
- NEUR
- ROCO
- WHISP
- PIP
- TSUKA
- QVRS
- OMNOM
- TANK
- $SCRATCH
- AGIXBT
- CNHT
- BEEPER
- MEDIA
- REV
- PERRY
- AIXCB
- NTMPI
- TNQ
- XTN
- AIKEK
- BODEGA
- ADM
- GOD
- UNIBOT
- USDC.E
- POOL
- CAIR
- $SMH
- MDX
- PMT
- SEXY
- RIKO
- BOOP
- BOO
- USDC
- BOZO
- YUSD
- TGC
- MYT
- TLX
- WEFI
- COCO
- MTRG
- FAR
- WARPED
- SWAN
- U
- KIZUNA
- AREA
- BRAINLET
- FREYA
- SOL
- XCB
- ION
- SWCH
- X314
- AIMONICA
- AGENT
- DOBO
- USDC
- DG
- POWER
- MINIDOGE
- FLRETH
- ASCAKE
- IQ
- WAAC
- KPOP
- STARS
- EPIK
- ANDY
- ADO
- X
- FJO
- ALL
- SAFEMARS
- JAM
- AA
- CTN
- USDC
- CONVO
- HAPI
- RAI
- APX
- LIQUIDIUM
- SLC
- TTG
- PIDOG
- Q*
- BABYSHARK
- SG
- ORT
- OXI
- FRIEND
- BROCK
- BALN
- SHRUB
- KASPY
- AUDF
- LAKE
- WOOLLY
- SAN
- UPT
- TXT
- RATS
- WIBE
- THC
- TANGO
- DOMI
- CHAT
- $KIT
- TWIN
- G3
- MAJOR
- DEFX
- TIRED
- BLND
- MAZZE
- CABAL
- DAI
- RAMEN
- PHIL
- HUAHUA
- DREAMS
- DOJO
- GIZMO
- BSX
- BITCI
- BENDOG
- RXD
- MTD
- UNFI
- MIR
- CTRL
- BRO
- COMAI
- CAT
- BYTE
- BOND
- STRIKE
- NEXT
- WIT
- 0XGAS
- GARI
- WACME
- GNON
- NEST
- BFT
- INTX
- EDUM
- WBTC
- WHALE
- CTG
- VOI
- TON
- CAT
- DREAM
- USOL
- KEX
- GET
- MDAO
- SPORE
- PAR
- TAG
- BILLY
- PERC
- RSAVAX
- BXBT
- GRELF
- GTCBBTCC
- PAPPLE
- WUD
- SMURFCAT
- LMY
- EVAN
- MDEX
- DUCX
- RIZ
- TALK
- TUSD
- BRN
- JAV
- CNG
- USDT
- XNET
- MCONTENT
- OOE
- ZJOE
- LI
- SSDX
- AION
- RIZO
- ARCAS
- SATORI
- IBEUR
- DVI
- SERO
- FAN
- RFD
- BTC2
- PEPPER
- ZERO
- ANDY
- TRKX
- FLY
- ECS
- TPRO
- SCP
- TBULL
- VIA
- ROKO
- VPAD
- COR
- M
- SCI
- BABY
- TERMINUS
- HXRO
- BIB
- DOGEGF
- CYB
- PLSR
- GAU
- MAXETH
- NXS
- USDT
- WSDM
- USUI
- HSUSDC
- CLARITY
- PRD
- NINJA
- LUFFY
- LIXX
- NAV
- MKL
- FACTR
- NFD
- KRAV
- RWA
- ARGO
- REALIS
- MINTME
- FP
- BLOCK
- XAR
- HENLO
- NUTS
- TURBOS
- UCO
- LKI
- RKEY
- NX
- SCIHUB
- AIV
- PONGO
- GRPH
- BRAINERS
- $ROAR
- SCPT
- SOLAMA
- DAI
- DAI
- WHISKEY
- LIQD
- SKOP
- BRLN
- AIN
- GNUS
- LYNK
- ((=ↀωↀ=))
- GO
- TOLY
- PEP
- AIAGENT
- NILE
- DTRXBT
- FU
- WART
- SAMA
- SEAMANIA
- SXETH
- METAL
- SILK
- DOGC
- KOTO
- DEPAY
- OGV
- ISC
- JYAI
- FAYA
- GROW
- SCLP
- RDPX
- BEPRO
- FXN
- SDT
- SILLY
- CARR
- MUSD
- VEX
- SUDO
- ZOO
- IBTC
- NYX
- SAGE
- IPOR
- ZBIT
- GRC
- CHATOSHI
- BUTTCOIN
- POGS
- FOMO
- CKETH
- USDT
- $MONKO
- APES
- AXOL
- KEKE
- WQOM
- LOULOU
- GOATSEUS
- HODL
- ONI
- SWTH
- DIO
- TNT
- LUCA
- MVI
- STABLE
- IOUSDT
- LAUGH
- ETH
- RING
- UP
- EXA
- AI23T
- CAT
- MACHI
- HEU
- SLAP
- USDC
- ETHOS
- JOY
- UXRP
- WLTH
- LNDX
- CATBAT
- KNIGHT
- POOH
- GOODBOY
- WOLF
- RNT
- LBR
- COFE
- GEEQ
- HEHE
- $WOLF
- SCUSD
- BMP
- BM
- MARSH
- UNIT0
- ARI
- GAMMA
- USDT
- CAI
- SFI
- PHRZ
- JURIS
- LAVA
- THE DOGEFA
- ITA
- PENG
- RDT
- NOVA
- SIGNA
- RFOX
- SEAL
- USDC
- SKR
- WMC
- SERSH
- VMANTA
- XPX
- XOXO
- LQNA
- TRACY
- CRASHOUT
- SHU
- THUSD
- SDM
- YOSHI
- FLORK
- NUUM
- RWA
- UBT
- OTK
- GYAT
- IVFUN
- WEPC
- AIR
- WARS
- RUSSELL
- DEDI
- TIME
- PBX
- VSP
- DARK
- SHIBDOGE
- MONG
- FAKEAI
- KASPER
- ARTHERA
- GAINS
- KUDAI
- MONOPOLY
- NEOX
- SMOL
- SABAI
- TDE
- LOU
- FOUR
- SKBDI
- MUSIC
- BABYBONK
- INSP
- GZIL
- GCR
- WSM
- PUMPIT
- TSUKI
- ONE
- XTT
- VAPOR
- GALAXIS
- TABOO
- FRA
- PEPO
- QI
- CLXY
- VERSE
- BREW
- BOB
- RTM
- EMC
- CTA
- FER
- CBY
- AIFUN
- ROME
- FILM
- TARDI
- RDD
- CONWAI
- SPACE
- HINT
- GOATS
- YUSD
- UFI
- WBTC
- KBL
- HTS
- SQR
- DEFI
- OOKS
- NAV
- FARTY
- SC
- $RIF
- LPETH
- ORX
- LIKE
- CHKN
- EURR
- PZP
- BRAIN
- HVH
- MBTC
- HELIO
- RAKE
- OPTI
- XPI
- MTO
- MET
- RC
- BZRX
- KOS
- STEAKUSDC
- DOGA
- MUSIC
- DUST
- TOKE
- POX
- TETSUO
- AMORE
- AWR
- $H2
- DOK
- WCHI
- 4EVER
- SLAM
- DOR
- HYDRA
- UMJA
- PACE
- STS
- MPS
- GOOFY
- LYRA
- RMNER
- DYOR
- FXN
- GZONE
- QUNT
- BSCPAD
- DEPIN
- ANC
- SOMM
- FLD
- CATS
- XER
- WIGO
- NBT
- AIINU
- IOUSDC
- AKA
- WATER
- FLX
- STASH
- $NMKR
- MOBI
- SPH
- CONDO
- UX
- KIMBO
- BODEN
- CHAPZ
- TDC
- PEEZY
- DICKBUTT
- MDAI
- LEGIT
- HOA
- CITADAIL
- SP
- ENQAI
- DUSD
- WSI
- KDX
- CHADETTE
- SPHYNX
- WOLF
- XDEFI
- PNIC
- CRYO
- STAVAIL
- XELS
- TROG
- 21BTC
- ENF
- DBR
- TNSR
- WETH
- BREW
- VETH
- XIDO
- SENATE
- DFL
- CHRP
- USDT.E
- PIP
- TAPT
- BVM
- ZF
- LFT
- RWN
- NCR
- XCFX
- SONIC
- $ANTY
- PLEB
- FU
- CAI
- USDC
- MORI
- DDX
- VCX
- AAX
- BOX
- $URO
- SEND
- EYWA
- ABR
- GBEX
- KHAI
- YAPSTER
- ALTT
- RTB
- HST
- BTRFLY
- FAFO
- DCI
- USDT
- BOOMER
- SAY
- SSWP
- PTC
- SIMP
- LBL
- PART
- NCDT
- LSS
- ZAI
- BOOT
- RGT
- NVT
- KOI
- EGO
- ASKJ
- DOGE
- UNO
- KALIS
- EURQ
- OBOT
- BIT
- FULLSEND
- RSVETH
- KM
- IXC
- BLACKDRAGO
- CKUSDC
- STEAM
- BLUSD
- MAIAR
- LOC
- GRG
- FOX
- MTA
- DEFIT
- MANC
- $WELL
- GUSDC
- DEUS
- MLT
- POLC
- BRRR
- NASDAQ420
- GG
- RMV
- ELU
- FLX
- DDBAM
- $OG
- SELFIE
- ICE
- OMNIA
- WPAY
- XR
- AIYP
- $UNFK
- VEXT
- MEME.SSI
- GOTTI
- YUKO
- MORPHAI
- CGV
- SYL
- XNK
- JBX
- DMAGA
- PIKA
- BERRY
- DOP
- GRP
- WING
- SUIP
- USV
- YEL
- XTM
- IST
- HACD
- CLANKFUN
- BIRDDOG
- TOMB
- BULLY
- XFUND
- PUPPIES
- TRONKEY
- DOOM
- TREB
- RWAX
- IDO
- PROJECT89
- BDOGITO
- MNT
- BABYNEIRO
- C3
- HUND
- BUZ
- BCAT
- NGL
- SEIYAN
- NITRO
- SYK
- CHUD
- BTX
- OBI
- PEUSD
- USK
- VIS
- FOLD
- TYPE
- MAMA
- LCC
- KOL
- BOOK
- DOGL
- UPO
- IOL
- TALENT
- LUNAR
- REV
- MEMESAI
- BNX
- EGC
- FDX
- CLUTCH
- FLNCHY
- SUNCAT
- SHA
- CHONKY
- LYNX
- DSRUN
- HELP
- ATETH
- VPT
- INTOS
- STELLA
- CATCH
- BONZO
- SIN
- KARAT
- RPLS
- BPT
- UBC
- GMRT
- HEEHEE
- $BLS
- CNFI
- ID
- MBP
- EMYC
- HART
- RBD
- PIRATE
- ADAPAD
- SAGE
- OKI
- GHOAD
- ZKF
- DYAD
- WHALES
- ANZ
- $FATCAT
- SKYA
- TEMA
- VIDYA
- BUBBLE
- EQUAD
- REVV
- NOTE
- LUX
- RST
- ZULU
- CAG
- TONY
- SUIAI
- PKF
- UMB
- NAMI
- SOBULL
- PROB
- BAG
- VELAR
- MCHC
- LIBRE
- PURSE
- SAL
- QOM
- TUT
- PXC
- ASH
- AI9000
- PER
- COVAL
- ORC
- SKH
- DITH
- FMC
- DETF
- FREN
- BWEN
- FEENIX
- MTV
- PSY
- SATOSHI
- CLOUDY
- WANUSDT
- SHROOMY
- MARS
- VBNC
- USDT
- HOTCROSS
- PRISM
- FLOPPA
- BDP
- KNINE
- MINX
- CAS
- SMT
- CVP
- COSA
- PND
- OSCAR
- USDC
- $JIM
- MNTL
- MNFT
- MELD
- NATO
- KOM
- TAONU
- SUGAR
- MIND
- USTRY
- EDEN
- PEAR
- BRWL
- WETH
- FUZN
- DIME
- BSX
- PIPO
- INDI
- UFC
- CJPY
- BIGSB
- HZN
- BENFICA
- SAVM
- QBIO
- NOTAI
- SKAI
- $KOKU
- USDC[HTS]
- BANANA
- RUGPULL
- CALVIN
- LUM
- CHIRP
- EJS
- AIW
- SPACEM
- FTC
- EDOGE
- CARD
- LEV
- GQ
- RE7USDT
- SNS
- VOYAGE
- IXO
- DTF
- WBTC
- SPLASH
- PLYR
- VSYS
- PIG
- CPT
- ORAIX
- NFTXBT
- TRCL
- SENSI
- VDA
- FSN
- ASX
- VEE
- GMTO
- JEST
- USDT
- DINO
- KRO
- HVLO
- WAR
- GUMMY
- SEILOR
- AMB
- SYNK
- WAVE
- HAMMY
- CRAZE
- IVY
- RITE
- USDS
- DISTRIBUTE
- USDC.E
- GUAC
- SOPH
- STGWETH
- BSKT
- ZARA
- POT
- MIM
- WYAC
- MM
- DORKY
- LVL
- STDYDX
- VTX
- GLUTEU
- NORMIE
- MC
- TIA
- SENTAI
- QST
- STATE
- BONDLY
- RIDE
- OKAYEG
- IBIT
- ASYM
- PKT
- AXV
- RTBL
- DTEC
- PANDA
- RAM
- SOBA
- USDC.ETH
- VMINT
- ART
- YBTC
- XKR
- ACQ
- XI
- CHAMPZ
- XFI
- DESCI
- APY
- KAON
- MZC
- EFC
- DESU
- ELONRWA
- AIX9
- BABYPEPE
- NOTE
- FROGE
- AI
- RING
- BTORO
- ANTIRUG
- STEPSOL
- MP
- TRONPAD
- RAMON
- QAI
- KLAUS
- RICH
- ROCK
- ASM
- LESTER
- SBX
- NIBBLES
- MK
- GST-ETH
- NAV
- HLN
- FUKU
- USDT
- MUNDI
- GURU
- XSP
- APM
- POWSCHE
- BAZED
- OUSDC
- ENG
- NGC
- NOBL
- YAKU
- GRRR
- RETIRE
- XYRO
- T3AI
- INTR
- LOL
- MOOV
- FLUT
- SNIFT
- EXPERT
- TERMINAL
- FA
- WECAN
- PUPS
- NSTK
- XENCAT
- TEN
- WANUSDC
- BLEND
- POLY
- PIRB
- OMIRA
- BRICK
- SHR0
- JUSDT
- XGC
- PPCOIN
- MUMU
- CAU
- TOONA
- GIV
- LBLOCK
- KITE
- CRASH
- BORED
- ELITE
- HAC
- WWY
- XODEX
- DYP
- VLXPAD
- AZC
- ITMT
- CHEESE
- VCF
- USDC
- TOWER
- ARTFI
- ███
- BLOCX
- SRK
- HEMULE
- NOMNOM
- MOAI
- XMONEY
- NEIRO
- LUNR
- $LOTTO
- DRUGS
- RETH2
- WLKN
- ARTEM
- BEE
- UBXS
- WOZX
- DAN
- SIMMI
- $TOAD
- NICP
- AMKT
- DRIP
- TSHARE
- LLM
- EMP
- MD
- ORNJ
- AVER
- KAP
- MAPS
- 4CHAN
- AVAC
- LIMITLESS
- MBET
- IZE
- SOUL
- VIRGIN
- ZKB
- ANGLERFISH
- JPEG
- LEO
- NEROX
- WUSDN
- SUSX
- SKY
- BABYBNB
- STBU
- USDC
- RACKS
- PEN
- FOX2
- CHELON
- OPXL
- DTIA
- BULL
- NGL
- INCA
- USDC.E
- BB
- SYNTH
- MNRY
- BAMA
- 5IRE
- $THREE
- BSR
- SHY
- IMF
- PIZA
- ZUSDT
- KDAI
- ALOR
- 589
- SPS
- AEG
- ZCN
- CHAD
- SERAPH
- BABYFWOG
- ABYSS
- MIST
- MINEBTC
- ARIA
- AURA
- PLANET
- NEURA
- STYLE
- STAR
- BAI
- DEVAI
- WSTASTR
- CRWNY
- FACT
- SMILE
- AGENT
- TRUMPCOIN
- SHIBOO
- SPICE
- VNXAU
- DEVIN
- CRYSTAL
- SAINT
- HOTKEY
- TALIS
- FCON
- LADYF
- BROCCOLI
- GIB
- CARLO
- BRLA
- TRD
- PDEX
- CPAL
- RSP
- BEFE
- EDN
- SOAR
- GOFX
- TERRA
- BOOSHI
- ANALOS
- TRADE
- RPG
- EBULL
- HLG
- XMON
- JARVIS
- RBLS
- BALLZ
- AIOS
- PYTHETH
- NEOT
- RBT
- GM
- FCTR
- VELAI
- ZPAY
- MATES
- STAR
- STAR10
- GURU
- TEER
- ANDR
- TRUST
- SHIB
- HONK
- USA
- WOM
- TAROT
- RAVEN
- NET
- ZAP
- MTARD
- NVIR
- SLR
- TRENCH
- SEER
- ICOM
- AIRENE
- CKUSDT
- STBL
- ALPHA
- TAOLIE
- FIGHT
- HUSKY
- AVG
- ITHEUM
- ZTG
- TUT
- BGG1
- SDR
- BANX
- BIFI
- BRD
- AGIALPHA
- RECORD
- FEFE
- DATA
- USDC
- $TOAD
- SSG
- PGX
- FALX
- USDT
- XMONEY
- SHR
- SAIL
- PEPE
- ERTHA
- E4C
- CHONK
- THALES
- SB
- GAME
- KEK
- SOLID
- CDOG
- PACA
- BNA
- BONSAI
- JRT
- LA
- GMAC
- AAA
- MENGO
- FROC
- FOLO
- CATBOY
- $PANANA
- NODL
- MAICRO
- UBSN
- BIOFI
- PYTHUSDC
- BONSAICOIN
- U2U
- PUT
- CRTAI
- $PEPE
- TOMO
- XMD
- NEIRO
- HIBER
- FERMA
- OMNI
- WEIRDO
- GYMNET
- JAM
- PEEZY
- HUG
- TRUST
- BABYBROCCO
- XFT
- TST
- IDOGE
- RE7CBBTC
- IRA
- TAXI
- CYI
- C4E
- GAIA
- MND
- KEKE
- MARS4
- FUZZY
- WAM
- SOLENG
- USDC.E
- AM
- GOA
- GRK
- PROPHET
- SYNTH
- FYN
- CHENGU
- ATF
- VAL
- HSUI
- BOOH
- BNBXBT
- ELDA
- HOPE
- HABIBI
- EXD
- SPEEDY
- BOYS
- USDT
- GOZ
- BKOK
- JGN
- MNB
- NGM
- TORCH
- SHIFU
- TRUBGR
- XOXNO
- SHEKEL
- AIT
- BLP
- KAI
- LUCKY
- PHI
- SPORT
- POLK
- NEOS
- DETO
- KOIN
- HONK
- YEC
- UCX
- GSWAP
- $BADCAT
- MUC
- EUROE
- GFI
- NIKO
- WETH
- SAUBER
- PAK
- AYIN
- NABLA
- FAIR
- KNJ
- CCV2
- KOIN
- QWACK
- WAT
- QUARTZ
- WOOF
- NSAI
- WCTC
- KINT
- MIZUKI
- AME
- MINT
- DOSE
- FILTER
- CEP
- ZAP
- GULF
- BGVT
- P3D
- LITH
- DINO
- THC
- KLS
- WBTC
- IGU
- NSFW
- RFL
- $DRIP
- SEUR
- XALPHA
- W3W
- FUJI
- MOO
- AMA
- UNO
- PAJAMAS
- LIT
- QUDEFI
- RET
- MBD
- USDT
- GMB
- SOLMAX
- HBOT
- LBM
- RAIN
- PRX
- HUDI
- UUSDC
- FOR
- AGENT
- EGG
- FORM
- DCN
- ISAACX
- GORA
- NXT
- BTSG
- ATN
- ESTEE
- $CLAP
- LYP
- LSHARE
- DAIGE
- MORE
- P
- EARLY
- MORRA
- IQ50
- UDAO
- NFTB
- RYO
- BCB
- FISH
- NEBO
- MOBY
- KIBBLE
- BRG
- BULLY
- GSTS
- RAZOR
- NICK
- SWP
- NFTL
- DCOIN
- ODIN
- PROOF
- CTI
- HATCHY
- MENDI
- UNV
- ELIZA
- SUSDX
- SCAR
- PUSSY
- $BURN
- CHAI
- WBTC
- WANETH
- BSWAP
- INT
- USDT
- QUANT
- TCC
- CHIDO
- JHH
- AVRK
- ARV
- PEPE
- SAFE
- CZRX
- BERAMO
- RVC
- FWT
- ST
- MELLOW
- MXM
- REVO
- BCUBE
- VOLT
- WEWE
- DERI
- JAIL
- AROK
- FOREST
- WRKX
- DFYN
- SNFT
- ELK
- KROAK
- NOMAI
- CDT
- FUNGI
- HLO
- MTVT
- DAI
- ZAI
- LAMB
- KUMA
- GINNAN
- INFRA
- SOULS
- SHIK
- USDT
- XY
- AURA
- KIBA
- SUGAR
- AVL
- SPHERE
- NUT
- WNK
- DNA
- OAX
- FOFAR
- CHANGE
- MUNCAT
- MIMO
- GNY
- JOK
- RIZZMAS
- DAI
- BABYGROK
- SOLI
- VCG
- $REALKENDO
- FREE
- OPAI
- PANDA
- SOCIAL
- FPS
- ECLD
- AIPUMP
- DOGEFATHER
- ZOO
- CBC
- OCE
- BRIAN
- EVERETH
- DSLA
- OCTO
- VIKITA
- X2Y2
- ZOOMER
- CRPT
- VPS
- BOF
- SKID
- AIPG
- CGT
- REVU
- MOAI
- PLS
- EMR
- STND
- DORITO
- PXP
- STC
- POPDOG
- TST
- SANDY
- GTN
- TRAVA
- MONKEY
- 🟥🟩
- BIAO
- BOBLS
- LAYER
- GST-BSC
- IDRX
- KROM
- $HWTR
- MILLI
- LUMOS
- BOLT
- RAT
- IGNIS
- RMRK
- $JOBSEEK
- WATER
- WOLF
- VAIN
- SALT
- CYPHER
- CBL
- $TRUMPAI
- KAT
- AVENT
- FRTN
- FIGHT
- GEMXBT
- BIS
- SYNDOG
- KFC
- KIT
- STEAK
- $CCC
- BIOHACK
- BETS
- WASSIE
- ZOON
- GLORP
- J3FF
- BTTY
- SSR
- CZ
- EVAL
- DBX
- FLOW
- HNTR
- HORD
- BASED
- MEGA
- NUSA
- CYDX
- NMX
- KEROSENE
- URUS
- AUTO
- LZM
- MOONED
- ◨
- AJNA
- TUA
- BMR
- TTK
- SATX
- CHORUZ
- EQX
- AIT
- CHO
- WAIFU
- X
- SDFXN
- HON
- GRUMPY
- BLEND
- SHITZU
- MAIA
- MOSS
- L8CAP
- PBTC
- BFT
- GROWAI
- SHFT
- QKNTL
- STRUMP
- ROOST
- BENI
- FCL
- PREME
- $HAMI
- TAMA
- BABA
- 21M
- SAGE
- JAIHOZ
- NOOOO
- MAX
- DVY
- CWS
- ITGR
- MBTCS
- MBXN
- GSNAKE
- VIBE
- OXYZ
- CERTAI
- CROW
- INF
- UNQ
- S
- GHOST
- EXCC
- HAN
- LEND
- PLR
- HESTIA
- QCK
- DOG
- CBM
- GASP
- MPS
- BARIO
- AMU
- RONNIE
- BUMP
- BRB
- PICA
- MMPRO
- WALV
- MZERO
- WETH
- BMT
- CROWD
- TOKO
- SQDGN
- WBLT
- BSOP
- BUNKER
- STUPID
- PKR
- PAY
- WANA
- K21
- WHALE
- QMALL
- $IRL
- ATEHUN
- DXD
- FATHA
- PUMPCORN
- AGX
- ASTRL
- CIG
- XAVI
- TOTO
- YAI
- HAKKA
- TURBO
- ABDS
- TURT
- BELT
- VZ
- BURN
- KIRA
- XUSD
- ANON
- VU
- CONVO
- PMX
- CATANA
- AIP
- DOAI
- X
- PEGG
- VSTA
- $SHARBI
- WBS
- POGAI
- $PUCCA
- NORDO
- TITCOIN
- OK
- $ELON
- HEFI
- CUZ
- CLS
- STARSHIP
- OOKI
- LILAI
- KCCPAD
- KICK
- SHOGUN
- MEME
- DSETH
- HBB
- RTIME
- KITTENWIF
- PERQ
- PEN
- LARA
- HEDGY
- BTCBAM
- XET
- APPLE
- GONDOLA
- PTRUMP
- AWS
- NETT
- PRNT
- CYBRO
- BESC
- HYVE
- ANDYMAN
- CLINK
- TUBBI
- EXO
- COOL
- AQUARIUS
- RVST
- MURAD
- DEOD
- MISATO
- YOKO
- JUP
- MUTE
- BSCS
- NEST
- AI
- CHIPPY
- OSEAN
- USDFI
- SOURCE
- DFX
- FEAR
- CIRCLE
- WEALTH
- BED
- TES
- FLSH
- NIZA
- MKUSD
- WNT
- SP
- AKRE
- TROVE
- BCAT
- BOOH
- BRITTO
- RKFI
- QUAD
- ETHO
- LOA
- SAKAI
- NABOX
- GEMINI
- FKR
- CHARLES
- SEVILLA
- DJI
- DUREV
- REGENT
- FOUR
- AMO
- BCDT
- KWANT
- $BROKE
- EGG
- GBCK
- BUILD
- PANO
- PHTR
- RAFT
- KDR
- PEPES
- MUT
- F/ACC
- KEIRO
- SUT
- NORMILIO
- PONCHO
- OMNI
- AUR
- BLINK
- CRGPT
- WOOP
- UNICORN
- POINTS
- OPIUM
- SOONX
- BNBAI
- MARCO
- FREN
- WDOG
- ALPHA
- FIT
- USDT
- USDT
- SUNTRON
- COST
- CND
- FLP
- EZ
- AIM
- MOE
- 8CHAN
- CWAR
- PLENA
- SOLA
- FLU
- JKC
- WDC
- ARC
- CLO
- CPAI
- TAURUS
- MOOMOO
- CATALORIAN
- PRONUT
- WIGL
- COQAI
- SBR
- REV3L
- MTH
- DORA
- MA
- TRENCHAI
- WOMBAT
- EARN
- WEHMND
- BINGUS
- OGSM
- 99BTC
- CURE
- 0XBTC
- ASI
- TDM
- XBLAZE
- PSSYMONSTR
- SOLO
- COME
- DACAT
- KOMET
- $AMEN
- EMILIA
- MELD
- SONE
- HYDRA
- SHIBC
- FAME
- ZMN
- SOLVE
- SOLARIS
- ANDY
- FIRST
- TORSY
- WIFE
- TOOKER
- SECOND
- FLOWER
- KWAII
- CNG
- RIC
- WGR
- MAIV
- SMARTCREDI
- INJX
- AIX
- $GNZ
- PUMPKIN
- FOFAR
- LOAFCAT
- GEKKO
- TSWAP
- SNAIL
- SPERG
- GRLC
- AVIVE
- DEEPAI
- WORK
- MCL
- BCOIN
- BONE
- W3GG
- HERMES
- PSWAP
- GAMI
- HTERM
- SAI
- SAM
- PNDR
- PGOLD
- SUB
- USACOIN
- LINU
- SPARTA
- NFTFI
- YOUSIM
- WNDR
- $CROAK
- FINC
- ROAR
- CHEESE
- BLUESPARRO
- BEENZ
- BIAI
- BEATAI
- ARCA
- LONK
- WONG
- HOGSCOIN
- HIM
- BRO
- TETU
- SPHYNX
- BCCOIN
- OLYN
- BMON
- GORILLA
- IONA
- SHAR
- CIA
- OPTR
- PLQ
- E/ACC
- TRUMPIUS
- CATGPT
- WF
- COINYE
- $SPACE
- AIRI
- KINGSHIB
- IPAD
- ALEPH
- SEED
- PSL
- BTF
- GEKO
- D
- SPIN
- STAM
- SPEX
- COMSWAPWLI
- BTCZ
- TECH
- LEO
- REXBT
- SUNWUKONG
- MYAN
- DFP2
- BHAD
- TKST
- ATRI
- ROCK
- ZACK
- DEFROGS
- MEOW
- BIP
- AICM
- UNISTAKE
- STOIC
- BOP
- LOKY
- YAY
- BITZ
- DUCKAI
- ZYN
- STRONG
- CHAMP
- CLEV
- CELA
- AUTISM
- CNCT
- ROP
- SOLARBA
- CNDY
- PARTY
- ZELIX
- METH
- PAPER
- CNV
- WAI
- $TIMES
- HEDGE
- NIGHT
- CATGIRL
- ASSCOIN
- GEL
- GRAV
- VEGA
- RSN
- CREA
- NEON
- DOGECAST
- KEE
- SPORE
- DEPLOY
- LOON
- MEWC
- MARVIN
- NEMO
- JONES
- $UOS
- MGT
- ROCKY
- HNST
- PURPLE
- HBARK
- OCH
- DMOON
- CHEXBACCA
- CHUCK
- DZOO
- CVAI
- ORDS
- HNC
- WNRG
- INT
- USDT.ETH
- LEND
- PARA
- CADAI
- SCORPIO
- GODL
- SAGIT
- ZIK
- MONAI
- MYST
- ROOK
- CDOGE
- XYZ
- $ACE
- KOVU
- CAPRICORN
- BLAZE
- TENET
- LONG
- ARIES
- XD
- BAG
- GEC
- SENSUS
- CBPAY
- FATAL
- DASHD
- ABOND
- VOLS
- FWB
- PEW
- 🐕
- GARY
- PISCES
- CANCER
- MONSTA
- GUILD
- XPE
- ZOO
- STELAI
- GRV
- OCADA
- NEURAL
- COAI
- BFIC
- PEAK
- PI
- COAL
- YMACH
- SUIYAN
- MUDOL2
- PEPE
- RPK
- GGTK
- GC
- WALTER
- UPTOS
- FCOD
- CLASH
- BIST
- YEETI
- GFT
- BIX
- $BEAT
- BLT
- PIGGY
- PINKM
- RADIO
- WANNA
- VIRGO
- YAM
- ZUSD
- SKICAT
- OVER
- DWEB
- ACS
- SANSHU!
- ZCL
- WGC
- BFT
- KIM
- ATOLO
- AGI
- BURT
- FUEGO
- PESTO
- VEIL
- CGAI
- RM9000
- MINIDOGE
- BHAT
- DEGA
- COVN
- WEB3D
- COV
- XMY
- ROOBEE
- $AGENCY
- KIF
- WECO
- $COOK
- DBI
- PEARL
- LIBRA
- POV
- $PLATH
- TWX
- PAC
- MMA
- APU
- SOLANA
- GOVI
- HYDRA
- KTON
- JULD
- MOTOKO
- BEND
- KEK
- RNB
- NAZAREAI
- DGNX
- GLDT
- SLICE
- YOU
- JIM
- RCAT
- ILOCK
- PROTEO
- DOGK
- GMB
- XSEED
- NCTR
- DTX
- XWG
- DAI
- ZEE
- ADASOL
- $SAIKO
- $UPDOG
- FORTKNOX
- DPS
- VERDAO
- THC
- BRIUN
- CARAT
- XENO
- ELAND
- TASTE
- NAILONG
- FORT
- DEGENC
- FIRE
- AIWS
- HOP
- DNA
- CHAOS
- WYNN
- LC
- EOLAS
- IXI
- WILDNOUT
- PINU
- SETAI
- MANE
- FREE
- TKAI
- WN
- MPH
- PLOT
- TRG
- BTN
- UNICE
- VITE
- XUSDT
- $ARKEN
- SUPERCYCLE
- EX
- 🏦
- VAULT
- SATOX
- CGT
- KAT
- DCT
- CHEEMS
- SMI
- LAKKHI
- DONUT
- BARRY
- TRC
- TRAXX
- MEMEAI
- APAD
- NFE
- BIS
- RYOSHI
- HAUS
- $CATS
- CLH
- EXM
- KREX
- SIM
- MONK
- MELON
- BZE
- MANA
- ZRS
- PEPE
- USDX
- ANDY
- FRM
- INETH
- MSR
- BANDIT
- BRLY
- COBY
- Y2K
- UXD
- ELFI
- UNI
- INSUR
- OMEGA
- $KANSTAR
- USDT
- VNST
- THECAT
- ENKI
- KDG
- WAT
- TC
- VERSA
- BOB
- DRINK
- LOOT
- HOLO
- RBTC.B
- KABOSU
- QUIDD
- TIFI
- DOGSHIT2
- TIGRES
- HIT
- MILKBAG
- QRX
- REX
- XEQ
- RIDDLE
- FWT
- LYRA
- NOT
- SHROOM
- RELAY
- FURY
- ENKI
- SMACKM
- GOCHU
- WTFO
- SYLVIAI
- DRAGGY
- POLYPAD
- ARBX
- FLI
- PAC
- MVX
- IVPAY
- FYDE
- SHIBU
- PMON
- IVN
- BANGCHAIN
- $WEEDE
- KLY
- GENI
- ION
- SHEGEN
- CREATE
- VKA
- $RUG
- EKKO
- CMDX
- SATA
- $CHESTER
- BABYBTC
- SYNC
- SHIFT
- METAV
- ASSAI
- FLIPPY
- AGLA
- WOOF
- CIV
- BLOC
- AIEPK
- ADOGE
- TAOSHI
- RATING
- USDV
- SIRIUS
- DUCKIES
- DEFAI
- BROTHER
- TREAT
- AIVIA
- TITAN
- STOG
- PLASTIK
- KSK
- GXT
- ZEN
- DNOW
- DYOR
- CASH
- GYOZA
- DACKIE
- CHONE
- SHROOM
- RAJ
- SWARM
- NEWO
- BTRUMP
- THAT
- BONUS
- B20
- SKITTEN
- NAYM
- KNOT
- CORN
- GM
- SMOL
- YF-DAI
- $DICE
- SUITE
- XBC
- KLEE
- XLA
- VATRENI
- BOPPY
- LABZ
- FWC
- XVN
- ECTE
- CATF
- DFNDR
- CYB
- $SOULS
- LMNL
- AIDA
- POSI
- YES
- INUINU
- DIME
- KEKE
- $LOCKIN
- REGENT
- GOR
- $OTTO
- XNV
- KIRA
- GLDS
- BUILD
- CBX
- AXI
- BORING
- SPX2.0
- ELGATO
- SIMSAI
- L7L
- ODDZ
- SWOP
- XCREDI
- MON
- FOAM
- ETHUSDC
- PYM
- ONC
- EQPAY
- ECLIP
- NSTSTRK
- KONAN
- FREN
- C2H6
- DRX
- VIP
- MEFA
- RAB
- USDT.BSC
- SSSSS
- TGMETRICS
- CGG
- RCN
- WEWE
- REALM
- WAIFU
- SPR
- CPA
- $OZONE
- OCI
- MARO
- ZMT
- LULU
- GLINT
- PINGU
- APED
- COC
- W3F
- MPUP
- DUCK
- TORI
- BIGFACTS
- CHOCTOPUS
- EMBER
- AIMBOT
- PEANUT
- IDNA
- EXA
- SHUI
- TORI
- WSG
- TRUMPSFIGH
- JUICE
- THOL
- CT
- UNIO
- CCX
- USACH
- PVU
- $INTERN
- AUDAI
- SHIELD
- SANI
- HOKK
- WANDER
- TIPS
- NAVAL
- FLIES
- BITCAT
- THE1
- RHUN
- FLAME
- ALPHA
- SHIRYO-INU
- MOON
- H
- KOLZ
- 2DAI
- BLB
- BONKERS
- EDG
- MTS
- BOOJI
- USDC
- RUNNER
- STAPT
- STJUNO
- XPNET
- CHMB
- CHILLGUY
- DNVDA
- PAPERCLIPS
- TOKI
- CENTS
- ETI
- KNIGHT
- PSYOP
- PONCH
- RAMA
- DOOMER
- USDT[HTS]
- TTM
- SOBULL
- TSLT
- USDW
- SEED
- LTD
- H4CK
- CHAD
- ARO
- $QBIT
- OCAI
- R/SNOOFI
- JPOW
- PYRATE
- SUIMON
- ESOL
- ONION
- HARAMBE
- USDT
- NALS
- PFL
- RUM
- WETH
- LOD3
- ARTH
- GIA
- QLIX
- CLEO
- APOLLO
- GOME
- NINA
- KNUT
- ETP
- $MYST
- KM
- INX
- MEOW
- SWPR
- KIRAI
- POCHITA
- DIDID
- $MARU
- BOTON
- SPICE
- DEFAI
- OCC
- NCASH
- ILY
- LINDA
- THUMB
- BWS
- KACY
- DPET
- MAG
- VENT
- VEMP
- FLS
- SATT
- XRP
- ALL
- VES
- DELAY
- MARS
- SUIB
- SILVA
- ZAPO
- DOGAI
- PILL
- NSBT
- PIGU
- FLAT
- STINJ
- SACI
- WIT
- POOKA
- $HOKK
- VASCO
- OKY
- BRIDGE
- HID
- MVD
- EDAT
- GYSR
- $SITCOM
- AIT
- KCH
- XLG
- SAG3
- YDA
- INSC
- KNOX
- CIRUS
- VAR
- BDX
- CONE
- BASKT
- SCC
- QAI
- CATDOG
- DEFAI
- LOT
- GRAI
- USDC
- WHALE
- NEER
- AXIS
- CLND
- O3
- WOLF
- DAWAE
- VSX
- USDT_T
- CYBA
- $PRO
- MFT
- USDT
- PEPO
- BET
- $BOOB
- MANIFEST
- SUWI
- ETH2X-FLI-
- MT
- KORI
- STSEI
- BONECOIN
- FROQ
- FXUSDC
- CHAN
- EVEAI
- GLINK
- NETZ
- TOR
- ZGEN
- VYPER
- AX
- HND
- MRSMIGGLES
- CLOAK
- MYRC
- NDX
- KITTY
- PAD
- LOLCAT
- BBOT
- MONA
- TIME
- BULLIEVE
- BANK
- RIBBIT
- CTT
- EGG
- FELY
- KRA
- CRAPPY
- 🖕
- LRT
- TIMI
- $VAULT
- FATGF
- DRAC
- INBRED
- SHAKEY
- AI
- YGATA
- PEPEC
- SCOTTY
- NFTART
- OVO
- USDT
- CBANK
- LUDWIG
- WICKED
- EPIKO
- FRIN
- LAB
- GOON
- SHIBUSSY
- SHEZMU
- KDAO
- MARVIN
- LUCI
- JETTON
- OGGY
- MANYU
- RISE
- TCAT
- BROT
- KRIPTO
- GLS
- GM
- HOMO
- UME
- RVLT
- SIZE
- PAC
- SOLFUNMEME
- BANJO
- DOGGO
- SHEESHA
- PLEDGE
- REUNI
- NUX
- USDC.E
- CATHEON
- TOPG
- TT-WBTC
- OGME
- BAKKT
- FURY
- CRISPR
- GLCH
- CAT
- PICKLE
- KOY
- TOBI
- ROCK
- NEP
- SAAD
- NR1
- DOG
- GULL
- SPACE
- HMQ
- BLAST
- GOO
- ATD
- CHEYENNE
- KAPPY
- ANARCHY
- GUAN
- ACTUAL
- LDY
- SLOP
- CSW
- KAAI
- IRT
- ZACHXBT
- HYPER
- ALR
- YLD
- ORBIT
- VETME
- MIND
- PROL
- MONK
- WAIT
- BRNX
- MUG
- X
- BLXM
- LOOK
- ZYRO
- QUAIN
- 3P
- BOG
- TAGGR
- PET
- ROCKET
- MOCA
- SUIJAK
- VOID
- EML
- WABBIT
- DND10
- RHYTHM
- BABYSHIB
- WBTC
- SPINDASH
- CS
- MVP
- CHPD
- PEEL
- ELMNT
- CATO
- PLATY
- JELLYFC
- DIP
- FLOCKA
- BMI
- LQDX
- BRO
- BAINANCE
- BUILD
- ATHENA
- CHITAN
- ✖
- WOOF
- AXL-WSTETH
- AX
- UAI
- XRUNE
- CALICO
- LANDWU
- TYRANT
- $LILLO
- WETH
- VAL
- TAX
- TFI
- EBERT
- PTOY
- LPUSS
- OGC
- APR
- USDC.E
- USDC
- OLY
- MOOSK
- AYB
- XKI
- VFOX
- DOUG
- FCO
- BIAO
- SCB
- ETHEREUM
- SCCP
- BCMC
- MAGAA
- PTF
- KT
- SWIFT
- LOS
- SPO
- USDC.E
- KEKIUS
- HOPPY
- L2
- ZWAP
- HUSH
- CAINAM
- CAN
- MIMANY
- FAI
- USDC
- GUA
- SUITRUMP
- TRUTH
- ZHOA
- FFM
- DGH
- $BETH
- RMT
- RICK
- INK
- WELT
- LOOBY
- NOOT
- KAT
- ETHEREUM
- SUIDEPIN
- SANTA
- WIN
- NAI
- BUTTHOLE
- DOGE
- EVAI
- SORA
- MIA
- DEER
- API
- UDOGE
- VIRTU
- SFD
- BLACK
- PICA
- PEPE
- NYAN
- ARA
- EVOLVE
- BANK
- ECOIN
- MOGUL
- NIGELLA
- SHOP
- FLAME
- MF
- REPOALYZE
- ACE
- UGLYDOG
- CNS
- FLASH
- ONTOS
- COK
- USTREAM
- DCHEFSOL
- $LOCG
- ZAI
- CRYORAT
- LNR
- ARCH
- @DOGE
- SHEZETH
- IB
- WBAR
- BLOCK INN
- MFG
- SAINT
- KHEOWZOO
- LOE
- OLT
- METO
- RMT
- ITP
- CABO
- MIHARU
- $RAINI
- USDC
- EOSDAC
- INVITE
- WIK
- LIQ
- CCP
- IETH
- SVMAI
- XWIN
- RODAI
- SL
- WETH
- USDT
- PASTERNAK
- MTRM
- NORA
- PHONON
- CORGI
- FFTB
- CARBON
- CORN
- EUSD
- GEOFF
- SHATS
- MOON
- GROYPER
- TREEINCAT
- SHRED
- DELI
- NAVI
- AIMX
- SPUNK
- RABBIT
- BPT
- RSTK
- BUILD
- ZYGO
- ZKEX
- ZODS
- PYRA
- LEMON
- NAWS
- LYM
- PEANIE
- HLT
- BTCST
- BUNBUN
- SWM
- BAO
- RBW
- CLO
- BORK
- NAIFU
- SOV
- 1ART
- LUIGI
- NOVA
- OOZY•GOOZE
- HUNNY
- NONJA
- MOVE
- ZLK
- PCORN
- VISION
- VIX
- PAINT
- MEOW
- ERN
- $WSB
- PSY
- GOMU
- IAMAI
- SOLCAT
- MERGE
- NOCHA
- TRI
- ERIC
- MILK
- DXY
- WSB
- ENTR
- PBTC35A
- ETH
- XCASH
- $CULTUR
- KASJAK
- SYNO
- MAGICK
- LRS
- BRKL
- KMC
- TSUBA
- MFAM
- ILLUSION
- AICMP
- POTUS
- KWAK
- MEGA
- NSDX
- DAD
- O3
- SHARKI
- DYNA
- CROS
- DNT
- KEN
- LOOT
- ELONIA
- F2C
- USDT
- USDT
- $AIGG
- ∅
- ROT
- MCG
- AISTR
- MATT
- MVRS
- $ICONS
- TRDG
- BLUES
- WMM
- CRODIE
- DTI
- HOL
- IFSCI
- $BLU
- SUNPIG
- NOTI
- TOP
- NEUROS
- DOGMI
- MMF
- ATAI
- SPR
- TOH
- TCT
- RACCOONDOG
- BONK
- DLTA
- AVAX
- BEATS
- TATE
- RAIN
- PRIME
- OCN
- MTG
- SYBTC
- OSIRI
- WIRE
- SEBA
- BASE
- TRAI
- BAT
- DALGO
- ATA
- CLUBMOON
- SCOUT
- BETA
- DRPAL
- DON
- OF
- ARSW
- LOOTER
- CUR
- POD
- GDUPI
- TXN
- FLC
- TIDAL
- NODE
- COMCOIN
- $COFFEE
- MS2
- ZAPCAT
- POODL
- SECT
- NEPT
- NFTBS
- XMX
- PNT
- AGA
- UNEAR
- LEG
- YBO
- KCN
- FTW
- CONV
- PEFI
- LUCHA
- KAGE
- PERI
- HAIR
- INXT
- CAPPY
- NOX
- MONA
- MTRC
- EBYT
- DCI
- CLX
- ZSC
- LUBE
- BBL
- PODGE
- CODE
- SMTY
- ESS
- MEVETH
- WAS
- TOPKEK
- PIPE
- ALF
- DGI
- RE7FRAX
- $BIRDFLU
- ROGEN
- MAHA
- OATH
- WPSG
- OSMI
- BONKEY
- WHACKT
- BEZOGE
- RDX
- PUMLX
- BUU
- RUGGA
- DMND
- TICKL
- $CAT
- SOS
- XMS
- $ONION
- MTR
- RFUEL
- $BABYLONG
- ALLIN
- ANTI
- VOLTX
- PORTX
- BSTY
- FORKY
- BENT
- DYOR
- BTA
- WOG
- ECO
- FOMO
- FAP
- CTR
- CODEX
- BTW
- ARTX
- BAHIA
- NEURONI
- HEC
- TULIP
- ROUGE
- VBELLS
- ARROW
- SPCTRM
- KONO
- $TORO
- CHIB
- GATSBY
- MEAI
- CRP
- OPK
- TZPEPE
- DPLN
- PLANT
- CHEERS
- WHALE
- PARAM
- LION
- MILK
- FODL
- IDEA
- COMFY
- GODEX
- 39A
- RADAR
- AWARE
- MBAG
- CURTIS
- THGUY
- GOAT
- SOH
- $RICH
- RURI
- RADIO
- CORGI
- BSEN
- HSAI
- GMPD
- USDC.BSC
- ODIN
- VOLT
- GAGA
- SPIRIT
- DAW
- CAT
- WJUV
- BUILDX
- AXE
- SANTA
- SU
- REBELZ
- GHSI
- CANDLE
- PIX
- DOGECAST
- SHI
- GSE
- OCEANS
- IONX
- FIRST
- MMAI
- NEW
- DEGENOS
- GKAPPA
- $DAPY
- MORUD
- MOO
- UTS
- BLANK
- TUX
- JEFF
- AAG
- MOON
- ASHA
- PRO
- LEE
- DANCE
- DEEPAI
- UAPT
- CUT
- PRAWN
- ELMO
- ZFI
- QDFI
- CWT
- AEGIS
- WBTC
- HBARBARIAN
- LAD
- URS
- CORE
- CYT
- TTC
- USDT
- PBR
- DEPINS
- MEOW
- MOOSE
- CFI
- SI
- SVTS
- SHIH
- NFTL
- SUUSD
- CSI
- AUDD
- BEEG
- CULT
- BRETT2.0
- DAFI
- KOGIN
- BRO
- MVC
- DRC
- $PIGGY
- PXL
- MINDS
- MOX
- RELIGN
- USDT
- SNAPCAT
- CAI
- AART
- $SHRUB
- AIVA
- APTR
- SPFC
- KUMA
- SOY
- CRYPTIQ
- PAI
- $HORNY
- BNSD
- KANGAL
- $SNIFF
- JAK
- AA
- FECES
- STARGATE
- HAROLD
- APEMAN
- ETHPAD
- IKB
- BD/SOL
- JOI
- CRX
- MAYO
- IMMORTAL
- SBAE
- GRAIN
- LQC
- BNY
- BLADE
- LEXICON
- IFC
- ZAPI
- 42
- PROME
- GOLD
- TALK
- TONE
- QUA
- WATM
- OPM
- SBOY
- BERRY
- AVA
- $DMP
- ARQ
- VRSW
- ORE
- BTM
- MERT
- MERO
- MOB
- LIZA
- GGG
- FEVR
- BOMB
- 1HUB
- NAFT
- VXL
- SHND
- NAOS
- DRU
- WIF
- DFIAT
- WASP
- OBX
- GAIB
- MET
- COOK
- WPR
- LED
- MITHR
- BOSSIE
- BIRDDOG
- DOLLAR
- ARMY
- RIA
- MWD
- HALO
- GREG
- TAI
- YT
- BALTO
- SEN
- INS
- THX
- ETHM
- $CRAMER
- ECHO
- $JANI
- WDOT
- SPIKE
- LILY
- KENDU
- PPAY
- DECHAT
- FLUFFI
- INU
- TURBO
- EFR
- FOMO
- $VOX
- WOWO
- BASEX
- TMSH
- PPBLZ
- ODIN
- CEB
- ZUN
- NFTD
- LUMI
- DOMES
- PAC
- LILB
- GAI
- PWROSE
- BULL
- SOG
- RGEN
- EAGLE
- WORM
- HDAO
- GFY
- CHATTY
- GHFFB47YII
- FREECZ
- PMA
- LINK
- XIDR
- WSPP
- SKAI
- PETER
- HELMET
- SYNC
- $TINYP
- YAP
- IUSD
- MONKEY
- RETRO
- EYE
- POLTER
- CSWAP
- WIF
- BAOS
- YES
- BTCACT
- SPELLFIRE
- DEV
- HANA
- CLAUDE
- BCOIN
- AFC
- LIQQ
- SUIMAN
- MATRIX
- KMON
- DREP
- BABYPEPE
- CKOCT
- ACHI
- RISITA
- EDAS
- NAMI
- GOB
- HER
- PLY
- PING
- PIZZA
- ZER
- SHOPX
- GORPLES
- $RECA
- TIN
- DIGG
- MSMIL
- GOH
- GARY
- VUSD
- GAL
- WEBSIM
- LENDA
- TRUTHFI
- VELA
- MAKE
- AURORA
- SHIT
- USSD
- SWINGBY
- CATBOX
- SQRCAT
- WAWA
- LITT
- XY
- KOBA
- ATM
- AQUA
- SEAL
- BNU
- GOBI
- STX
- NEU
- XNL
- STRNGR
- PLANE
- KOVIN
- KWIF
- DINU
- WOPTIDOGE
- NEZHA
- DBTC
- BRIGHT
- ROGUE
- STA
- JANRO
- MUST
- DAWN
- FARA
- ARG
- GAYCOIN
- CHAD
- BWORM
- DOGECAUCUS
- STV
- DUCKER
- MIST
- GALO
- TRC
- LUFC
- NOWK
- WASR
- TDS
- GIDDY
- ICE
- CALLS
- ZEREPY
- KFT
- COINBT
- DDD
- DMAGA
- CROFAM
- ZILLIONXO
- FINA
- GRAF
- MONKE
- ZAT
- HELIA
- $ITO
- MOLLARS
- FREGO
- STAKE
- LIEN
- $BEFFAI
- MAO
- SPEED
- BANDIT
- NFT
- KAKA
- PEPE
- BETBIG
- RUFF
- QUINT
- GDOG
- INTAI
- BLOCK
- WATCH
- PNUT
- SCR
- SIMON
- PEANUT
- JARVIS
- JAM
- META
- FWOG
- PUPPERS
- BALLZ
- MET
- SPEED
- TXL
- SKILL
- SNAP
- PHX
- WETH
- BLEU
- SAM
- HSC
- DRAGONKING
- CATS
- APU
- CYBER
- GROGGO
- $PULSR
- DORA
- GROKINU
- HYENA
- BASED
- TRACKEDBIO
- ARBI
- LUCHOW
- SWAPZ
- HINAGI
- CLIP
- $GIGAI
- VSG
- NYXC
- XED
- GCOIN
- BABYTRUMP
- MOBY
- DUSD
- MOG
- SKRT
- BSV
- TH
- HOBBES
- MEGALAND
- JARVIS
- MONI
- VCTRAI
- VRX
- SCHRODI
- KABOSU
- WCITY
- OUTIE
- NIOX
- BTX
- CHULO
- WACM
- UFARM
- DCAU
- UTG
- CORN
- BIF
- GDOGE
- YBR
- GNME
- FLUX
- KEYCAT
- DGI
- ZTH
- HPAY
- SBKPT
- PYI
- CUPSEY
- LGTB
- BERF
- XDN
- BRETTGOLD
- CO
- GOOBY
- RFSTETH
- CSAS
- BABYNEIRO
- HOOT
- LOTTY
- GEM
- UTU
- AETHER
- HGT
- RAIDER
- TRIBE
- MUG
- PSM
- SELF
- BIRB
- BKIT
- ACT
- ALICE
- SOLAYA
- CHRONOEFFE
- MOON
- SGT
- SQUAD
- SHEESHA
- IBR
- LIFE
- AVERY
- $BOOTY
- CROGINAL
- BABY
- SIZE
- WETH
- RFR
- GMX
- NOODS
- UPDOG
- FLY
- $BROKIE
- ANIME
- KOAK
- CATEX
- KOAI
- EKTA
- NEVER
- GAMBLE
- D.O.G.E
- COLON
- DOPE
- AFIN
- $KEYDOG
- NIOB
- KING
- HGET
- COIN
- RYIU
- MILTON
- COPE
- UNB
- PINEYE
- USD3
- PFI
- GFT
- HEMPY
- BLOB
- TT-WETH
- WAGMI
- OCAI
- ALL
- SEN
- PLANETS
- BOWSER
- EON
- DYOR
- SASHIMI
- KEIRA
- SACA
- $MRKT
- PROPS
- KALM
- GEM
- KPAW
- FRENS
- ZILPEPE
- SHIKOKU
- ROY
- MVDA25
- DAI[HTS]
- LGNDX
- EEUR
- SOURCE
- HUMO
- BOSHI
- DOCUSOL
- PEPEW
- BANANA
- SOL
- MITH
- PORT
- ADX
- MASS
- MEDUSA
- MER
- $FRANK
- USDT
- SENDOR
- CHEDDA
- KIDEN
- HOP
- NEBL
- TERN
- FORE
- DREAM
- 8PAY
- CAT
- ETF
- LABSV2
- VERSE
- COBE
- THOG
- SDOGE
- UNIX
- MEWING
- MARV
- BAI
- SEDUX
- FROG
- AKITA
- ANTC
- YAWN
- KRIDA
- MGPT
- NICO
- META
- HAWK
- SHDZ
- BOSSU
- MOTH
- MEI
- CB
- BRY
- MVRWA
- SNTR
- PADAWAN
- $SCARF
- SDOGE
- AGORA
- SOLO
- CAKEDOG
- MKAT
- AGB
- NOHAT
- BCRE
- SOLY
- ARBOT
- RB
- PUMPAI
- CHILLAX
- SQR
- LONG
- CHRIST
- DFX
- XCEPT
- BREAKER
- TPAD
- OS
- SLB
- ASTRO
- RUG
- MUSTARD
- PRNT
- JASON
- EDOG
- NCAT
- AIC
- 2077
- PINO
- MEDUSA
- NFTY
- RNA
- FOXGIRL
- SSTR
- NEIREI
- ABX
- OPSYS
- CHWY
- DUCK
- PLOP
- CIRCLE
- ORBK
- POLX
- D2T
- XCT
- FEETCOIN
- ONI
- SCOOP
- MITTENS
- ORACLE
- BUCK
- H1DR4
- SABLE
- RAINBOWTOK
- POPSMILE
- FOMO
- DRIFT
- DRGN
- ROPIRITO
- KTC
- NEONET
- STAB
- MOOVE
- VDT
- OMOCHI
- BEAST
- MEMETIC
- CHICKS
- LVM
- MINIGOUT
- MEARTH
- ONX
- UNLUCKY
- EGG
- SLCL
- CRAFT
- GNRT
- DEFIDO
- VETH
- BABYNEIRO
- SCALE
- OPTION
- LIQ
- YETI
- TOAD
- USEI
- DFY
- ASTRADAO
- PCNT
- GF
- 霞
- GAIM
- SMF
- ALASKA
- SMR
- CHEEMS
- BENJI
- ISLAMI
- NULL
- MYRA
- YOTO
- NEROBOSS
- FIT
- SHORK
- GNX
- SUB
- BRRR
- BALPHA
- AAI
- PLY
- TPU
- DFND
- FARTDADDY
- SAFU
- BCP
- SCRAT
- BISO
- CERES
- ROCK
- SOLAR
- PILLZUMI
- BS
- ASCN
- DATAWITCH
- GINNAN
- ISHI
- TOKITO
- UNVAXSPERM
- ALGT
- MOTA
- KICKS
- EROWAN
- BABYPOES
- SI
- PUSO
- DAI
- MTOS
- HAT
- JOHN
- JASPER
- ARKI
- FBX
- STEAKETH
- MELO
- CUMINU
- CASH
- MVTT10F
- CU
- BABYCATE
- TERMINUS
- INF++
- CRYING
- AUTIST
- IBFK
- TOSHE
- SOL
- SHIBX
- IZZY
- DAWGS
- EYE
- PAC
- AMI
- TRIANGLE
- TINU
- SHITCOIN
- ODDS
- PEPE
- SVD
- ZEBRO
- REAL
- WOKIE
- WHALE
- BTL
- NFAI
- LARRY
- CPL
- CEWBTC
- GOWOKE
- HENAI
- CATWIF
- REM
- MONKE
- NXR
- LBA
- EMC2
- KWT
- GSC
- CORA
- MFI
- BAC
- HAWKTUAH
- NUGGET
- USDT
- SCREAM
- $DCAY
- CHIPI
- HOD
- AEON
- BTO
- SFT
- VCAT
- TAY
- SAVG
- CWH
- DOM
- CRA
- ORION
- CATGF
- BALT
- ZCO
- 32
- POPEYE
- HUAHUA
- DUCKY
- ANDY
- KOI
- LQT
- MFW
- JORGIE
- TWRAE
- 47
- RFT
- NIKITA
- SWRV
- GLP1
- CRUSADER
- GONE
- FORK
- SCF
- MMT
- COR
- DXGM
- LEO
- ESPORT
- OCD
- ZOOMER
- WSPURS
- VPK
- CNC
- BLUE
- IKIGAI
- PEPE
- $ZKITTY
- LILPUMP
- RIZO
- SADMEOW
- SRN
- CHIPS
- BIRD
- OCTO
- DOGIN
- GOAT
- CRE8
- NOAHAI
- LUCY
- ROCKY
- FABS
- SONNE
- COLLAB
- ALP
- GAP
- FRUDO
- BLAZEX
- SADANT
- FORM
- GNOCCHI
- FUNG
- NORD
- CNNS
- MAGAPEPE
- ROBO
- SUNPEPE
- VAULT
- MDS
- MERGE
- ARES
- INTERN
- $DOGE
- HUM
- A16G
- DINU
- BABYSOL
- EGG
- ARX
- BGA
- AGME
- AVN
- STSTARS
- SEED
- FROGS
- HIPP
- FOMOON
- FINS
- TCAT
- WHAT
- GINNAN
- NDAO
- GATTO
- NEXT
- FLURRY
- LMF
- PSEUDO
- ANI
- BIRDDOG
- DAI
- POLI
- PONZIE
- USUALUSDC+
- NIPPY
- PHX
- ARXIV
- GNFTY
- DEGENT
- RCH
- BIAO
- KCAL
- CORTEX
- MCEN
- ONC
- VDL
- EQZ
- CATVAX
- GECKO
- CORSI
- OINK
- PEDRO
- FLAT
- BUSY
- ZZ
- FROG
- SUPERBID
- UNN
- DUK
- HOPPER
- KAPSA
- ALA
- DINO
- STAR
- USDCAT
- BULL
- OMEGA
- DMT
- DTC
- JUNGLE
- GAS
- SSTX
- MISHA
- $CHILL
- MXNE
- MOONY
- BSDX
- BAKSO
- IUS
- GAMEFI
- SOLAPE
- KAMPAY
- MAGNET
- ELEC
- BAZINGA
- RLP
- COT
- GOU
- KINE
- TRIVIA
- QHUB
- DXL
- AGURI
- EMON
- KOL
- AIR
- HAGGIS
- KAMA
- SSNC
- BUTTPLUG
- FA=FO
- DGENAI
- FOXXY
- MIDLE
- DAI
- STICK
- ALETHEIA
- MNST
- BRUME
- ZODI
- GORT
- HANBAO
- SCA
- FXF
- KANDO
- WORKIE
- KOHLER
- VTF
- ARCD
- BLEP
- PWR
- ATS
- DRPXBT
- APES
- SOLX
- NYZO
- PENGY
- SAIL
- BRAZA
- EDX
- GLAM
- OMAGENT
- MEME
- MEAN
- HSM
- STD
- PUFFY
- PACOCA
- PRERICH
- ISAAC
- BOG
- AFFI
- SWAY
- NLC
- FTP
- GWIRE
- BASED
- FUKU
- TYBENG
- LSD
- CTF
- FLUX
- MEMD
- TMANIA
- MSCP
- DXAI
- CAPO
- GAG
- ZINU
- UWU
- PANA
- IDYP
- ITXS
- GENESIS
- EVA
- FNT
- UBTC
- JORKIN
- SINK
- SQUID
- ZORRO
- SPIKE
- STAKELAYER
- BULL
- XYRA
- FIWA
- SAI
- PARADOX
- SOLGOAT
- $RRT
- ARTTO
- BULLA
- BLADE
- TRUST
- FLAVIA
- IF
- SHRIMP
- SPOODY
- LCD
- FINE
- AI69X
- DHV
- AGI
- TURBO
- SHIA
- DYP
- QORBI
- REAP
- MINT
- BASED
- AES
- WAGIEBOT
- GIRLE
- IDV
- OCX
- MOLA
- ERY
- DISCO
- GLFT
- YOURAI
- SNN
- WBTC
- TOSHI
- PANTERAI
- ORBIT
- NINJA
- ARMOR
- FOUR
- GM
- GG
- CITDEL
- SCUBA
- HOG
- YAWN
- RABBIT
- TOGA
- FST
- KWL
- OPEN
- UDO
- CMONK
- CONK
- ANDY
- EARL
- KAKAXA
- DUCK
- TAD
- 🐈
- WAA
- WETH
- TIGRA
- SOB
- DEC
- MATT
- LUCKYSLP
- PRIMAL
- HERIA
- $MOXI
- JFP
- FRF
- FUEL
- FOREXLENS
- WPOR
- AXE
- ROSX
- CZGOAT
- WETH
- COINE
- LAMBOW
- $MUST
- KSTT
- ARB
- MMIT
- POPPY
- 0NE
- DKUMA
- MINU
- DAI
- BULLS
- URD
- SFIL
- TUNA
- ORO
- BONK2.0
- YAKA
- BABYCHEEMS
- WARPER
- WARG
- BOOP
- PUNCH
- PUFF
- OD
- BECOIN
- COIN
- ANDY70B
- GOLDEN
- HULVIN
- STOIC
- RENA
- NITRO
- UNQT
- MCOIN
- SZAR
- ANDY
- PROPEL
- A51
- XWP
- WAVL
- AGTS
- KILLA
- WINTER
- WZRD
- NCASH
- POOLZ
- BASEDGUY
- INCI
- HOOD
- BOG
- RZNDE
- SAM
- $LANDLORD
- BOOSEY
- MEME
- ANTT
- PCH
- BELUGA
- MOTION
- ARCONA
- WGAL
- FINA
- KYRO
- D.O.G.C
- PLSPAD
- KEYFI
- KIETH
- ADILLO
- ARGO
- FUND
- BASEY
- FTPXBT
- FOREX
- $BTC25
- GOLDEN
- POPKAT
- SUICY
- INU
- HADES
- DEEBO
- FNX
- WAFC
- EHHH
- FIJI
- WEX
- BMONEY
- LOTUS
- WSG
- PEARL
- SUILAMA
- ENKI
- PAPO
- ZIX
- NORM
- ET
- 42069K
- ALCH
- USDC
- DONTDIE
- DAI
- GOV
- MONKEX
- $GRASS
- SHIP
- SMART
- SLAYER
- LAB-V2
- PEAGUY
- FVT
- RANDOM9
- CPFC
- VGC
- TURT
- FROP
- FXBT
- ZAZU
- PRICK
- ARG
- QQQ
- ANKA
- KZL
- WATERBEAR
- WVG0
- JEOING737
- OFAC
- URQA
- UGG
- TROPPY
- GOOD
- REMILIA
- CROC
- WOOFI
- SPACE
- BABYMARVIN
- PLATA
- TALES
- JENNER
- MEF
- UAP
- MORK
- CATA
- BUMSHAFT
- ANDY
- PAR
- BAE
- ADE
- SHAO
- GBSK
- $STABBY
- POINTS
- ZKID
- LMT
- SHAWK
- STINKCOIN
- ASTEROID
- TRRXITTE
- CATWIF
- MMO
- PFIRE
- CZ
- SLRS
- MIRX
- ALPACA
- $TUSK
- DAFT
- TAMATEST
- DCM
- UNAI
- GFLY
- TIG
- ERGONE
- MOMA
- MBERRY
- OP
- FIN
- AWX
- LODE
- TODD
- $ACAT
- MIN
- TAJ
- BUTTER
- DIS
- FUTURE
- EXMPLR
- COFI
- XOR
- SAKE
- SUMO
- FTX
- BCDN
- MXNBC
- X8X
- MAD
- BRICK
- DG
- DST
- RIN
- JASON
- MSHEESHA
- PSDN
- HELA
- VISION
- SUNNY
- ISTAR
- HOPE
- FARM
- CGO
- ODE
- WSTV
- POPO
- SUPA
- HEC
- OPCT
- JOWNES
- BGCI
- CLU
- ESPR
- NERD
- SFX
- BRAINS
- WALLY
- GOLDEN
- MIR
- SHEERLUCK
- SUCKYP
- SYPHER
- SENT
- CATFROGDOG
- ONDA
- URO
- DAM
- JANET
- HIBS
- CALUM
- MOD
- BLOX
- $KEKIUS
- CAVE
- UFR
- PRINTR
- KLO
- VALUE
- ARCHI
- SCOMP
- BITT
- ZEN
- ILIS
- $SHIBASHOO
- CHOW
- ZB
- LOLA
- DAETA
- BUL
- IB
- PIXI
- MOCHI
- HIVP
- WSAM
- YODE
- BLOB
- BLAP
- DOPE
- APY
- $HOUND
- KOTARO
- WPFL
- PUSSY
- DOGGO
- KS
- FLUF
- BURN
- SUGARB
- USDTSO
- SHARE
- BORPA
- BOBBY
- AMERICA
- AIDP
- SFT
- SONNY
- HEIDRUN
- SHIELD
- CHIKUN
- KIRI
- BUILT
- LUC
- FOXX
- EYE
- DWC
- RETIREMENT
- SIGMA
- HXAI
- STPR
- MRUN
- PETUNIA
- KAKA
- DACKIE
- BWLD
- AVATLY
- DOGEC
- CCOP
- USDC
- QSWAP
- GODS
- $TRUMP
- POCHITA
- INUKO
- KZ
- WTH
- BCOIN
- MEOW
- LESTER
- BAKED
- TENFI
- FRGST
- $FARTMOMMY
- MAD
- KABOSU
- SKU
- $SMACK
- SYDNEY
- DUN
- MAF
- MTN
- TARIFF
- TERRY
- KEKIUS
- WBRGE
- WAIT
- ROCK
- MIYA
- HIPPO
- WAP
- DARK
- SNM
- CTO
- $GENE
- ORB
- TSLA
- STORM
- GAY
- MU
- KTN
- BLUE
- TAB
- MOOO
- CLANKTARDI
- XCAT
- ALPA
- MSPC
- WINTER
- POPO
- MOLECULE
- BULL
- LUCE
- CFT
- USDT
- OISHII
- DAM
- CLANKSTER
- RAPTOR
- HVN
- WYBO
- BZN
- MAO
- PUBLX
- HAT
- DPAD
- SMG
- SC
- N
- BABYHIPPO
- CHAIR
- GOOF
- SPORT
- MILKY
- GREMLINAI
- BURN
- WPERSIB
- SHIB
- XTK
- SABR
- SS
- OCP
- ADANA
- FROTH
- BOBE
- RARE
- OCP404
- SANTA
- WHOREN
- DAWG
- BIO/ACC
- DAI
- SALD
- SUBF
- ROCKI
- USDT
- BANK
- INU
- 4GS
- GOON
- ZAZU
- GLTR
- $PIXE
- SENKU
- 0XMR
- AIDI
- MUGI
- MAGADOGE
- WOKE
- KENJI
- PHMN
- JAI
- SAFU
- UFO
- WCAI
- PINE
- EAR
- SKINUT
- SUISHI
- ME
- HOSHI
- TOPCAT
- HOODRAT
- MXGP
- SUNNED
- HEFE
- CZAR
- HEHEH
- ONGO
- VITAI
- DANA
- PIVN
- SKY
- WBAHIA
- OCTO
- COFI
- BRK
- YNBNB
- BERAFI
- $LOGE
- D/ACC
- IRD
- KPAD
- BLKC
- LUIS
- INCEPT
- LENS
- DRONES
- WODS
- WUFC
- BABYPNUT
- GDAO
- MUNCH
- WTF
- MEGA
- BUN
- HACHI
- SNAP
- TYKE
- SASHA
- IOV
- BORK
- WLEG
- ARIX
- SPUNK
- BOB
- COG/ACC
- MAPE
- MAX
- WNAVI
- XGN
- VICKY
- SNOW
- $JACKY
- PEPEGA
- MAD
- ETF
- MINIDOGE
- COLANA
- OPPIE
- GUS
- EFX
- PIZZA
- $PLPC
- MIHARU
- GINGER
- TRONDOG
- ARIE
- XIO
- ZERO
- ZEEK
- 1ON8
- PIX
- EQUAL
- AUDIT
- ND
- ZENITH
- WVERDAO
- SOCKS
- CELT
- GENIE
- DVINCI
- KPOP
- PRICEAI
- SCOIN
- DVT
- MIS
- ABE
- ALPHA
- W$C
- CMPS
- RIZZ
- SNK
- CORGIB
- FROYO
- WHASHTAG
- CAT
- ELE
- LINQ
- PARRY
- TSUJI
- AEJO
- SHIRO
- ORCL
- EDEN
- PEENO
- CURLY
- OMNI
- SOX
- CHEF
- $MEMES
- DUSTY
- LAPUPU
- YELPE
- LOL
- FIU
- SCAN
- $CRDN
- DUDE
- CRUNCH
- ANON
- FILTER
- SUIDOG
- BLUFF
- WATER
- BHOLE
- HYPU
- WVASCO
- MONA
- PEPEAI
- GECKY
- XP
- PEPE
- SENC
- TORA
- BOYSS
- JEWELS
- LORE
- XSEI
- BABYMIGGLE
- WTIGERS
- BLS
- FIGS
- BUDDHA
- ETHPRINTER
- REM
- SHIMMY
- LET
- BTCAT
- MPX
- PAPU
- KAPPY
- WSARRIES
- FINN
- QGG
- TCP
- WFOR
- FINE
- BOGUS
- FUN
- PHX
- UNIPCS
- VERA
- CUSD
- QUBIT
- LCN
- RAIN
- PMD
- SPQR
- DAM
- CNET
- DAOS
- WSACI
- FKSK
- POG
- DPY
- WBENFICA
- SUNLION
- FLS
- WISTA
- MILK2
- FAPTAX
- WIZARD
- WFLU
- CULO
- MIKO
- DOKY
- LONGEVITY
- FEDJA
- TILLY
- SYNTH
- TONIC
- BPX
- CHINU
- SOLY
- LIQ
- KET
- WSHARKS
- AETHER
- TCAP
- MOON
- CHEESEBALL
- UT
- AZUKI
- $NODE
- MORE
- RS
- DOE
- TUCKER
- FRUG
- CWC
- WTRA
- DOOGLE
- VOLTA
- ALN
- DJCAT
- PEW
- PAWSY
- BLUBIA
- TBFT
- MAGASHIB
- SMILEK
- SAI
- SNIFFS
- THN
- PLEB
- WSFP
- TIRED
- NINJAPUMP
- DOGIUS
- BHC
- BAO
- TNC
- TIME
- HHGTTG
- NEIRO
- AIKA
- BTCW
- BRIDGE
- PRARE
- STORAGENT
- P3NGUIN
- XENO
- DEARBOOK
- FUR
- KFUCAT
- KAIA
- BEING_AI
- EGOLD
- XTT-B20
- QOAT
- GOATX
- WALL
- CHADCAT
- HARAMBE
- LOTION
- صباح الفر
- VERA
- HODL
- GMAT
- PETOSHI
- BALLS
- LFG
- WNAP
- AGV
- PTS
- AAAHHM
- PCHF
- DELAY
- CAT
- DRA
- WAGMI
- GOF
- SONIC
- RIDERS
- SPQR
- HAVA
- UNDEAD
- CHUANPU
- BABYPNUT
- CCTV
- HUHCAT
- BDRM
- ATLAS
- DWA
- SOLPAC
- GIF
- PEPE
- KINGNEIRO
- DOGER
- FDREAM
- NERDY
- LAMA
- BAILEY
- RONDA
- SPEX
- ATH
- ABI
- LUN
- YOBASE
- FUD
- PWAR
- 8008
- APRIL
- SOOTCASE
- PEL
- MILEI
- SANIN
- BOLI
- CHILLGIRL
- ICE
- TMNS
- NDAS
- SPLASH
- KEK
- BRACE
- KOI
- OGGY
- BINARY
- TETHYS
- ROSSCOIN
- GUBERTO
- VIOLET
- BBK
- FX
- CAT
- 69420
- LILA
- ALAN
- $KEK
- LABZ
- BWED
- NSURE
- COCAINE
- LOOPY
- STACY
- 0XDEV
- GAMMA
- FVM
- GARD
- NEIRO
- TRUMPIE
- LONER
- IZUMI
- XMAS
- SAMI1
- ADAX
- SUPAI
- CMST
- BICHO
- N1
- ZOA
- PST
- BOBY
- MAYA
- SPIKE
- WAM
- COPE
- $YUMI
- DND
- BPRIVA
- ONE
- DEGEN
- PAL
- CHEEKS
- ERC-AI
- OKANE
- FMT
- HONKLER
- PDOGE
- EAGLE
- WGFK
- DOGY
- ASTRO
- WMIBR
- SANTINO
- SKULL
- MAN
- NIGI
- SAP
- GINNAN
- REGI
- SOLANA
- PNUT
- POU
- MTK
- PREDICT
- BRUH
- BABYGOAT
- SBET
- YDF
- $CHEUNGUS
- ASTRO
- BUFFI
- $PMW
- BALLS
- WAPL
- POPO
- PRCY
- 1%
- $MAMA
- COOL
- PEPITO
- AGI
- NOTWORK
- NFI
- MATRIX
- ROAD
- WRSO
- OMOCHI
- BTC
- $ROBIE
- SOFAC
- MOFI
- SCHIZO
- JUJU
- FOMO
- DOS
- BOY
- BUB
- CAT
- MWM
- ZYB
- SUNPUMP
- JUSTICE
- CLX
- LUMIO
- MOLLY
- QMIND
- MOCHICAT
- RONOUT
- SQRL
- PNET
- RUSTEE
- SGTV2
- SUYA
- WLEV
- RAZE
- GERTA
- MAMOON
- RINO
- CHANT
- KEN
- LEV
- SOLALA
- COZY
- LAB
- CHOCCY
- WAGMI
- MONGY
- ZOLA
- SANTA
- OASIS
- CRAB
- DONT
- UNO
- BITCAT
- CATFISH
- FOMO
- USAID
- GHNY
- STANDARD
- NWO
- CUFF
- DEGEN
- $BBT
- 1EX
- NAMI
- YANN
- WSAN
- CULTEL
- EXO
- BABYDENG
- WLUFC
- FINKEY
- VISION
- WGOZ
- FUSION
- DNZ
- GUDTEK
- BLAKE
- CAPY
- WJDT
- ROCKETAI
- RUNNER
- ZAAR
- FPFT
- MEE
- RHINO
- TRUMP47
- PDOGE
- GMMF
- CYS
- SHOOT
- PUNK3493
- PTSHP
- 🤡
- WUDI
- WCHVS
- WVCF
- CNTR
- WDZG
- WAIN
- WANNA
- AD
- KRYPT
- POCHITA
- SANTAHAT
- AESOPERATO
- CHILLFAM
- BUNNY
- WBFC
- LOVE
- DABOO
- PEPE
- GENZAI
- CYBORGISM
- SPIZ
- WQUINS
- PISSCOIN
- STENCHCOIN
- CEICAT
- GBOY
- TRUTHS
- GRINGO
- FARTGPT
- UTYAB
- WUCH
- 0KN
- MACKE
- DOGEX
- LEPER
- WITA
- DNXC
- LONG
- MONKEY
- DEGPT
- FTX
- JIN
- KUMA
- HACHI
- ANSOM
- KASBOT
- PUFF
- BAVA
- WROUSH
- REBD
- POLLO
- ENFT
- WVIT
- FEED
- WBUFC
- PSY
- CROW
- POD
- $MAN
- $KOLT
- DOTZ
- YUKIE
- YOUNES
- PFROG
- ∅
- YIELD
- FLEX
- BICOIN
- SOUL
- JADE
- MPRO
- FRA
- CLEG
- VALUE
- SWQUERY
- AIDOGE
- WAWA
- DC
- UCM
- RIKU
- WOTF
- SITY
- ROPE
- BLEPE
- FUKU
- RITO
- WMFC
- WIFI
- PAN
- TREEB
- ANCHOR
- KNIGHT
- PREAI
- SS20
- LESTER
- SHIB
- DUCKY
- RACEX
- LINGYAN
- YSU
- CEUSDT
- SUMMER
- RING
- BURRRD
- POPPY
- PUNCH
- MIVA
- DSM
- BAMBIT
- BULLY
- SNY
- FRED
- QUASAR
- GOOCH COIN
- CATOUR
- DERP
- IDLE
- FTI
- WSCCP
- GINGER
- LMAO
- PHILL
- FLOCKY
- AISCII
- MSWAP
- HTO
- H2W6GM6JZ
- $HUSKY
- RETARDIA
- ARATA
- TRUST
- BUG
- CAF
- MAXWELL
- POPFISH
- GIAC
- STACKS
- FLUXT
- ZORA
- IF
- EARLY
- BUTT
- FIONA
- WAND
- KUSH
- RINA
- DORKL
- $EGG
- URANUS
- DOGEI
- BMS
- HIVE
- OMNI
- OAKS
- ARGON
- KIRBY
- SHIGGA
- DOP
- BUTTCOIN
- WAIFU
- AD
- NODE
- AILIVE
- $FROGS
- GOOMPY
- NEIROH
- $1
- SENTAI
- BOBBY
- $GOODLE
- DONTDIE
- IHT
- JACKPOT
- DRONE
- TRONCHES
- RODOLFO
- MARSK
- BBC
- PE
- MEOW
- MAGAPEPE
- PHTEVE
- KITTY
- DADDYCHILL
- PSOL
- HMX
- GARBAGE
- AITRUMP
- POPDOG
- GIB
- APRT
- CRYPTO
- MOLLY
- AUTISTA
- ISHND
- HANABI
- DWB
- SHILL
- PIZZAGUY
- CORGI
- CHIBI
- WUKONG
- GOOSEPUMPS
- PONK
- PICKLE
- SAD
- H0L0
- DIOM
- TITAN
- PVP
- AII
- CHLOE
- BVM
- MOM
- EFT
- RDOG
- USC
- BWULL
- BILL
- PPDEX
- OTIA
- SULLY
- CHAD
- WOLF
- BABYPURPE
- AITT
- SHARK
- BLITZ
- START
- AINTI
- HYPR∞
- MOON
- QUBE
- JAPAN
- MARS
- LINK
- KRON
- CLAMS
- LIQ
- $MIHARU
- SILLYCAT
- RAGE
- TI
- MOBIC
- HOODRAT
- POI$ON
- POWERAI
- WGALO
- SKULL
- BKN
- CROCDOG
- ESES
- WRACING
- WSEVILLA
- WMENGO
- NEVA
- LSD
- LOLA
- DARK
- BULL
- PMPY
- FARM
- DOGE1
- SOLCAT
- MDEL
- GUM
- LOVECOIN
- CROY
- CNC
- AGENT2025
- APYS
- VBEA
- YIN
- GONESLER
- TAO
- WALA
- DOLA
- WOLFINA
- WENDCEX
- OMN
- SHITCOIN
- SBF
- TIM
- WDAVIS
- PINEOWL
- GRIN
- ALPHR
- USTX
- DLT
- SKM
- REEE
- BOB
- HMMM
- PLANKTON
- BOLLY
- LEGEND
- LOONG
- FOMO
- SWORD
- BUDDY
- SUICAT
- VIDAI
- CHARLIE
- $R3D
- FRYER
- SNEK
- SUIEET
- FRATT
- HAMMER
- EGGY
- WATLAS
- BCPAY
- D.O.G.E
- MMO
- TEST
- DOGE
- AVXT
- POW
- ATO
- UP
- SOLITO
- WEFC
- MEFI
- BEE
- ETHARDIO
- PONKEI
- CA
- ALIENB
- DOGER
- HIGHER
- AUC
- BLES
- TRUMP
- $TRAIMP
- BEE
- REMILIA
- FALCON
- SHIB
- CTO
- CROC
- SION
- GENIE
- CONVICTION
- DOV
- GCAT
- BROWSER
- LONGAI
- BABI
- BOPPY
- ZNZ
- RARE
- DJT
- PONZI
- DESY
- QAI
- MIW
- JENNA
- ENVOY
- CTOAD
- 9TO5
- DEXAI
- $SCOT
- XEN
- WHY
- AM
- UPG
- ATHENA
- DOLAN
- SNOB
- KAMABLA
- TOX
- SEALS
- UPI
- ALINAINTEL
- PEPE
- MALAKAI
- AICRYNODE
- ANIME
- SLAV
- BEZOGE
- DANNY
- $VENKO
- SHIB
- COVE
- TARDI
- $SPACE
- WSPFC
- DAVIDO
- BADGER
- POTATO
- CODERGF
- LOGOS
- SQID
- DHANDS
- DUCK
- FUFU
- SUID
- YOD
- BABY CZHAO
- JRRY
- GFR
- SARAH
- RICH
- WTIGRES
- M7F
- DAK
- KCAT
- AOC
- BUDDY
- PEBLO
- BIBI
- KIT
- BABYLOFI
- $BANE
- PUMPTRUMP
- GMEOW
- STUPIDCOIN
- MAT
- VIVEK
- FROG
- GIGA🧠
- PUMPCAT
- SBTC
- NOFAP
- BOMB
- SUGAR
- OOF
- AVS
- MECHAZILLA
- BOOBS
- CODED
- SHOE
- BRAIN
- KUNDALINI
- BARON
- GATO
- ROXY
- MIND
- UNW
- RYOSHI
- POPGOAT
- BASED
- $PXAI
- MATRIX
- $HONEY
- EPEP
- ZKE
- BSIM
- CSR
- PCT
- GAME
- $LOUIE
- MYB
- RUNEVM
- FARTGUY
- METAIVERSE
- WAGMI
- LKR
- PAT
- $WEN
- CAIRO
- DMLG
- KAFKA
- ALTOID
- BABYGOAT
- POOWEL
- L24AI
- ATHCAT
- SCRL
- WCC
- WAG
- ALIVE
- HUNTBODEN
- GEM
- COIN
- YESBUT
- CRAB
- AQUA
- MST
- WASM
- LUS
- PAUL
- SUNNEIRO
- PULSE
- RAFF
- SOLPOD
- FANX
- SHARDS
- WCPFC
- CEDAR
- MOCK
- MEMEGAME
- DOT
- GUUFY
- INC
- E
- MORRIS
- WEVE
- LORIA
- HAMMY
- CRW
- WOOFER
- SNAKE2025
- X/ACC
- MINJI
- SHUFFLE
- TANGO
- $XAI
- LONG
- TROLLICTO
- ZALPHA
- SDOGE
- JINX
- GRUG
- MENG
- GOP
- $SADDY
- ZOAI
- NERVE
- YOU
- BOB
- AFYON
- MDF
- DEGEN
- MAXX
- HODL
- BTCWIZ
- CRC
- XETRA
- DRX
- TYLER
- SMZAI
- MOONTHAT
- JETCAT
- MULA
- NUT
- FLOWER
- MOON
- IRENE
- KOK
- GLEBE
- BABYMAGA
- KRAMPUS
- SPARTA
- SWIO
- BROTON
- TRUMP
- ACCORD
- DEO
- MRCH
- GNT
- SPELL
- LUV
- CRISP
- MOOCAT
- BOOTS
- CSTR
- ZKGPT
- OBS
- CATJAK
- WSOH
- DOGSHEET
- QUANT
- MOON
- FFF
- POS
- MSTR
- AURA
- TON
- SSF
- BABYDEGEN
- XLN
- CAL
- SIKA
- DEUS
- WSTETH
- HGAI
- X
- $POOKU
- IRO
- BLOCK
- PAWPAW
- GEO
- POPWIF
- JMTAI
- PERA
- ACHI
- FLOOF
- MARIE
- EARN
- SCINET
- AGXBT
- FTS
- XPOW
- OMNIT
- GROOMER
- BITS
- $AIGCR
- PIM
- GRIFT
- FROGIE
- N64
- NXR
- PEPEWIFHAT
- DOPAMINE
- HACHI
- FOMO3D.FUN
- CICADA
- FLOYX
- AURORA
- HAT
- MONDO
- WIBWOB
- TWOCAT
- DMG
- CHANGO
- LCY
- APL
- SNAKES
- LFW
- THL
- FNC
- TUKI
- HMU
- SHRUBIUS
- BKC
- TOMMY
- XMUSK
- BDOGE
- CORE
- WOW
- CHINAU
- DISCIPLINE
- SUPR
- AURI
- GTUSDC
- FROX
- YUNA
- BULLISH
- BUSTER
- KOMA
- GM
- GRUMP
- BABYSHIRO
- BTM
- PWOG
- DOGO
- KOLANA
- GOATSE
- DP
- O3D
- ASAP
- BBANK
- 4WIN
- WIBFK
- QUEEN
- USH
- CATINO
- FAML
- $PACO
- SOAI
- MAGA
- PGEN
- LATENT
- AZIZI
- TAD
- $TRUST
- LOLA
- TDX
- HENTAI
- SOHOT
- OLIVE
- LAPUTA
- MEH
- HAMI
- $VERTEX
- TRUMP47
- TAOTOOLS
- BUENO
- FROG
- ESTEE
- KHA
- MEOW
- DECKO
- SEAT
- WOMEN
- MWH
- NPC
- WSAUBER
- UMI
- BEEP
- CHILLCAPY
- ODIE
- POZI
- CHART
- FUG
- TWURTLE
- BANKSY
- PAUL
- DGOLD
- XENO
- WRT
- MORE
- CFT
- COIN
- DOUG
- WSB
- COPE
- CBK
- RUBY
- CIG
- VAB
- GAISHA
- BITORB
- SEDGE
- MAIN
- PEMDAS
- QUIL
- MAAI
- W
- MDOGAI
- DUEL
- YOWIE
- GIGA
- MIKU
- ESP
- NEURO
- CUB
- KONG
- 2025
- DINO
- RIB
- HOOT
- JONAH
- BTB
- EUROB
- GPUINU
- RETARD
- APE
- YUP
- SWEG69
- ISA
- BOB
- PHNX
- CMFI
- FELICETTE
- THOL
- SHR00M
- $DUB
- ORI
- AKACHI
- KNU
- BRO
- LATTE
- GOBLINTOWN
- DOMO
- PINKY
- CET
- SPECU
- PACATO
- CRYPT
- MCAIFEE
- CAPY
- SCROLLY
- TOGE
- COW
- SLAP
- IMGX2
- $GOLDEN
- GRIDDY
- POOTI
- ALMC
- HORUS
- WOP
- CHONK
- POP
- DRIFTY
- APEDEV
- BL00P
- ROBOCOIN
- TRILLY
- GAPE
- VIORA
- XERAI
- SLIME
- SUMI
- $TALAHON
- KAILY
- RAJU
- DEERMAN
- PTP
- NOOSUM
- MORTI
- SKG888
- CHARM
- $KHAMOO
- CUCK
- GOSPODIN
- WELF
- COC
- NDX
- PC
- POWER
- LOVELY
- BITCORN
- RIZZYEAR
- FOTUS
- MANYU
- TUNE
- KSG
- MAXI
- SAI
- PARROT
- FERG
- WIFMAS
- EGL
- BONSAI
- CHUNK
- Z
- RINTARO
- AICAT
- PUN
- PRAIST
- BCUG
- MORPH
- GNOME
- DOGETHER
- TRUMPED.AI
- DTORO
- NAS
- YUKI
- VDAO
- DATBOI
- JIFF
- SSE
- CAFE
- FLOW
- FLOOF
- FUBB
- AI99X
- SOLPAKA
- BETA
- TUCKER
- CRTB
- UPDOG
- SKULL
- MILO
- GM
- MARS
- IF
- BULLA
- RAINBOW
- SOK
- CATGUY
- KIKI
- KAI
- ONYX
- OTTI
- AVAXMINERA
- SPWN
- MTGRD
- SHSH
- JOSE
- BOLTAI
- GOOFY
- MONKU
- BRC20
- BTL
- SHA
- VS
- CROW
- MANDY
- EYARE
- BAKENEKO
- BITDOG
- MOZ
- MAND
- NIB
- SALTY
- $BULL
- STARRI
- RIA
- $COUCH
- YUGE
- ZEUS
- HOLI
- SEALS
- $DREAM
- KONGZ
- $VENTI
- BUBL
- PUB
- PEPE
- MEOWKA
- DONKEE
- MONKEYAI
- QUANT
- MTC
- PENOSE
- XNF
- AIPETS
- RBIS
- ERSDL
- ENT
- MARE
- SKILL
- CVT
- WAPE
- SIMAI
- OMN
- BULL
- GM
- DOKI
- OJA
- ETHA
- SARCO
- PUPPET
- ALPHADOGE
- BREAK
- GPUL
- DOGB
- ROMEO
- HIM
- SPCTR
- SIBERT
- JU
- CTO
- MBC
- $MANGA
- ISLA
- VIRUS
- MCRN
- CHILLA
- SOLA
- RPG
- WIZ
- CHERRY
- SIN
- $SLCE
- AIGMX
- SOLYMPICS
- SMCT
- DOCTOR
- YDR
- 4TOKEN
- OUTER
- BWOB
- SKYRIM
- STAK
- KAIA
- UP
- $JBM
- CAP
- FUBAO
- TXN
- EARLY
- $ERNIE
- PEPEMAGA
- GIGACAT
- POODL
- ECO
- OGLG
- $BLOOD
- KING
- WIZZIE
- PUPPET
- 3D3D
- BNOM
- PIPO
- LILCAT
- BUIO
- CRAFT
- CORTEXZERO
- DMTC
- ITA
- BROOD
- ERMINE
- PNG
- BOOF
- PRESS
- WIZARD
- UARB
- NUKEY
- EDM
- CHAD
- FAPCOIN
- HERMY
- WOS
- UMINT
- FATCAT
- MEMECUP
- JRIT
- WNETZ
- GLAZE
- SOAI
- PEG
- SAI
- DASH
- CSUN
- PUMP
- LIMON
- ACTP
- CROCHET
- LEMON
- DCC
- WOME
- GSLAM
- SED
- JACK
- PIPI
- KUMA
- FREAK
- JACK
- BIO
- 4547
- 1984
- BOL
- TOCO
- ETF
- PET
- PSYCAT
- TISM
- AIDAOVC
- WHISPY
- CHADY
- 777
- CAVIAR
- ORCL
- VRTX
- MOMO V2
- NEWERA
- EDSE
- ITX
- MIKI
- SKIBIDI
- SERALPHA
- ECO
- POP
- SUDO
- CASH
- KING
- ASCIA
- ZAZA
- BETA
- GEM
- KABAL
- DEGEN
- ORA
- VERTEX
- AAAI
- FIRA
- POPNUT
- SLURP
- WIFEAR
- POSHI
- EGG
- FROSTY
- BALD
- CANGURO
- FREG
- HODL
- HAPPYDOG
- SUKI
- MURTIS
- CONOR
- KACY
- $LUMI
- ONLYUP
- SOLYCAT
- ROCK
- UNREAL
- APED
- AMPLY
- PING
- EYZ
- VIVEK
- SKATECAT
- HORNT
- $CROCO
- ALOT
- $ROFL
- CLICK
- CNB
- XP
- $SHEESH
- BURNT
- JET
- PEPIG
- GOLDN
- FINDME
- WINSTON
- NOSE
- DUCKEY
- SMORE
- KRPZA
- VTRA
- ANGRYGUY
- BSOV
- TESOURO
- OP
- ECT
- WARS
- CUTE
- MOJI
- WOLT
- LS
- FUKUROU
- COOL
- HOTDOGE
- TYPEN
- $ILENCE
- SBABE
- EQU
- LAWN
- CHI
- ATROFA
- $WIF2
- GTM
- TYLER
- INFC
- GFN
- BAOLONG
- PCAT
- $MAX
- ERB
- PEW
- PLUTO
- WILLY
- BXNF
- MGOD
- LGCY
- KAPI
- MOON
- LEONAI
- WTC
- PONZIO
- FLY
- XTE
- SASHA
- LIDYA
- IAI
- KEK
- MOZART
- ROSIE
- KOZUE
- CHAT
- KURO
- METADOGE
- $WAIFU
- TRONARMY
- LOLCAT
- K
- MOFI
- HCAT
- NOAI
- HABI
- TGPU
- $HOPE
- MATRIX
- ISKY
- SQUARES
- EGGY
- PLN
- EMOTI
- $GODFATHER
- RETARD
- QRK
- $CATA
- GIZMO
- MNTA
- VOID
- HAZEL
- MCBROKEN
- CHED
- DISKNEE
- ETHFAI
- CHARLIE
- BRUCE
- DIF
- MM
- REIKO
- OPRV
- BBYDEV
- COCO
- GOLC
- DOGGO
- BARK
- BAOBAO
- SHAKE
- CHILLA
- NUM
- $PIVOT
- ORB
- DFAI
- HUB
- LICKER
- TOKI
- MOVEZ
- KOL
- JOOPS
- $INSORA
- WENIS
- IUX
- DWAKE
- LONG
- BG
- LENNI
- SIGHT
- GVR
- 0XP
- WORK
- SOON
- WADU
- GACHA
- STRESSGUY
- PEEP
- MOJO
- PHILLIP
- BOLGUR
- FEG
- NEXEA
- GEN
- POLAR
- TARO
- $VIBE
- LAIFU
- KITTEN
- RIVUS
- KYRA
- PITTY
- FLAME
- PUNGU
- YUNKI
- PWOT
- CRY
- TMFT
- NEBULA
- RICE
- DANK
- SMH
- GUGU
- $LOLA
- SGLY
- $ωMσGA
- FAT
- DEKOPON
- STARS
- DONK
- RPG
- MIGRAINE
- MINTYGIRL
- TRIANGLE
- DIGGAI
- BONG
- MOSHI
- $BUN
- MARSHALL
- NRC
- $OCCER
- AG
- URMOM
- NOO
- ODIN
- CYCE
- GENESIS
- KGC
- CERBER
- UFIL
- ACTII
- APED
- ALMAN
- WIMPO
- FROP
- DCT
- SNARC
- NFTS
- AIRENA
- IRS
- KIMCHI
- LTT
- TOLYCAT
- L
- SPIX
- ONIGCHI
- JILLBODEN
- EPOCH
- TODD
- WAGIE
- WEN
- BOB
- BITARD
- SWAN
- BONKEY
- CUMS
- PJ
- BCI
- BURGIIR
- $BLK
- BILLI
- NOTDOG
- PAMP
- APOW
- $BIRDIE
- SHNJ
- GLUB
- SHADOAI
- CZOL
- ZECK
- MIMAS
- MOOTUN
- NORM
- GLOOM
- $SQUISH
- ZERESCAN
- SENDR
- CHRYSTAL
- GDOG
- TWINNY
- BSPT
- CHADAI
- CHILLWHALE
- PELICAN
- VAI
- GOOSE
- AMAI
- PEWPEW
- MAGIC
- GIC
- VOTEDOGE
- ROK
- NOM
- FUG
- IF
- FCAT
- PEPCAT
- CROAK
- ALDIN
- SHARP
- SQRB
- AST
- FITT
- SWAGGY
- CANCER
- SFAI
- MOLLY
- ISEC
- TENDIE
- IUSDC
- HACK
- ORION
- MOON
- POLY
- KRATOM
- MOON
- RAINBOW
- XTCASH
- BLOOP
- BIC
- PKIN
- FUM
- CROISSANT
- ASTA
- BIAO
- MEEB
- FREEDOM
- CRINGE
- TOOT
- UWU
- LOAF
- LBW
- BABYP
- PEPEK
- CHOLO
- CRAZY
- DWOG
- BOT
- CHECKR
- CGF
- BLUE
- CTAX
- LOAF
- GIRLS
- GM
- MOB
- MAGIC
- NOD
- OIACAT
- JUMP4EVER
- BLUE
- RYNO
- HCAT
- SPURDO
- KLEIN
- DAIO
- PIGGA
- KINI
- DGEN
- ASAFE
- BOP
- FROGGY
- DECATS
- AGSYS
- GGAINS
- HAKU
- WHC
- GARGOYLE
- OGAI
- 2025
- PEPEWFPORK
- DWOLF
- CLAUDE 2
- MOO
- NODEV
- GBTC
- TITAN
- BULLCAT
- GONG
- UHOSU
- PRTCLE
- TRM
- POU
- FINE
- MEN
- SPOON
- BOBA
- NML
- MOON
- DOCTOR
- POPFROG
- MGGA
- YURO
- PEPINU
- LPP
- TDT
- TWOOD
- EVIN
- PUSH
- $NUKUMUTU
- PEPEZ
- FSC
- SASHA
- FIRA
- DRAKO
- PUMP
- SAF
- YEET
- DCA
- FINDER
- YOOMI
- $BITB
- KAKA
- ALPACA
- FRKT
- $COST
- RUNNER
- TETHER
- CORX
- IWBTC
- BUBBLU
- VRN
- BBAXOL
- RIZZMASEVE
- CRX
- ADEL
- BOOK
- FORKY
- MICU
- MX
- KAPSEL
- RAT
- CHENG
- NEB
- RGP
- SLOW
- MONKIE
- WEEBS
- BELUGA
- DUKIE
- LIFE
- DERMO
- ONAI
- DOX
- RUGRAT
- REGRET
- GRACIE
- BAND
- LFDOG
- GINGER
- AINAL
- ACM
- ABCDE
- SMOL
- TSU
- DWOG
- $SCANNING
- MLNR
- ROLLIE
- LARPAI
- SCALEX
- KOOKY
- CTT
- $SPOT
- AXIAL
- SANTAPEPE
- CT100
- NAME
- HOMELESS
- UPX
- STANK
- PIZA
- RE7USDC
- TOBY
- SOR
- $LILY
- TUB
- HYRAX
- APET
- APE
- MD
- GG
- AFEN
- BRRRIAN
- SPACE
- FLYCAT
- NYANDOGE
- CHUMP
- DEPIN
- SFX
- ELE
- AVI
- WRINKLE
- DOGM
- NIPZ
- AVA
- $HACK
- BSL
- ICE
- SAGEL
- FFROG
- ARGY
- MONET
- LOST
- GOLEM
- N.E.R.D
- RBT
- MIRAI
- MSI
- TUNP
- KICHI
- DOGGY
- MONKE
- CAESAR
- MAGNUS
- WOOF
- HYP
- SOLP
- FIBER
- SVN
- EGS
- LUI
- YNBTCK
- HELLO
- TRIP
- STI
- WQT
- SKYH
- USDT.B
- TURBO
- 1FLR
- JES
- OLUMPC
- MCAI
- ZOID
- PUGGY
- SUZAN
- MUSK
- REBEL
- TROOP
- BLACKY
- PSI
- MC
- UCRO
- YARD
- LOADING
- AOK
- TPCAT
- SSOL
- FRANK
- TECH
- PEPECAT
- JAW
- GRWV
- DDIM
- BUDDY
- MAWA
- NOLE
- WORMS
- DOGNUS
- SMAS
- SNV
- UBE
- TRX
- GARY
- WIWI
- CHOWIE
- SAO
- RIZZO
- $WANTED
- CRIP
- WERK
- SAIKO
- ARAI
- SWC
- NUBDOG
- BIR
- CLOWN
- BUNDL
- BRINT
- PEKO
- CRIPPL
- LOS
- TRUFF
- VIPER
- MOLECULAR
- INVIFY
- WAG
- SEAI
- ORO
- EYE
- CDR
- TRN
- $STICKY
- WRAP
- $SODA
- $CLUB
- S
- $🧲6900
- BATYA
- MEVR
- RPD
- APE
- ULTRAETHS
- CHILLMAS
- FOOKER
- MPAD
- DEG
- MTK
- SEX
- GORILLA
- MSHARE
- SOLOTH
- TXA
- EZETH
- TME
- MSHIBA
- AIS
- ARIA
- INME
- MOOND
- META
- APEDOG
- RUBY
- M
- UFET
- LEMON
- EGGP
- DOE
- NRFB
- NANA
- NON
- SXS
- COSMIC
- CRYSTL
- NEXIS
- SING
- RUN
- WIRTUAL
- KINQ
- DEXSHARE
- ROULETTE
- HAPPY
- KUNCI
- AGS
- ALEXIS
- STON
- TRANQ
- MN2
- TSAI
- FIRE
- COW
- NUTZ
- JOSH
- NYANTE
- ROOM
- R1
- ALAI
- WOOLY
- CPOO
- GRASS
- NET
- BB
- OPX
- $DUCKY
- KLAP
- LANA
- IME
- XHV
- LORDZ
- ONI
- BABY
- VST
- CPO
- TRY
- PRMX
- PNUTS
- W3KT
- SWINE
- KURO
- DIAMOND
- BRTR
- BITS
- V
- TOON
- HERB
- DRACE
- PALG
- DDD
- DEGENUSDC
- IDAI
- MC.USD0
- MILK
- PANIC
- VIBE
- DCNT
- FOTA
- FAB
- SHEZUSD
- GMICHI
- UADA
- SLX
- CATT
- USDT
- CRX
- BANANA
- HUSL
- ZM
- ARTR
- RNBW
- SHILL
- 1EARTH
- KFN
- HASBULL
- BABY NEIRO
- FROGEX
- MFTU
- AFN
- AED
- ALL
- AMD
- ANG
- AOA
- ARS
- AUD
- AWG
- AZN
- BAM
- BBD
- BDT
- BGN
- BHD
- BIF
- BMD
- BND
- BOB
- BRL
- BSD
- BYN
- BYR
- BTC
- CLF
- BTN
- BZD
- CHF
- CUC
- CAD
- CRC
- CLP
- DKK
- CUP
- CNY
- DJF
- ETB
- DOP
- CVE
- ERN
- GEL
- EUR
- GBP
- GBX
- DZD
- GNF
- GMD
- GGP
- FJD
- HRK
- HNL
- GTQ
- IMP
- GHS
- ILS
- ILA
- HTG
- JEP
- ISK
- INR
- KGS
- GYD
- KES
- BWP
- JMD
- HUF
- KRW
- KWD
- KHR
- LKR
- LBP
- IQD
- CDF
- KYD
- LYD
- LVL
- COP
- MMK
- JOD
- LRD
- MKD
- KMF
- MVR
- CZK
- MAD
- MUR
- KZT
- MNT
- EGP
- MZN
- NAD
- LSL
- FKP
- MWK
- NPR
- NZD
- GIP
- MDL
- NGN
- PHP
- HKD
- MOP
- OMR
- PGK
- RON
- IDR
- PKR
- MXN
- SBD
- QAR
- NIO
- RSD
- IRR
- SAR
- SHP
- SCR
- JPY
- PAB
- SLL
- SGD
- SVC
- PLN
- KPW
- SYP
- STD
- TMT
- RUB
- LAK
- TND
- TJS
- TWD
- SDG
- LTL
- TZS
- TTD
- UYU
- SOS
- USD
- USX
- UZS
- MGA
- WST
- VUV
- XAF
- MRO
- XDR
- SZL
- XCD
- TOP
- MYR
- ZMK
- UAH
- ZAR
- ZAc
- XOF
- NOK
- VEF
- ZMW
- XAG
- PEN
- XPF
- PYG
- ZWL
- RWF
- SEK
- SRD
- THB
- TRY
- UGX
- VND
- XAU
- YER
- SLE
- VES
- SSP
- MRU
- CNH
What is Bitcoin? The Revolutionary Digital Currency Explained
What is Bitcoin? The Revolutionary Digital Currency Explained
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency created in 2009 by an anonymous entity using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. It operates on a peer-to-peer network without the need for intermediaries, utilizing blockchain technology to record all transactions on a public distributed ledger. Bitcoin’s core purpose is to serve as a secure, borderless medium of exchange and store of value, independent of government control or financial institutions. Unlike traditional fiat currencies, Bitcoin has a fixed supply cap of 21 million coins, making it inherently deflationary. Transactions are verified through a process called mining, where powerful computers solve complex mathematical problems to add new blocks to the blockchain. Bitcoin differs from traditional currencies in several key aspects: it is purely digital, not backed by any physical commodity or government, and offers pseudonymous transactions. Its value is determined by market forces of supply and demand, leading to significant price volatility. As of 2025, Bitcoin has gained widespread adoption, with major companies accepting it as payment and countries like El Salvador recognizing it as legal tender. The cryptocurrency has sparked a financial revolution, challenging conventional monetary systems and inspiring the creation of thousands of alternative digital currencies.| Feature | Bitcoin | Traditional Currency |
|---|---|---|
| Issuance | Decentralized (mining) | Centralized (government) |
| Supply | Limited (21 million) | Unlimited (subject to monetary policy) |
| Transaction Speed | Minutes to hours | Days (international) |
| Transparency | Public ledger | Private bank records |
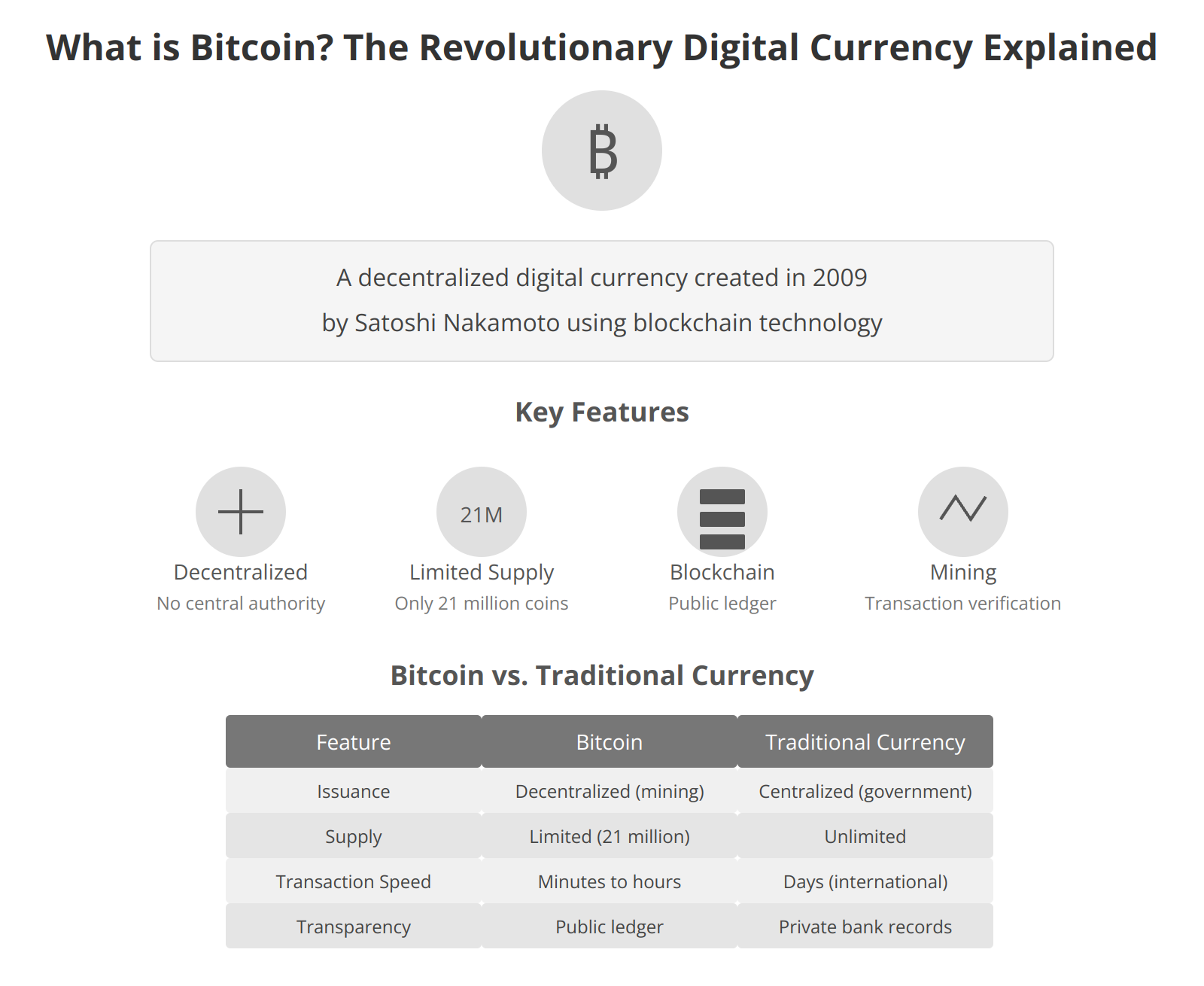
The History of Bitcoin: From Satoshi Nakamoto to Global Phenomenon
The History of Bitcoin: From Satoshi Nakamoto to Global Phenomenon
Bitcoin’s journey from an obscure whitepaper to a global financial phenomenon is a testament to the power of decentralized technology. On October 31, 2008, an enigmatic figure using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto published the Bitcoin whitepaper, titled “Bitcoin: A Peer-to-Peer Electronic Cash System.” This groundbreaking document outlined a revolutionary concept: a decentralized digital currency that could operate without intermediaries. On January 3, 2009, Nakamoto mined the genesis block, marking the birth of the Bitcoin blockchain. The first Bitcoin transaction occurred on January 12, 2009, when Nakamoto sent 10 BTC to cryptographer Hal Finney. Bitcoin’s early years were characterized by slow adoption and minimal value, with the first real-world transaction occurring on May 22, 2010, when programmer Laszlo Hanyecz famously purchased two pizzas for 10,000 BTC.Key Milestones and Major Events
Bitcoin’s history is punctuated by significant milestones and events that shaped its growth:- 2011: Bitcoin reaches parity with the US dollar, trading at $1 for the first time.
- 2013: Bitcoin surpasses $1,000, gaining mainstream media attention.
- 2014: Mt. Gox, the largest Bitcoin exchange at the time, collapses, leading to increased scrutiny and regulation.
- 2017: Bitcoin experiences a historic bull run, reaching nearly $20,000 in December.
- 2020: Institutional adoption accelerates, with companies like MicroStrategy and Square investing in Bitcoin as a treasury reserve asset.
- 2021: El Salvador becomes the first country to adopt Bitcoin as legal tender.
- 2024: The SEC approves the first Bitcoin spot ETFs in the United States, marking a significant milestone for mainstream acceptance.
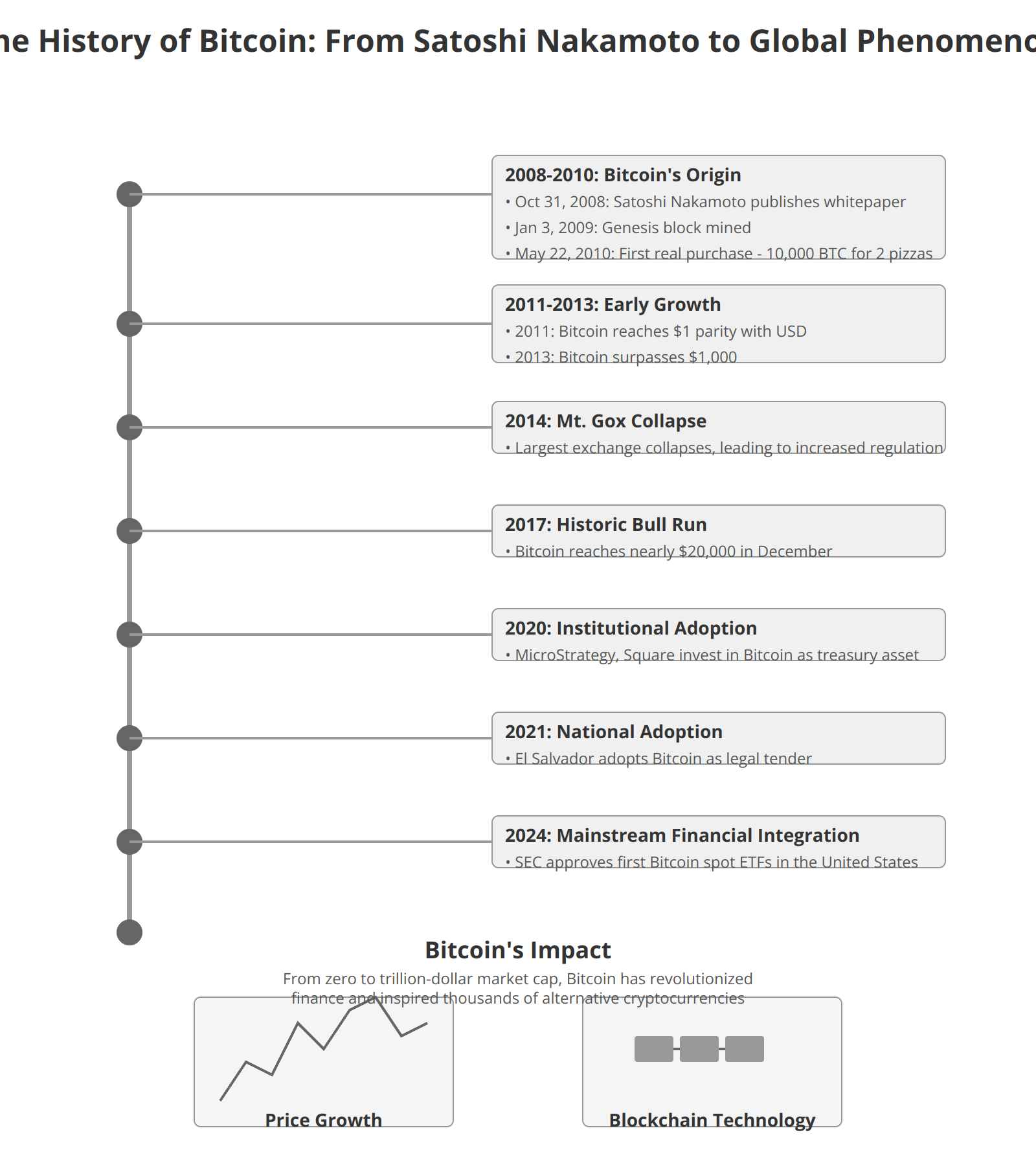
How Bitcoin Works: Demystifying Blockchain Technology
How Bitcoin Works: Demystifying Blockchain Technology
Bitcoin operates on a decentralized, distributed ledger called the blockchain, which serves as a public record of all transactions. This innovative technology ensures transparency, security, and immutability of data. At its core, the blockchain consists of a chain of blocks, each containing a group of verified transactions. These blocks are cryptographically linked using complex mathematical algorithms, primarily SHA-256, making it virtually impossible to alter historical data without consensus from the network. The process of adding new blocks to the chain is known as mining, a resource-intensive task performed by specialized computers called miners. Miners compete to solve a cryptographic puzzle, with the first to find the solution earning the right to add the next block and receive newly minted bitcoins as a reward. This proof-of-work system not only secures the network but also regulates the issuance of new bitcoins, with the mining reward halving approximately every four years to control inflation.Transaction Verification and Propagation
When a user initiates a Bitcoin transaction, it is broadcast to the network and placed in a memory pool (mempool) of unconfirmed transactions. Miners select transactions from this pool, prioritizing those with higher fees, and include them in the block they are attempting to mine. Once a block is successfully mined, it is propagated across the network, where other nodes verify its validity before adding it to their copy of the blockchain. This decentralized consensus mechanism ensures that all participants agree on the state of the ledger without the need for a central authority. Transactions typically require multiple confirmations (additional blocks mined on top) before being considered fully settled, with six confirmations being the standard for high-value transfers. This process, while seemingly complex, occurs seamlessly in the background, allowing users to send and receive bitcoin globally within minutes, regardless of transaction size or destination.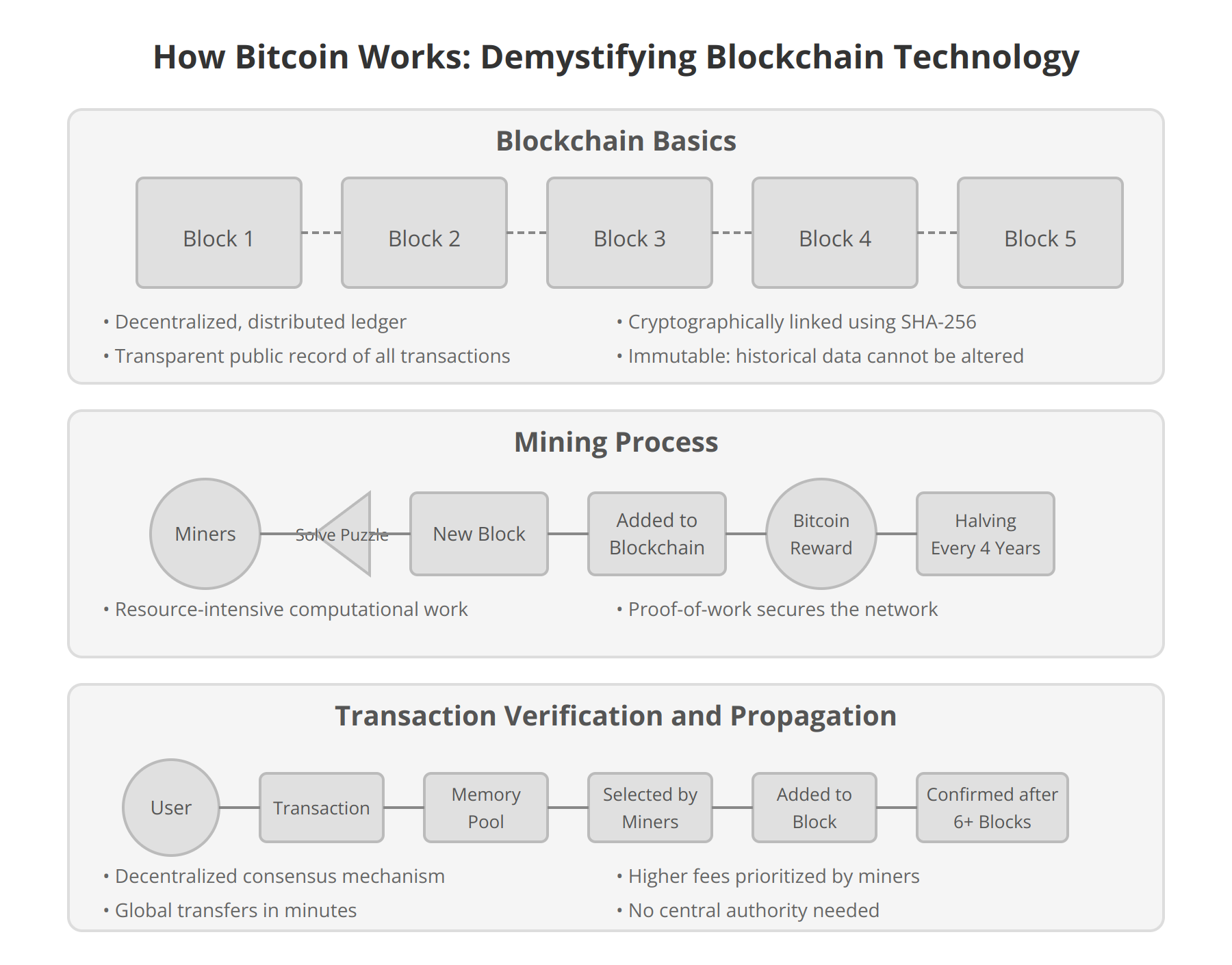
Bitcoin’s Market Performance: Price History and Future Projections
Bitcoin’s Market Performance: Price History and Future Projections
Bitcoin, the pioneering cryptocurrency, has exhibited remarkable price volatility and growth since its inception in 2009. Initially trading for mere cents, BTC reached its all-time high of $108,786 in March 2024, demonstrating a staggering return on investment for early adopters. The cryptocurrency’s market capitalization has surged to over $2 trillion, solidifying its position as the dominant digital asset. Historical data reveals cyclical patterns, with notable bull runs in 2013, 2017, and 2020-2021, followed by significant corrections. These cycles have been influenced by factors such as halving events, institutional adoption, and macroeconomic conditions.Expert Predictions and Future Outlook
Analysts and industry experts have provided diverse projections for Bitcoin’s future value. Conservative estimates suggest BTC could reach $200,000 by the end of 2025, while more ambitious predictions envision a $1 million valuation within the next five years. Key factors influencing these projections include:- Increasing institutional adoption and integration of Bitcoin into traditional financial systems
- The impact of Bitcoin ETFs and improved accessibility for retail investors
- Ongoing developments in blockchain technology and scalability solutions
- Regulatory developments and potential government adoption as a strategic reserve asset
| Year | Predicted Price Range |
|---|---|
| 2025 | $150,000 – $250,000 |
| 2027 | $250,000 – $500,000 |
| 2030 | $500,000 – $1,000,000 |
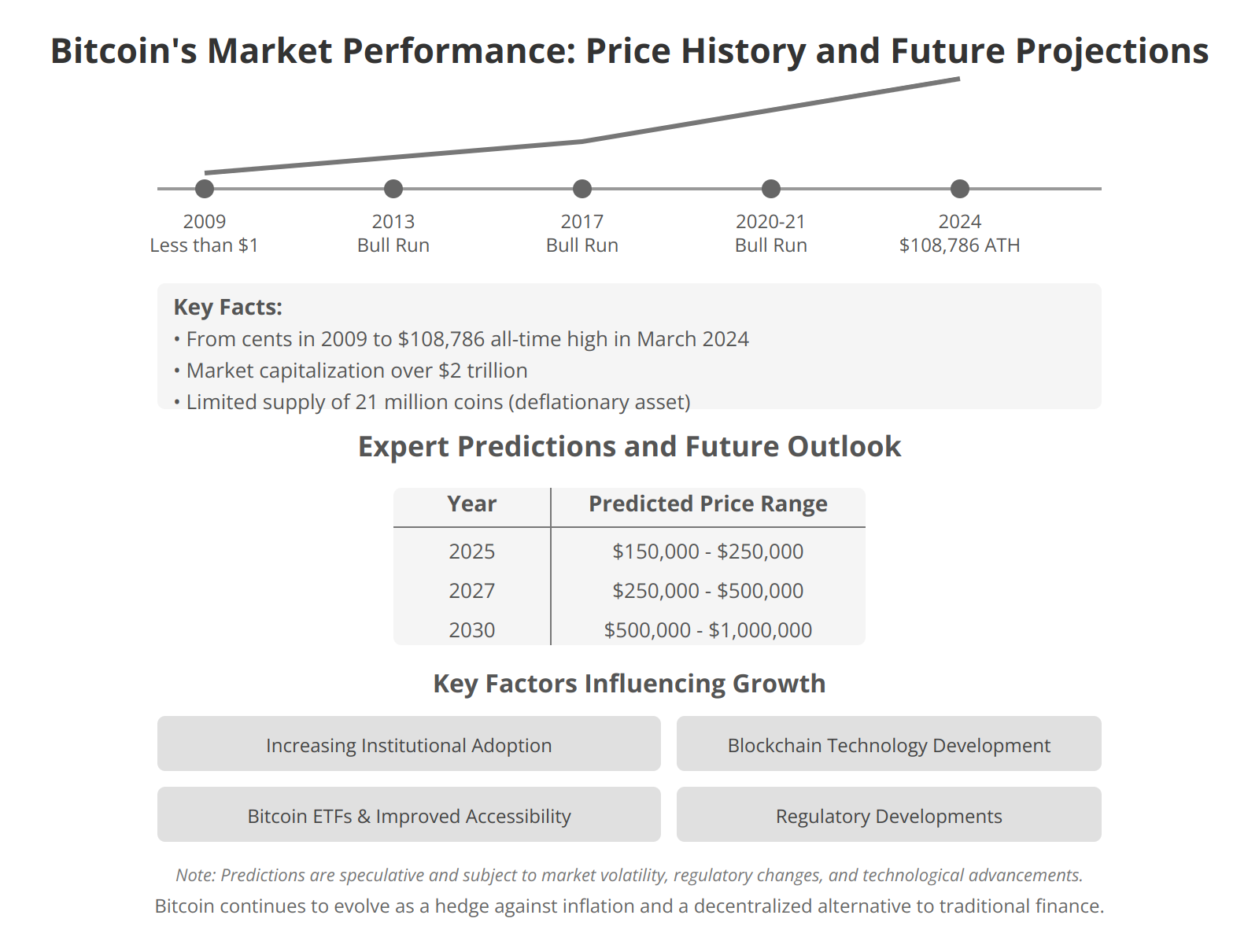
Investing in Bitcoin: Strategies for Beginners and Pros
Investing in Bitcoin: Strategies for Beginners and Pros
Bitcoin, the world’s first and most valuable cryptocurrency, offers significant investment potential for both novice and experienced traders. To begin investing in Bitcoin, individuals must first select a reputable cryptocurrency exchange, such as Coinbase, Binance, or Kraken, to purchase the digital asset. After creating an account and completing the necessary identity verification procedures, investors can fund their accounts using various payment methods, including bank transfers, credit cards, or other cryptocurrencies. Once funds are available, Bitcoin can be acquired at the current market price or through limit orders set at desired price points.Secure Storage Solutions
Proper storage is crucial for safeguarding Bitcoin investments. While exchanges offer built-in wallets, it is advisable to transfer significant holdings to more secure options. Hardware wallets, such as Ledger or Trezor devices, provide offline storage and enhanced security against hacking attempts. For smaller amounts, software wallets like Electrum or mobile wallets such as Trust Wallet offer convenience without compromising security. Regardless of the chosen storage method, implementing strong passwords, enabling two-factor authentication, and regularly backing up wallet recovery phrases are essential practices.Trading Strategies and Risk Management
Successful Bitcoin trading requires a combination of technical analysis, market awareness, and disciplined risk management. Dollar-cost averaging, where investors regularly purchase fixed amounts of Bitcoin regardless of price, can help mitigate volatility risks. For more active traders, strategies such as swing trading or scalping may be employed, utilizing technical indicators like moving averages, relative strength index (RSI), and Bollinger Bands to identify potential entry and exit points. Implementing stop-loss orders and taking profits at predetermined levels are crucial for managing risk and preserving capital.| Risk Management Technique | Description |
|---|---|
| Position Sizing | Limit each trade to 1-2% of total portfolio value |
| Diversification | Allocate investments across multiple cryptocurrencies and traditional assets |
| Stop-Loss Orders | Automatically sell if price drops below a specified threshold |
| Take-Profit Orders | Lock in gains by selling when price reaches target levels |
Remember, while Bitcoin has shown remarkable growth potential, it remains a highly volatile asset. Never invest more than you can afford to lose, and consider consulting with a financial advisor before making significant investment decisions.

Bitcoin Mining: From Home Computers to Industrial Operations
Bitcoin Mining: From Home Computers to Industrial Operations
Bitcoin mining has undergone a remarkable transformation since its inception in 2009. Initially, enthusiasts could mine Bitcoin using standard home computers, as the network’s computational demands were relatively modest. However, as Bitcoin’s popularity surged, so did the complexity of the mining process. The introduction of Application-Specific Integrated Circuits (ASICs) in 2013 marked a pivotal shift, rendering CPU and GPU mining obsolete. Today, Bitcoin mining is dominated by large-scale industrial operations, often referred to as mining farms, which utilize specialized hardware and consume vast amounts of electricity. These operations solve complex cryptographic puzzles to validate transactions and add new blocks to the blockchain, competing for the current reward of 3.125 BTC per block. The global hash rate, a measure of the network’s processing power, has reached unprecedented levels, exceeding 500 exahashes per second in 2024. This exponential growth has led to increased mining difficulty, necessitating substantial investments in equipment and energy-efficient solutions. Consequently, mining operations have gravitated towards regions with low electricity costs and cooler climates to optimize profitability. The industry now faces challenges related to energy consumption and environmental impact, prompting a shift towards renewable energy sources and more efficient mining technologies.| Year | Mining Hardware | Approximate Hash Rate |
|---|---|---|
| 2009 | CPU | 0.01 MH/s |
| 2011 | GPU | 100 MH/s |
| 2013 | ASIC (First Gen) | 1 TH/s |
| 2024 | ASIC (Latest Gen) | 100+ TH/s |
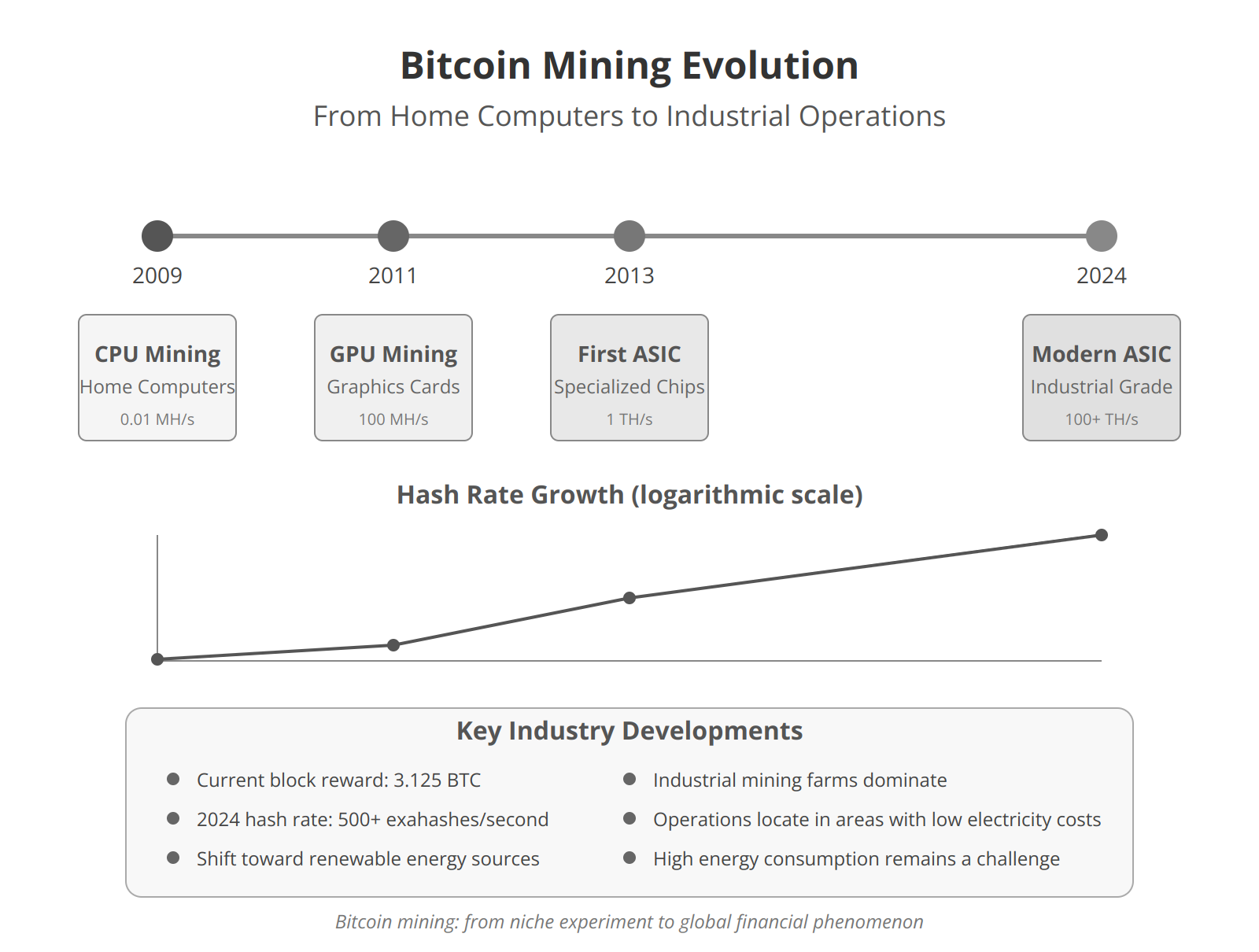
Bitcoin Wallets: Securing Your Digital Gold
Bitcoin Wallets: Securing Your Digital Gold
Bitcoin wallets serve as the cornerstone of cryptocurrency security, offering various methods to safeguard digital assets. These wallets come in two primary categories: hot wallets and cold wallets. Hot wallets, such as software wallets and mobile applications, maintain an active internet connection, providing convenience for frequent transactions but potentially exposing users to online threats. Conversely, cold wallets, including hardware devices and paper wallets, store private keys offline, significantly reducing the risk of remote hacking attempts. As of 2025, hardware wallets like Trezor Safe 5 and Ledger Nano X have gained popularity for their robust security features, including PIN protection, secure elements, and multi-signature support. For enhanced protection, experts recommend implementing a multi-layered approach, combining cold storage for long-term holdings with hot wallets for day-to-day transactions.Best Practices for Safeguarding Bitcoin Assets
To maximize the security of Bitcoin holdings, users should adhere to several critical practices:- Utilize strong, unique passwords and enable two-factor authentication (2FA) on all wallet accounts
- Regularly update wallet software to patch security vulnerabilities
- Employ multi-signature wallets for shared control over high-value accounts
- Back up wallet seed phrases or private keys securely, preferably in multiple offline locations
- Consider using hardware wallets for storing significant amounts of Bitcoin
- Verify transaction details meticulously before confirming transfers
- Use reputable VPNs when accessing wallets on public networks

The Bitcoin Ecosystem: Exchanges, Payment Processors, and More
The Bitcoin Ecosystem: Exchanges, Payment Processors, and More
The Bitcoin ecosystem encompasses a diverse array of platforms and services that collectively form the backbone of the cryptocurrency economy. At its core are cryptocurrency exchanges, which serve as the primary gateways for users to buy, sell, and trade Bitcoin. Leading exchanges like Binance, Coinbase, and Kraken process billions in daily trading volume, offering advanced trading features, fiat on-ramps, and custody solutions. Complementing these are decentralized exchanges (DEXs) such as Uniswap and PancakeSwap, which facilitate peer-to-peer trading without intermediaries. Bitcoin payment processors play a crucial role in enabling merchants to accept cryptocurrency payments. Companies like BitPay, CoinGate, and BTCPay Server provide tools for businesses to integrate Bitcoin payments into their existing systems, offering features such as instant fiat conversion, invoicing, and multi-signature wallets. These services have facilitated the adoption of Bitcoin as a payment method by major retailers and e-commerce platforms worldwide. The ecosystem also includes Bitcoin wallets, ranging from hardware solutions like Ledger and Trezor to software wallets such as Electrum and BlueWallet. These wallets provide secure storage and management of private keys, essential for safeguarding Bitcoin holdings. Additionally, blockchain explorers like Blockchain.info and BTC.com offer transparency by allowing users to view transaction histories and network statistics in real-time.Key Components of the Bitcoin Ecosystem
| Component | Examples | Function |
|---|---|---|
| Exchanges | Binance, Coinbase, Kraken | Facilitate buying, selling, and trading of Bitcoin |
| Payment Processors | BitPay, CoinGate, BTCPay Server | Enable businesses to accept Bitcoin payments |
| Wallets | Ledger, Trezor, Electrum | Secure storage and management of Bitcoin |
| Blockchain Explorers | Blockchain.info, BTC.com | Provide transaction and network data transparency |
Layer 2 solutions such as the Lightning Networkare enhancing Bitcoin’s scalability by enabling faster and cheaper transactions off-chain. Furthermore, institutional services like Grayscale’s Bitcoin Trust and ProShares’ Bitcoin ETF are providing traditional investors with exposure to Bitcoin without direct ownership, further bridging the gap between cryptocurrency and traditional finance.
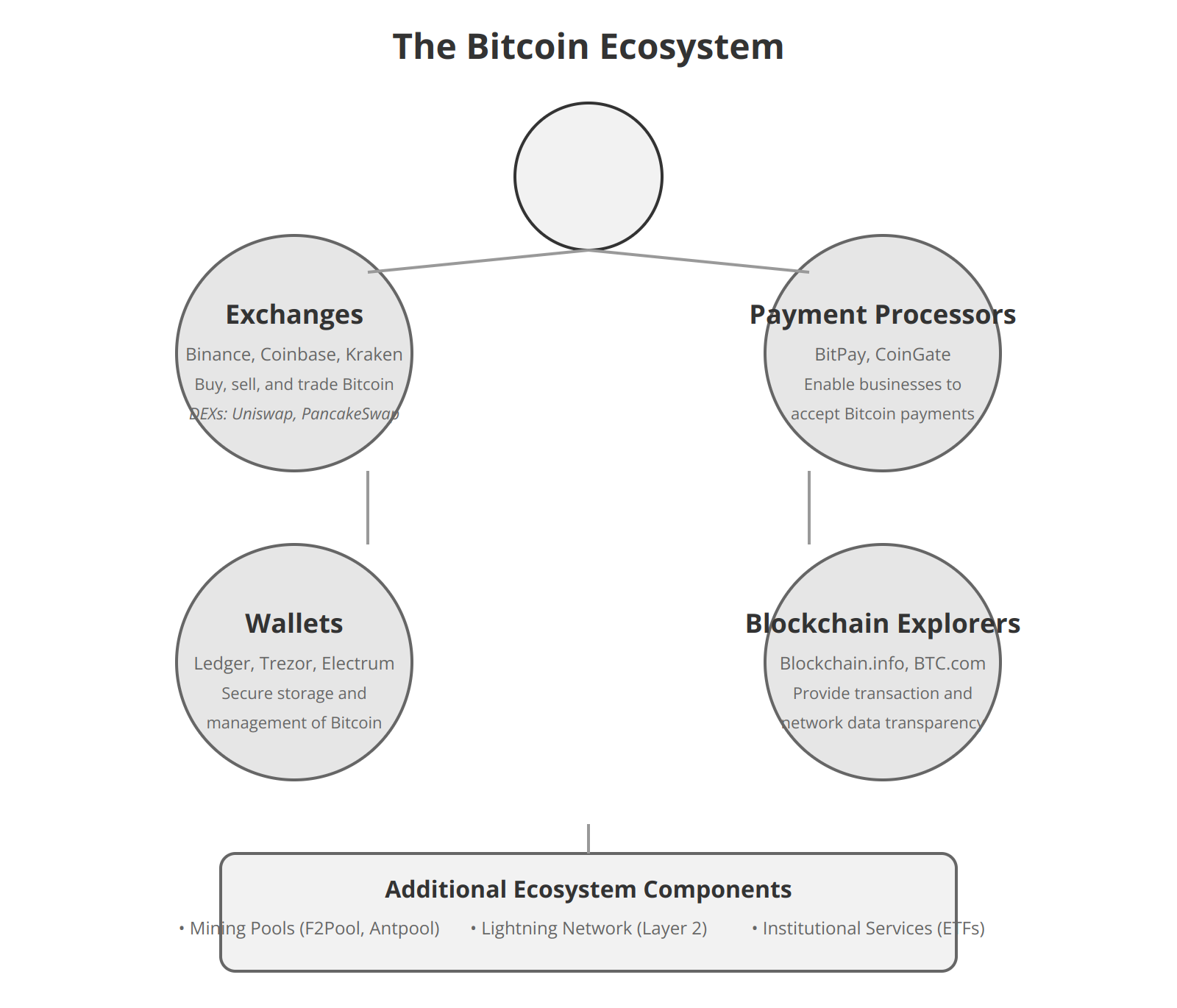
Bitcoin’s Impact on Global Finance: Disruption and Adoption
Bitcoin’s Impact on Global Finance: Disruption and Adoption
Bitcoin, the world’s leading cryptocurrency, has emerged as a disruptive force in global finance, challenging traditional monetary systems and gaining significant adoption by institutions and countries. As of 2025, Bitcoin’s market capitalization has surpassed $2 trillion, with over 4% of the global population holding the digital asset. The United States leads in adoption, with 14% of its population owning Bitcoin. Institutional investors have increasingly embraced Bitcoin, with major financial institutions like BlackRock, Fidelity, and Goldman Sachs offering Bitcoin-related products and services. The approval of Bitcoin spot ETFs in January 2024 marked a watershed moment, attracting substantial inflows and further legitimizing the asset class. Central banks and governments are also taking notice, with some countries exploring or implementing Bitcoin as legal tender. El Salvador’s pioneering move in 2021 has been followed by several other nations, while major economies are developing regulatory frameworks to accommodate cryptocurrencies. Bitcoin’s decentralized nature, limited supply, and potential as a hedge against inflation have contributed to its growing appeal as a store of value and medium of exchange. The integration of Bitcoin into traditional financial systems is reshaping cross-border transactions, remittances, and investment strategies, potentially reducing costs and increasing efficiency in global finance.| Metric | Value |
|---|---|
| Global Bitcoin Adoption | 4% of population |
| US Bitcoin Adoption | 14% of population |
| Bitcoin Market Cap (2025) | $2+ trillion |
| Institutional Holdings | 14.427% of total supply |
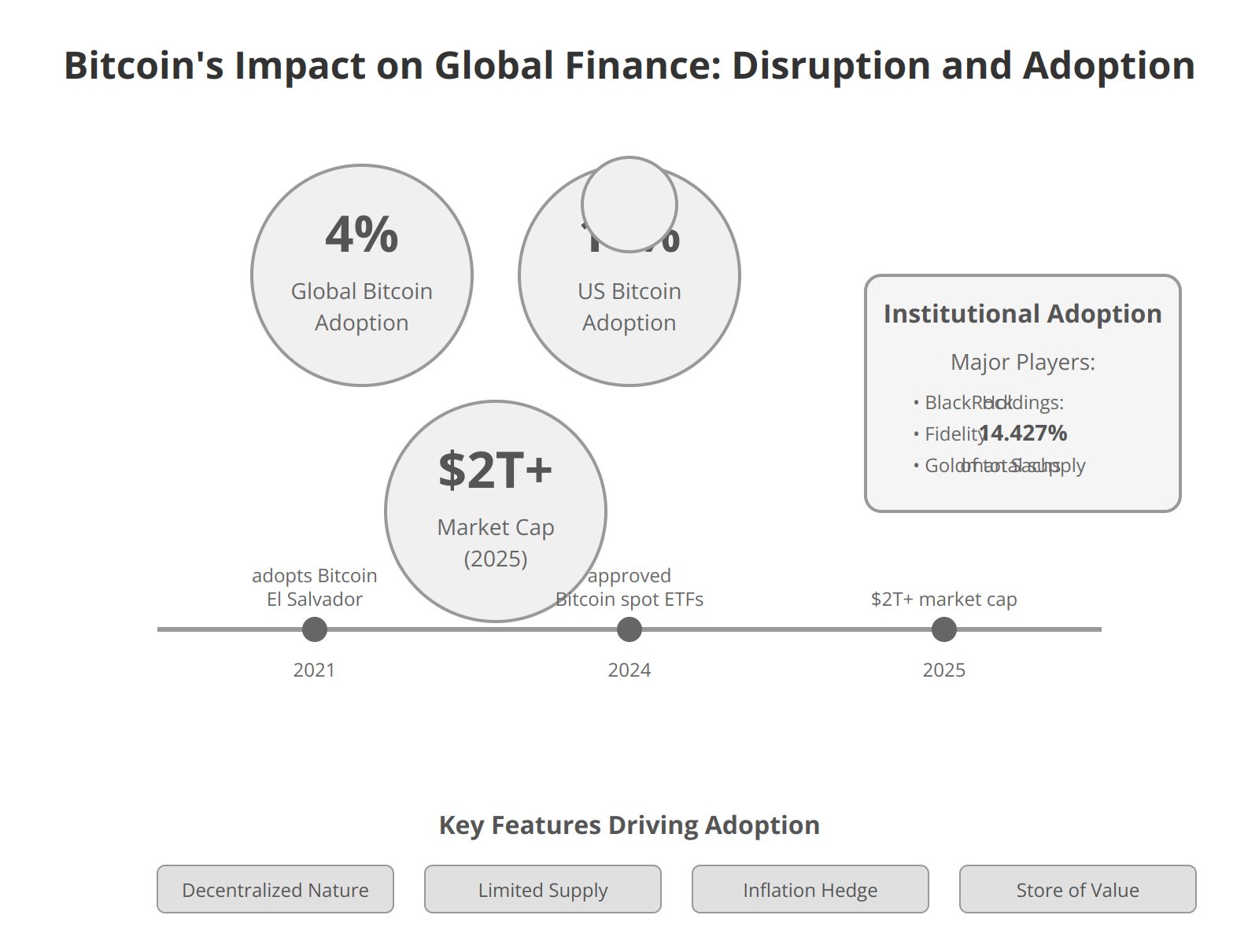
Bitcoin vs. Other Cryptocurrencies: What Sets BTC Apart?
Bitcoin vs. Other Cryptocurrencies: What Sets BTC Apart?
Bitcoin (BTC) stands as the pioneer and leader in the cryptocurrency space, distinguished by several unique features that set it apart from other digital assets. As the first and most widely recognized cryptocurrency, Bitcoin boasts unparalleled network effects and the highest market capitalization, currently exceeding $1 trillion. Its decentralized nature, powered by a vast network of over 15,000 nodes globally, ensures robust security and censorship resistance. Bitcoin’s fixed supply cap of 21 million coins creates digital scarcity, positioning it as “digital gold” and a potential hedge against inflation. The proof-of-work consensus mechanism, while energy-intensive, provides superior security compared to proof-of-stake alternatives. Bitcoin’s Layer 2 solution, the Lightning Network, addresses scalability concerns, enabling faster and cheaper transactions. Unlike many altcoins, Bitcoin maintains a singular focus on being a peer-to-peer electronic cash system, avoiding the complexities and potential vulnerabilities associated with smart contract platforms. Its longevity, having survived numerous market cycles and attacks, demonstrates unmatched resilience. Furthermore, Bitcoin’s development process, characterized by conservative upgrades and rigorous peer review, prioritizes stability and security over rapid innovation, distinguishing it from more experimental cryptocurrencies.Key Differentiators of Bitcoin
| Feature | Bitcoin | Other Major Cryptocurrencies |
|---|---|---|
| Launch Date | 2009 | 2015 and later |
| Market Capitalization | Highest (Over $1 trillion) | Significantly lower |
| Supply Cap | 21 million (fixed) | Often variable or inflationary |
| Consensus Mechanism | Proof-of-Work | Often Proof-of-Stake or variants |
| Primary Use Case | Digital currency and store of value | Often includes smart contracts and DApps |
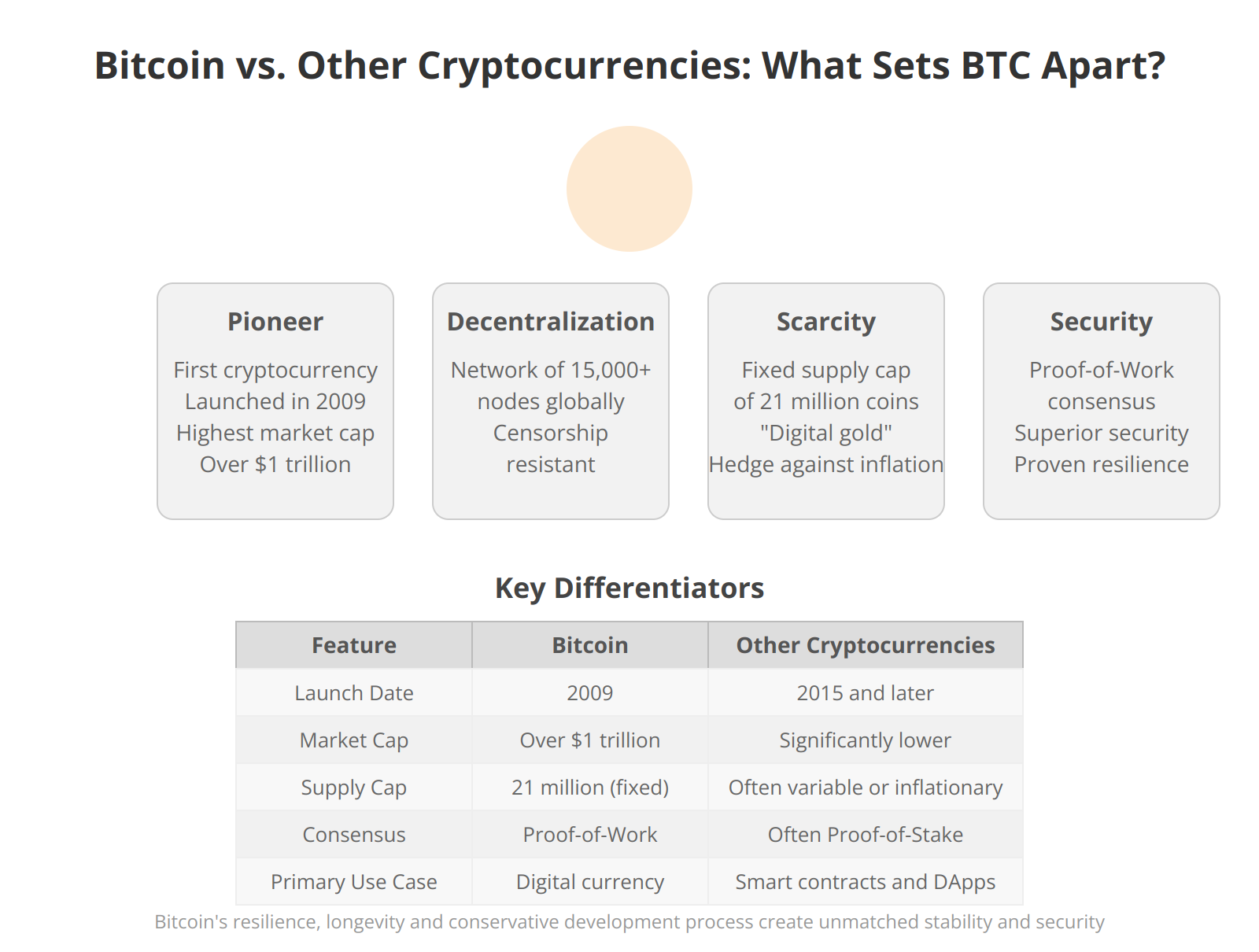
The Future of Bitcoin: Innovations, Challenges, and Opportunities
The Future of Bitcoin: Innovations, Challenges, and Opportunities
As Bitcoin continues to evolve, its future is shaped by a complex interplay of technological advancements, regulatory developments, and market dynamics. The implementation of the Lightning Network promises to address scalability issues, enabling faster and cheaper transactions. Simultaneously, the integration of Taproot technology enhances privacy and smart contract functionality, expanding Bitcoin’s utility beyond simple transfers. However, challenges persist, including environmental concerns related to mining energy consumption and regulatory uncertainties across different jurisdictions. The upcoming Bitcoin halving in 2024 is expected to impact supply dynamics, potentially influencing price trajectories. Institutional adoption continues to grow, with major corporations and investment firms incorporating Bitcoin into their portfolios and offering crypto-based financial products. Future use cases may extend to decentralized finance (DeFi) applications, cross-border remittances, and as a hedge against inflation in emerging economies. The development of Bitcoin ETFs and the potential integration with central bank digital currencies (CBDCs) could further legitimize Bitcoin in traditional financial systems. As the cryptocurrency landscape evolves, Bitcoin’s role as a store of value and medium of exchange may solidify, driven by ongoing innovations and increasing mainstream acceptance.Key Bitcoin Metrics (2025 Projections)
| Metric | Projected Value |
|---|---|
| Market Capitalization | $3.5 trillion |
| Daily Transactions | 1.2 million |
| Lightning Network Capacity | 5,000 BTC |
| Mining Hash Rate | 500 EH/s |

Bitcoin FAQs: Your Burning Questions Answered
Bitcoin FAQs: Your Burning Questions Answered
What is Bitcoin?
Bitcoin is a decentralized digital currency created in 2009 by an unknown person using the pseudonym Satoshi Nakamoto. It operates on a peer-to-peer network without the need for intermediaries or central authorities. Bitcoin transactions are verified by network nodes through cryptography and recorded in a public distributed ledger called a blockchain.
How does Bitcoin work?
Bitcoin functions through a process called mining, where powerful computers solve complex mathematical problems to validate transactions and add them to the blockchain. Miners are rewarded with newly created bitcoins and transaction fees. The total supply of Bitcoin is capped at 21 million coins, with approximately 19.5 million in circulation as of 2025.
Is Bitcoin a safe investment?
Bitcoin’s safety as an investment depends on various factors. While it has shown significant growth potential, it is also known for its volatility. The cryptocurrency market is subject to rapid price fluctuations, regulatory changes, and technological risks. Investors should conduct thorough research, diversify their portfolios, and only invest what they can afford to lose.
How can I buy Bitcoin?
Bitcoin can be purchased through cryptocurrency exchanges, peer-to-peer platforms, or Bitcoin ATMs. Popular exchanges include Coinbase, Binance, and Kraken. To buy Bitcoin, users typically need to create an account, complete identity verification, and link a payment method such as a bank account or credit card. It’s crucial to use reputable platforms and secure storage methods, such as hardware wallets, to protect your investment.
What is the future of Bitcoin?
The future of Bitcoin remains a topic of debate among experts. Some predict continued growth and mainstream adoption, while others foresee challenges from regulatory scrutiny and competing cryptocurrencies. Technological advancements like the Lightning Network aim to improve Bitcoin’s scalability and transaction speed. The next Bitcoin halving event, expected in 2028, may impact its value and mining dynamics. As with any emerging technology, Bitcoin’s future will likely be shaped by a combination of technological innovation, regulatory developments, and market forces.